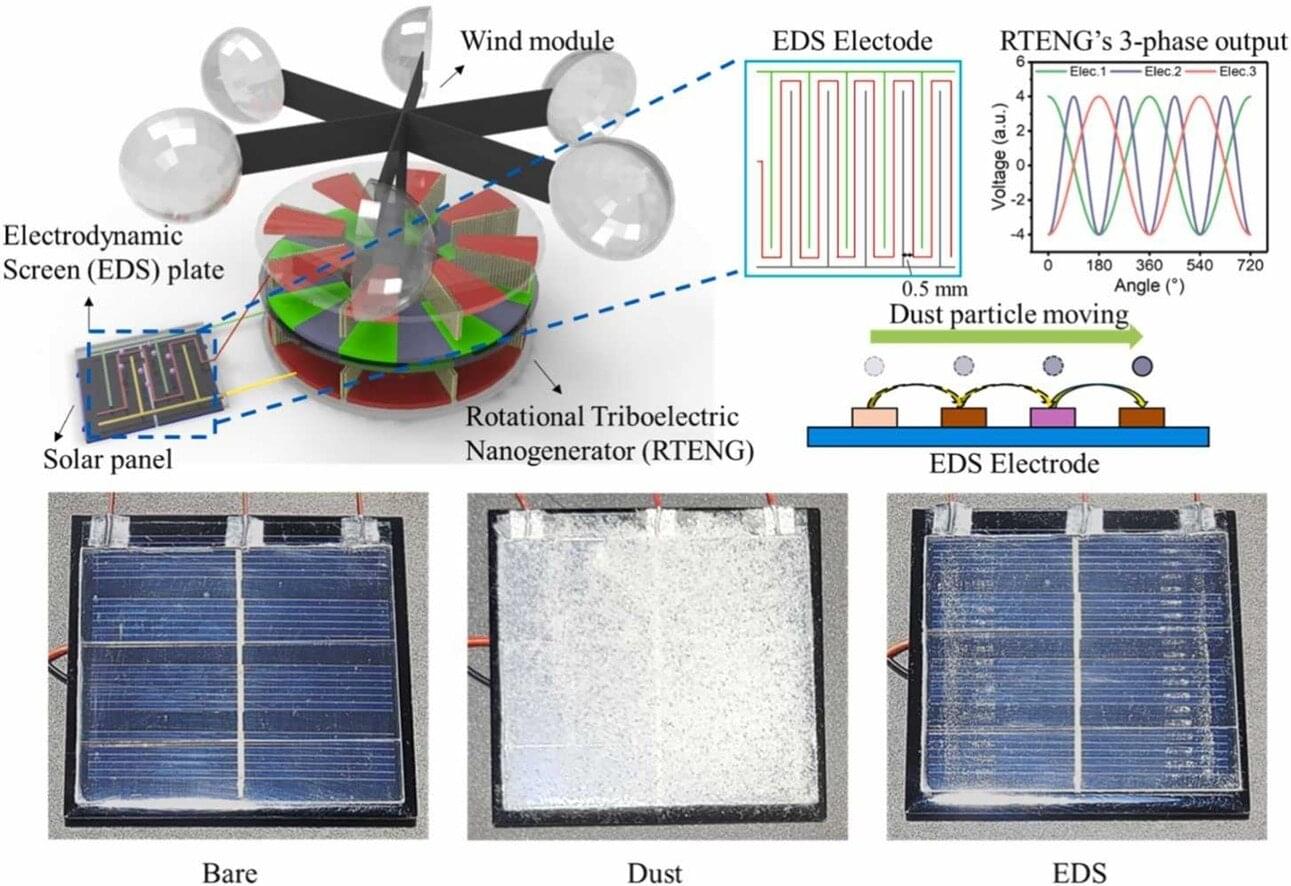
New research into topological phases of matter may spur advances in innovative quantum devices. As described in a new paper published in the journal Nature Communications, a research team including Los Alamos National Laboratory scientists used a novel strain engineering approach to convert the material hafnium pentatelluride (HfTe5) to a strong topological insulator phase, increasing its bulk electrical resistance while lowering it at the surface, a key to unlocking its quantum potential.
“I’m excited that our team was able to show that the elusive and much-sought-after topological surface states can be made to become a predominant electrical conduction pathway,” said Michael Pettes, scientist with the Center for Integrated Nanotechnologies (CINT) at the Laboratory.
“This is promising for the development of types of quantum optoelectronic devices, dark matter detectors and topologically protected devices such as quantum computers. And the methodology we demonstrate is compatible for experimentation on other quantum materials.”