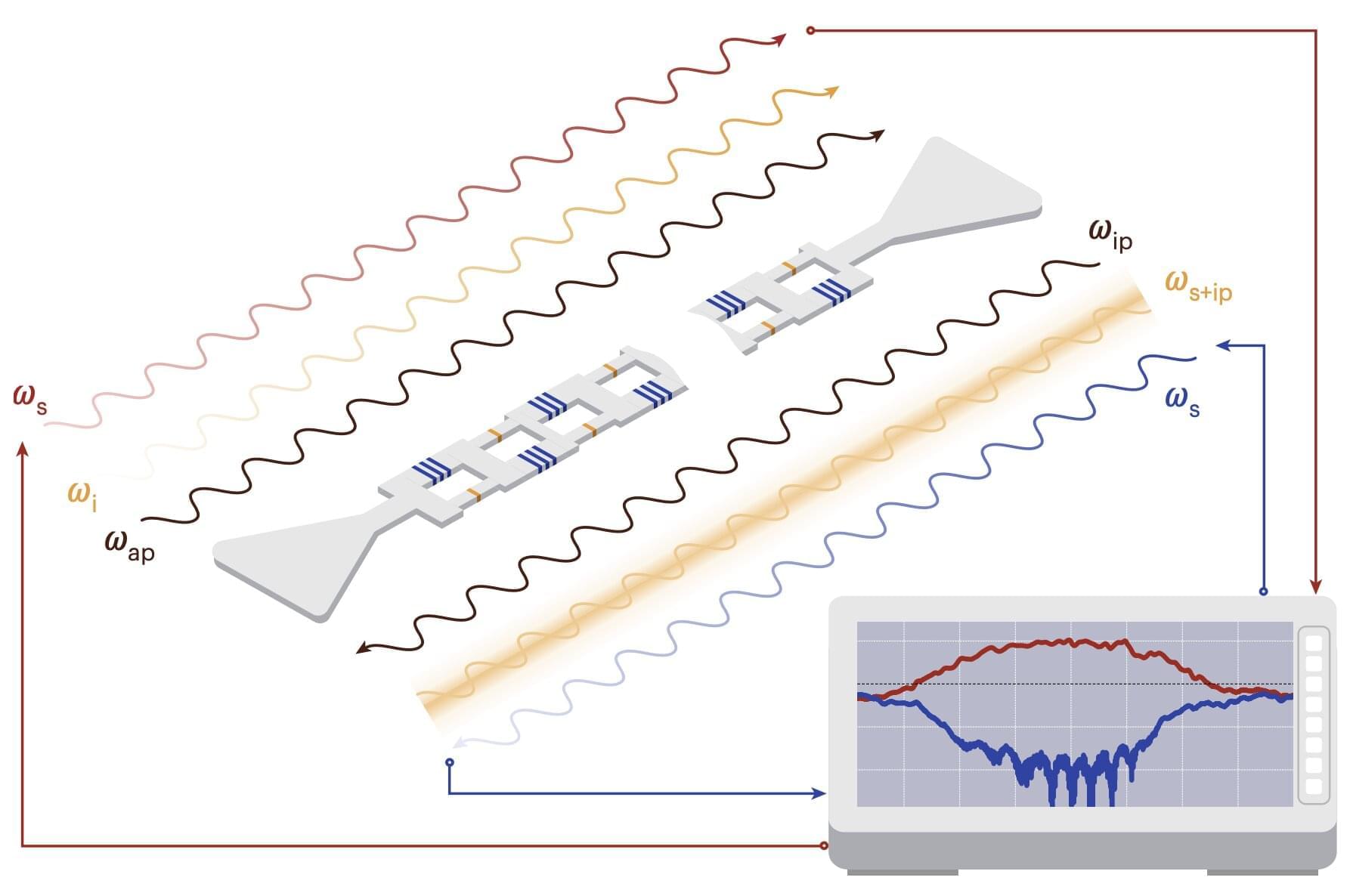
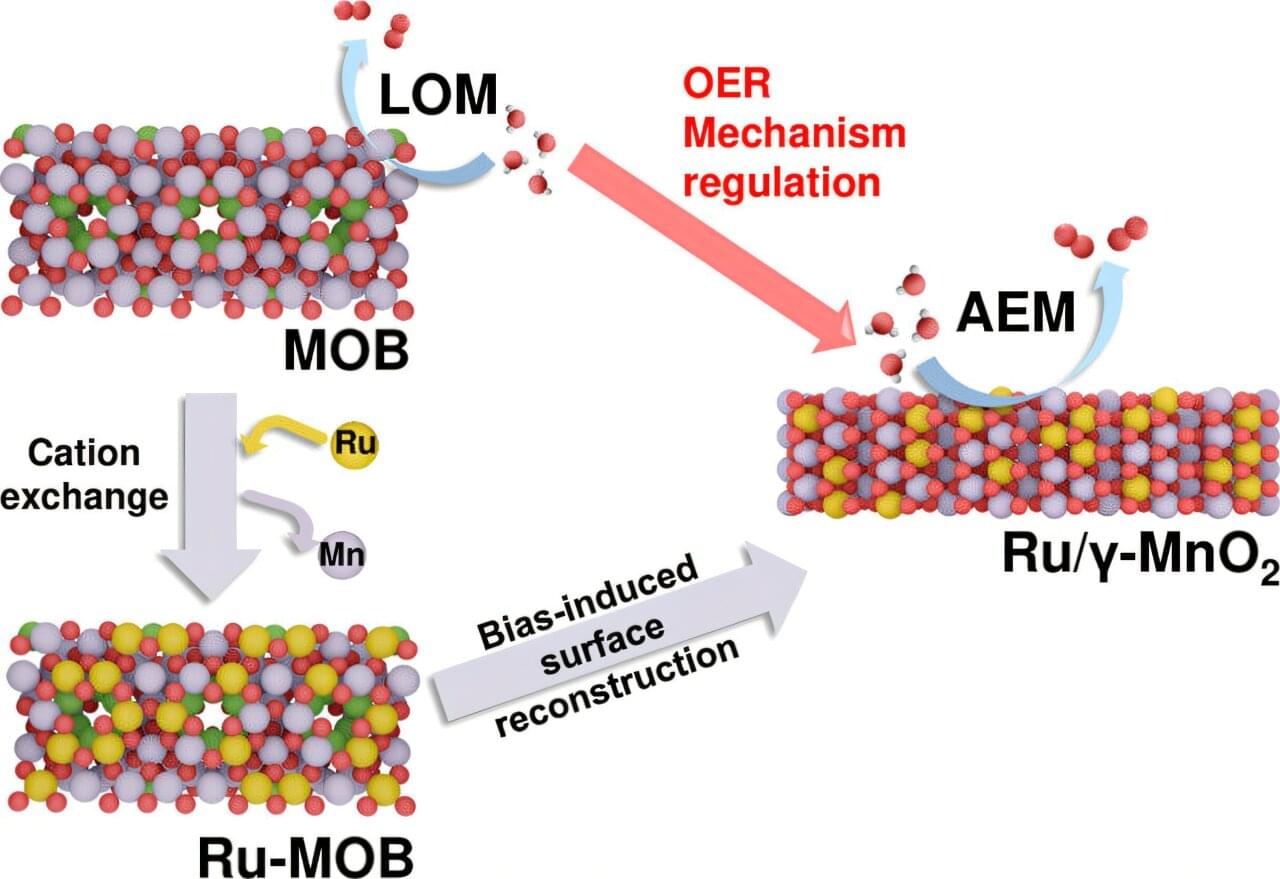
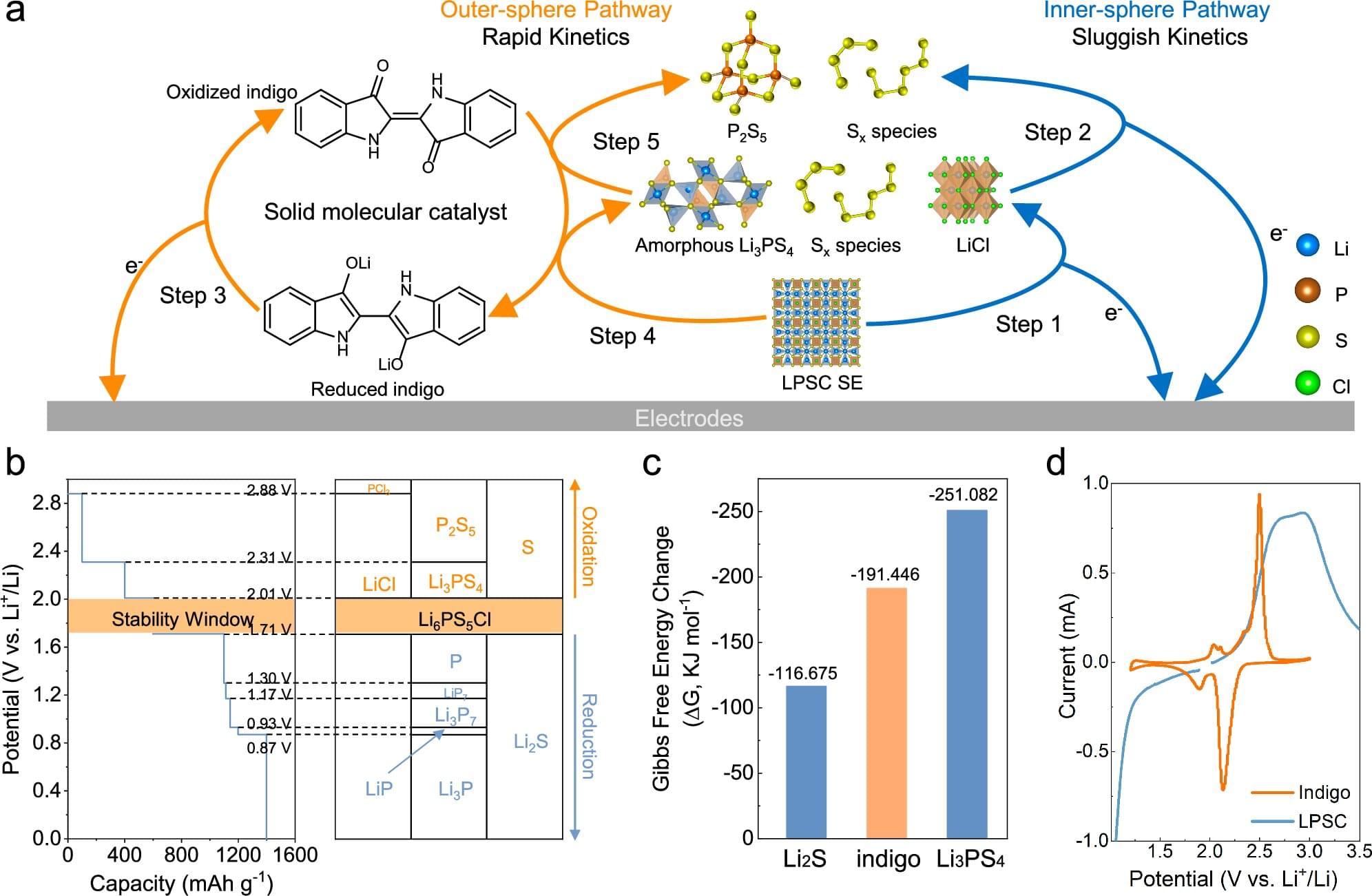
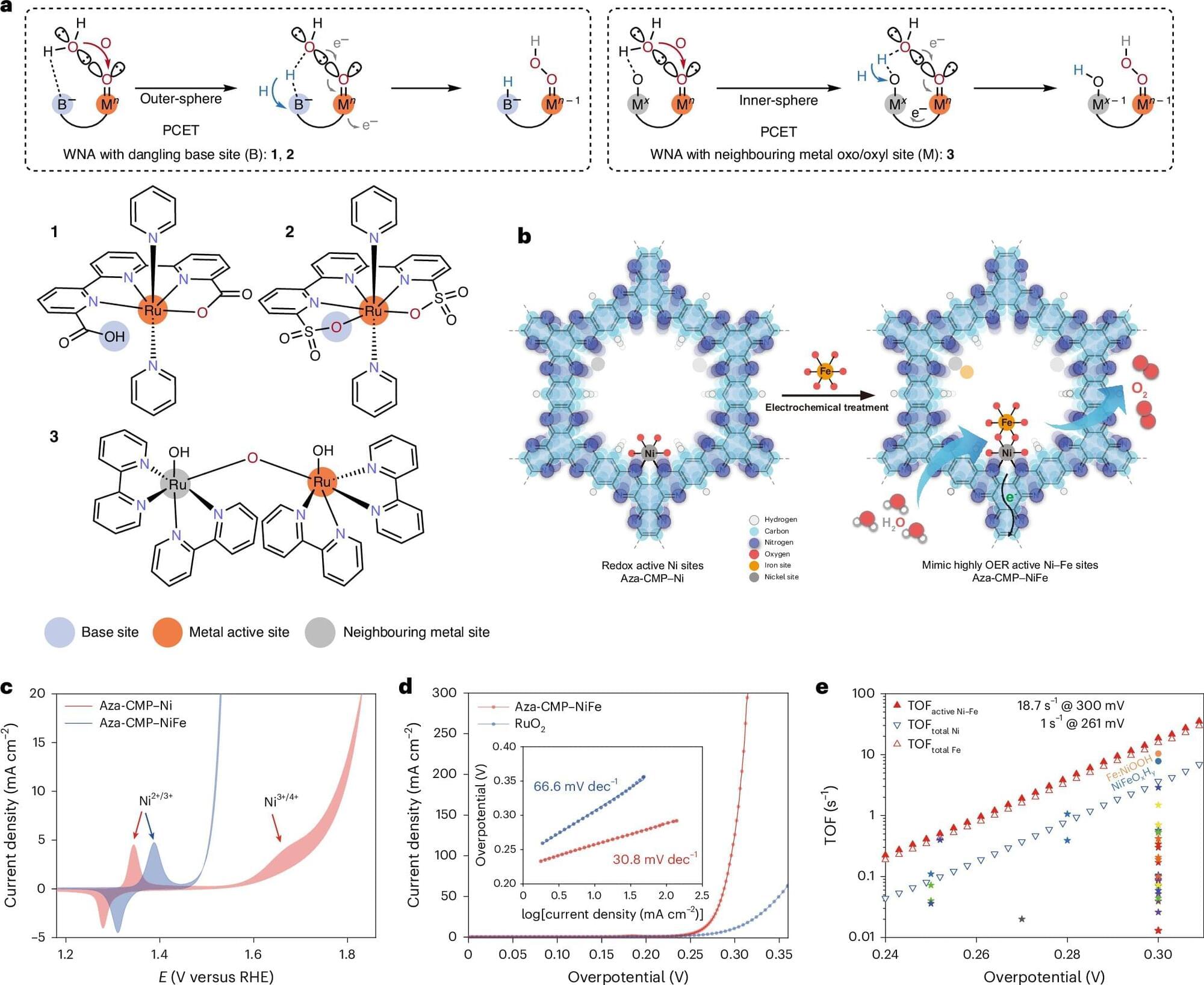
The full structure, if it is ever built, will likely take centuries. But the first pieces could be deployed within the next hundred years. Like the construction of cathedrals or transcontinental railroads, this is the kind of project that begins with a vision and takes shape slowly, across generations.
A Dyson sphere is not only about energy. It is about how we think. It challenges us to plan at the scale of a civilization rather than a single generation. It asks what kind of future we are trying to build, and whether we are willing to imagine a world of abundance rather than scarcity. It may take centuries to complete, but the mindset that makes it possible can start right now.