Scientists have found that human hair growth does not grow by being pushed out of the root; it’s actually pulled upward by a force associated with a hidden network of moving cells. The findings challenge decades of textbook biology and could reshape how researchers think about hair loss and regeneration.
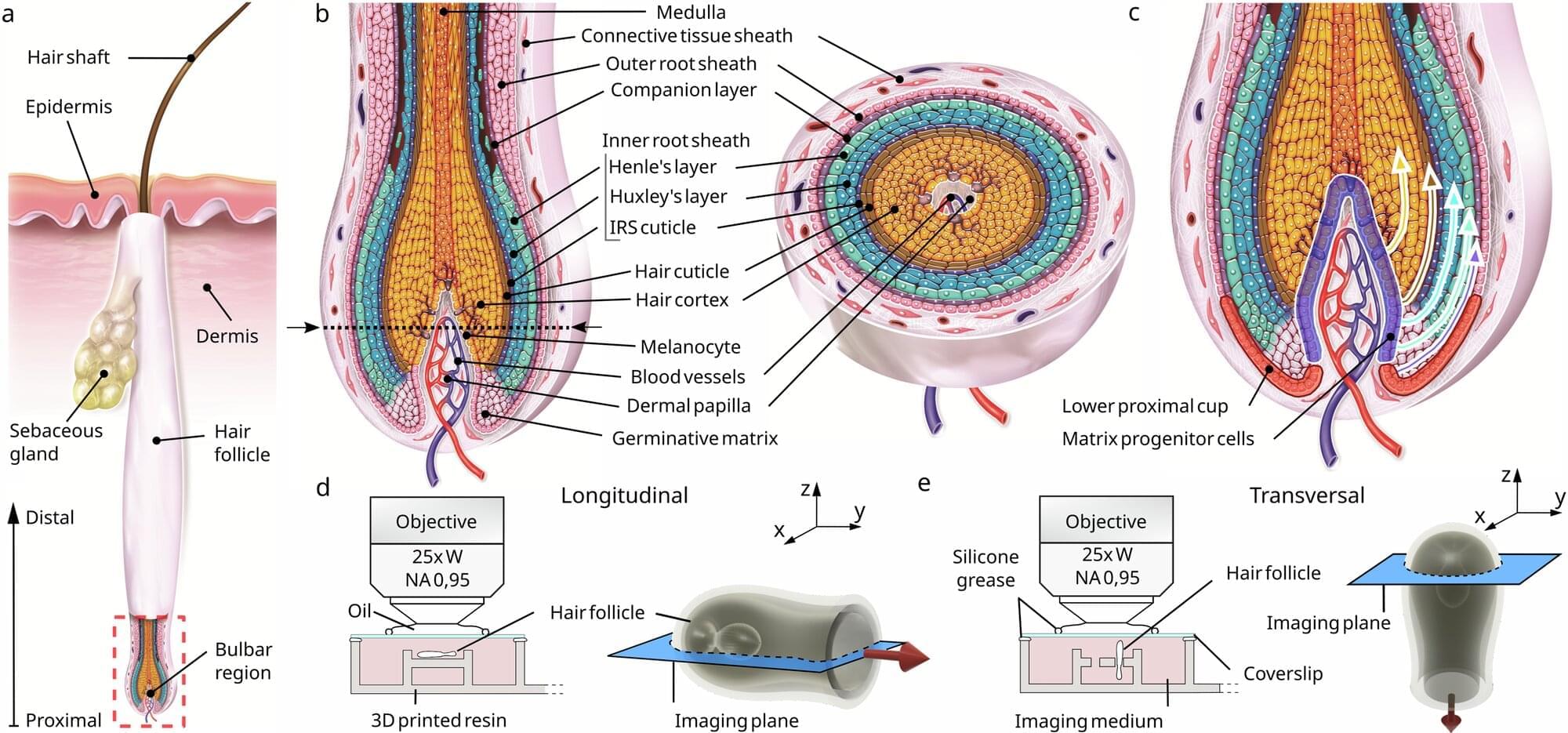
The team, from L’Oréal Research & Innovation and Queen Mary University of London, used advanced 3D live imaging to track individual cells within living human hair follicles kept alive in culture. The study, published in Nature Communications, shows that cells in the outer root sheath—a layer encasing the hair shaft—move in a spiral downward path within the same region from where the upward pulling force originates.
Dr. Inês Sequeira, Reader in Oral and Skin Biology at Queen Mary and one of the lead authors, said, “Our results reveal a fascinating choreography inside the hair follicle. For decades, it was assumed that hair was pushed out by the dividing cells in the hair bulb. We found that instead that it’s actively being pulled upwards by surrounding tissue acting almost like a tiny motor.”