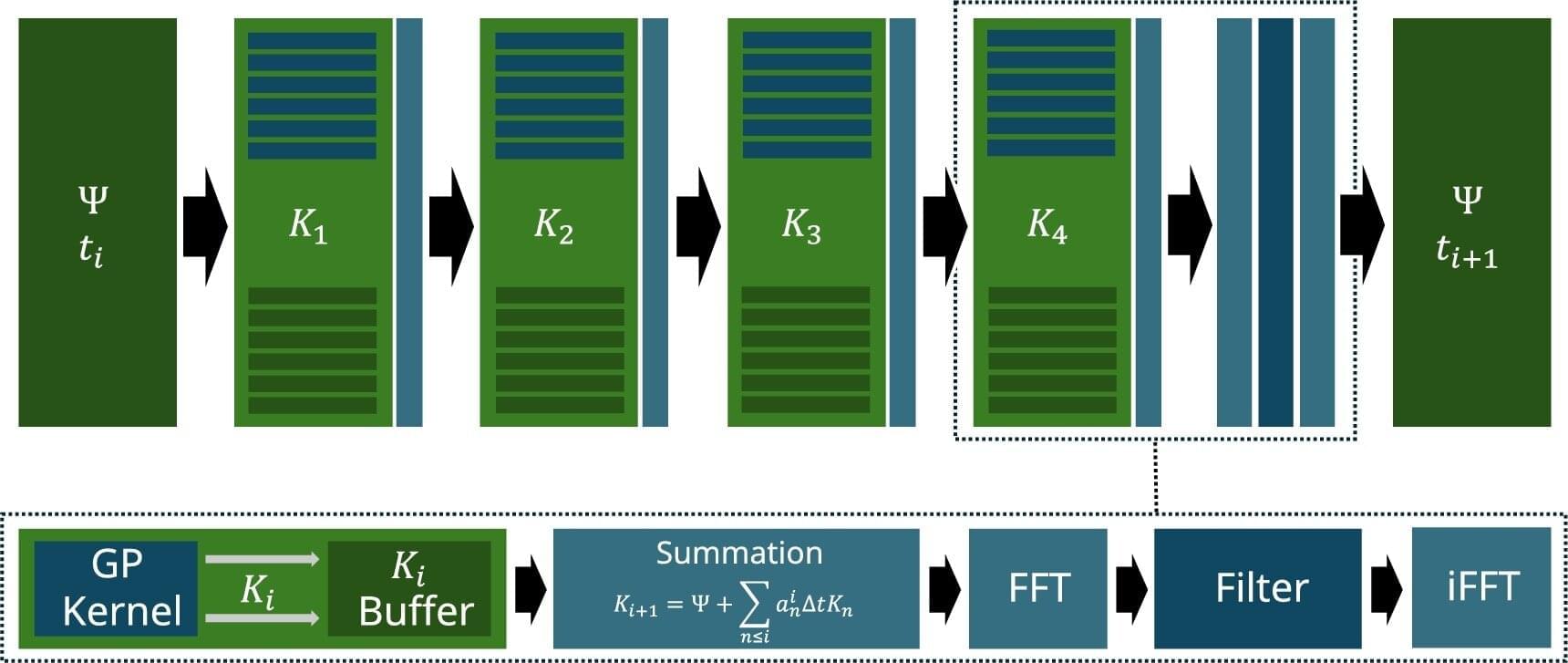
Scientists at the Institute for Photonic Quantum Systems (PhoQS) and the Paderborn Center for Parallel Computing (PC2) at Paderborn University have developed a powerful open-source software tool that allows them to simulate light behavior in quantum systems.
The unique feature of this tool, named “Phoenix,” is that researchers can use it to very quickly investigate complex effects to a level of detail that was previously unknown, and all without needing knowledge of high-performance computing. The results have now been published in Computer Physics Communications.
Phoenix solves equations that describe how light interacts with material at the quantum level, which is essential for understanding and for the design of future technologies such as quantum computers and advanced photonic devices.