It took Nicolas Neubert seven hours to make it his living room.


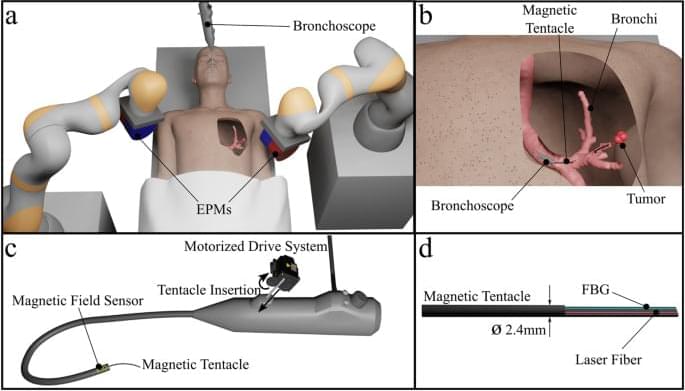
All navigations reported in Fig. 2 were performed autonomously within 150 s and without intraoperative imaging. Specifically, each navigation was performed according to the pre-determined optimal actuation fields and supervised in real time by intraoperative localization. Therefore, the set of complex navigations performed by the magnetic tentacle was possible without the need for exposure to radiation-based imaging. In all cases, the soft magnetic tentacle is shown to conform by design to the anatomy thanks to its low stiffness, optimal magnetization profile and full-shape control. Compared to a stiff catheter, the non-disruptive navigation achieved by the magnetic tentacle can improve the reliability of registration with pre-operative imaging to enhance both navigation and targeting. Moreover, compared to using multiple catheters with different pre-bent tips, the optimization approach used for the magnetic tentacle design determines a single magnetization profile specific to the patient’s anatomy that can navigate the full range of possible pathways illustrated in Fig. 2. Supplementary Movies S1 and S2 report all the experiments. Supplementary Movie S1 shows the online tracking capabilities of the proposed platform.
In Table 1, we report the results of the localization for four different scenarios. These cases highlight diverse navigations in the left and right bronchi. The error is referred to as the percentage of tentacles outside the anatomy. This was computed by intersecting the shape of the catheter, as predicted by the FBG sensor, and the anatomical mesh grid extracted from the CT scan. The portion of the tentacle within the anatomy was measured by using “inpolyhedron” function in MATLAB. In Supplementary Movie S1, this is highlighted in blue, while the section of the tentacle outside the anatomy is marked in red. The error in Table 1 was computed using the equation.

