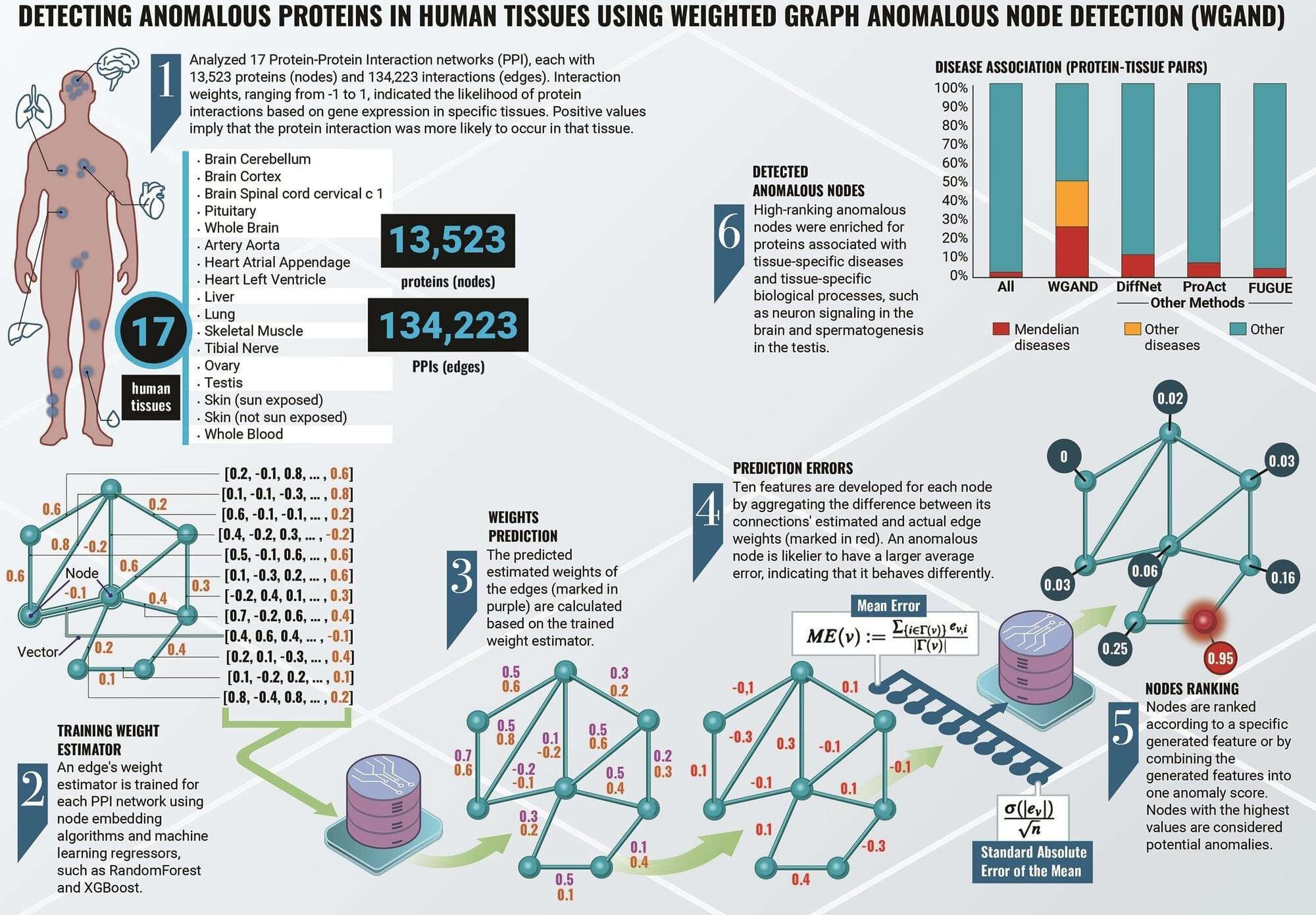
Researchers at Ben-Gurion University of the Negev have developed a machine-learning algorithm that could enhance our understanding of human biology and disease. The new method, Weighted Graph Anomalous Node Detection (WGAND), takes inspiration from social network analysis and is designed to identify proteins with significant roles in various human tissues.
Proteins are essential molecules in our bodies, and they interact with each other in complex networks, known as protein-protein interaction (PPI) networks. Studying these networks helps scientists understand how proteins function and how they contribute to health and disease.
Prof. Esti Yeger-Lotem, Dr. Michael Fire, Dr. Jubran Juman, and Dr. Dima Kagan developed the algorithm to analyze these PPI networks to detect “anomalous” proteins—those that stand out due to their unique pattern of weighted interactions. This implies that the amount of the protein and its protein interactors is greater in that particular network, allowing them to carry out more functions and drive more processes. This also indicates the great importance that these proteins have in a particular network, because the body will not waste energy on their production for no reason.