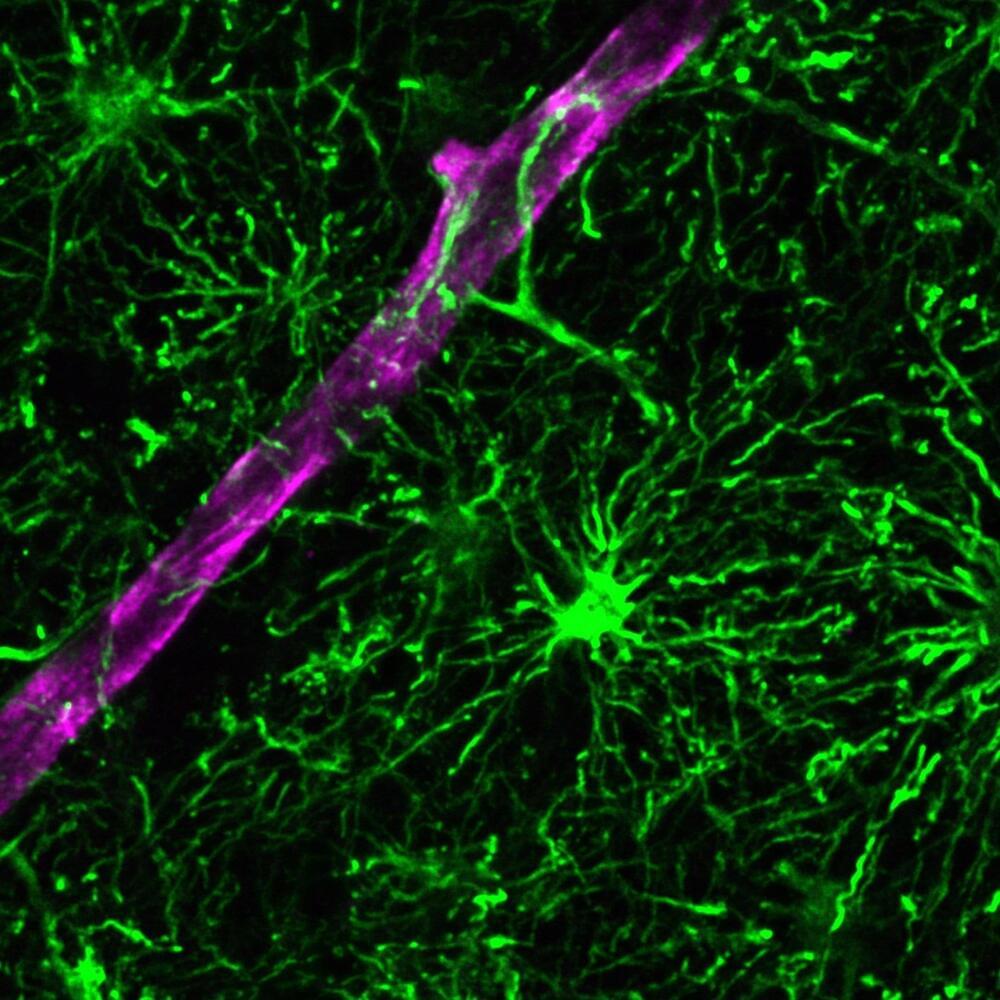
The brain is typically depicted as a complex web of neurons sending and receiving messages. But neurons only make up half of the human brain. The other half—roughly 85 billion cells—are non-neuronal cells called glia.
The most common type of glial cells are astrocytes, which are important for supporting neuronal health and activity. Despite this, most existing laboratory models of the human brain fail to include astrocytes at sufficient levels or at all, which limits the models’ utility for studying brain health and disease.
Now, Salk scientists have created a novel organoid model of the human brain—a three-dimensional collection of cells that mimics features of human tissues—that contains mature, functional astrocytes. With this astrocyte-rich model, researchers will be able to study inflammation and stress in aging and diseases like Alzheimer’s with greater clarity and depth than ever before.