James Cameron has no intention of using artificial intelligence to write a film script. In a new interview with CTV News, the Oscar winner expressed doubt over AI bots being able to write “a good story.”
According to Cameron: “I just don’t personally believe that a disembodied mind that’s just regurgitating what other embodied minds have said — about the life that they’ve had, about love, about lying, about fear, about mortality — and just put it all together into a word salad and then regurgitate it…I don’t believe that’s ever going to have something that’s going to move an audience. You have to be human to write that. I don’t know anyone that’s even thinking about having AI write a screenplay.”
https://youtube.com/watch?v=1131xTaVo8A&feature=share
1984 is a 1956 British black-and-white science fiction film, based on the 1948 novel Nineteen Eighty-Four by George Orwell, depicting a totalitarian future of a dystopian society.
This is the first film adaptation of the story, directed by Michael Anderson and starring Edmond O’Brien as protagonist Winston Smith, and featuring Donald Pleasence, Jan Sterling, and Michael Redgrave.
In 1954, Peter Cushing and André Morell starred in a BBC-TV made-for-TV adaptation which was extremely popular with British audiences, leading to the production of the 1956 film version. Donald Pleasence had also appeared in the BBC television version, playing the character of Syme, which for the film was amalgamated with that of Parsons. The script was co-written by William Templeton, who had previously adapted the novel for the US Studio One TV series in 1953.
For the US market, 1984 was distributed in 1956 as a double feature with another British science fiction film, The Gamma People.
Clip taken from my conversation with Professor Dean Rickles. Full episode: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=mGIsZW2kgXI
Patreon: https://www.patreon.com/thinginitself.
Discord invite: https://discord.gg/VnSjqmAgXx.
Social.
Twitter: https://twitter.com/thinginitself__
Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/thinginitself.pod/
Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/people/Thing-in-itself/100088163125850/
Podcast.
Spotify: https://open.spotify.com/show/0dUBLTl6qzOfA0xMndLFzq.
Google: https://www.google.com/podcasts?feed=aHR0cHM6Ly9mZWVkcy5yZWR…FhMw%3D%3D
Apple: https://podcasts.apple.com/us/podcast/thing-in-it-self/id1616881426
Amazon: https://music.amazon.ca/podcasts/9c6c08b2-e975-47d6-a897…in-it-self
Are back holes related to dark matter? Do the observations of black holes by LIGO hint at a signature of quantum gravity? Can we find evidence of black holes from a previous universe?
In 2019 second place in the Buchalter Cosmology Prize was awarded to two of the speakers you will see in this film which explores some of the above themes. We filmed this at the Loop Quantum Gravity Conference in 2019 and plan to make a follow up film exploring the latest ideas in the field.
Look out for the optical illusion around 8:12–8:25.
The Fine-Tuning Argument is often seen as the best argument for the existence of God. Here we have assembled some of the world’s top physicists and philosophers to offer a reply. Not every critic of the argument comes from the same perspective. Some doubt there is a problem to be solved whilst others agree it is a genuine problem but think there are better solutions than the God hypothesis. Some like the multiverse and anthropics other don’t. We have tried to represent these different approaches and so it should be taken as given, that not all of the talking heads agree with each other. Nevertheless, they all share the view that the fine-tuning argument for God does not work. Nor are all the objectors atheist, Hans Halvorson offers what we think is a strong theological objection to the argument. This film does not try to argue that God doesn’t exist only that the fine-tuning argument is not a good reason to believe in God. Most of the footage was filmed exclusively for this film with some clips being re-used from our Before the Big Bang series, which can be viewed here: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Ry_pILPr7B8&list=PLJ4zAUPI-q…4hnojoCR4m All of the critics of the fine tuning argument that appear were sent a draft of the film more than a month before release and asked for any objections either to their appearance, the narration or any other aspect of the film. No objections were raised, and many replies were extremely positive and encouraging. A timeline of the subjects covered is below:
(We define God as a perfect Omni immaterial mind as for example modern Christians and Muslims advocate, there are other conceptions of God which our video does not address).
Just to be clear, this is a polemical film arguing against the fine tuning argument.
Timecodes.
0:00 Introduction.
4:11 The universe as a roll of the dice.
6:15 what is probability?
7:28 probability problems.
9:25 measure problem.
15:45 deceptive probabilities.
20:23 the flatness problem.
22:14 counterfactuals versus probabilities.
23:59 fine tuning versus God.
37:02 necessity.
38:53 multiverse and anthropics.
47:34 Boltzmann brains.
49:45 Entropy.
52:45 Cosmological Natural Selection.
59:10 conclusion.
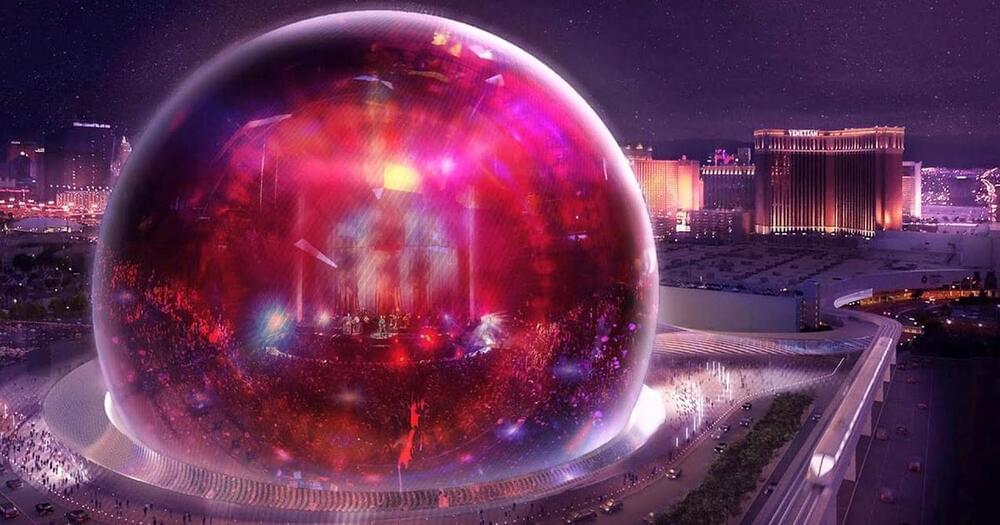

Sphere Entertainment, the Madison Square Garden-funded venture seeking to “reinvent” live music, has started testing its first — and impressively large — LED-laden, orb-shaped music venue in Las Vegas, which is already being billed as the “world’s largest video screen.”
First impressions: it looks absolutely bonkers, as evidenced by videos of the orb in action.
According to Engadget, the 17,600-seat stadium, which cost over $2 billion to build, is a good 516 feet wide and 366 feet tall. Its LED-powered displays, combined with its 164,000-speaker audio system and added sensory elements — think what you’d get at a 4D movie — are designed to create a completely immersive experience.

Android manufacturers tend to love big spec sheets, even if those giant numbers won’t do much for day-to-day phone usage. In that vein, we’ve got the new high-water mark for ridiculous amounts of memory in a phone. The new Nubia RedMagic 8S Pro+ is an Android gaming phone with an option for 24GB of RAM.
The base model of the RedMagic 8S Pro+ starts with 16GB of RAM, but GSMArena has pictures and details of the upgraded 24GB SKU, which is the most amount of memory ever in an Android phone. Because we’re all about big numbers, it also comes with 1TB of storage. Keep in mind a 13-inch top-spec M2 MacBook Pro has 24GB of RAM and 2TB of storage, and that’s a desktop OS with real multitasking, so Nubia is really pushing it. This suped-up 24GB version of the phone appears to be a China-exclusive, with the price at CNY 7,499 (about $1,034), which is a lot for a phone in China.
You definitely want an adequate amount of RAM in an Android phone. All these apps are designed around cheap phones, though, and with Android’s aggressive background app management, there’s usually not much of a chance to use a ton of RAM. Theoretically, a phone like this would let you multitask better, since apps could stay in memory longer, and you wouldn’t have to start them back up when switching tasks. Most people aren’t quickly switching through that many apps, though, and some heavy apps, games especially, will just automatically turn off a few seconds once they’re in the background.