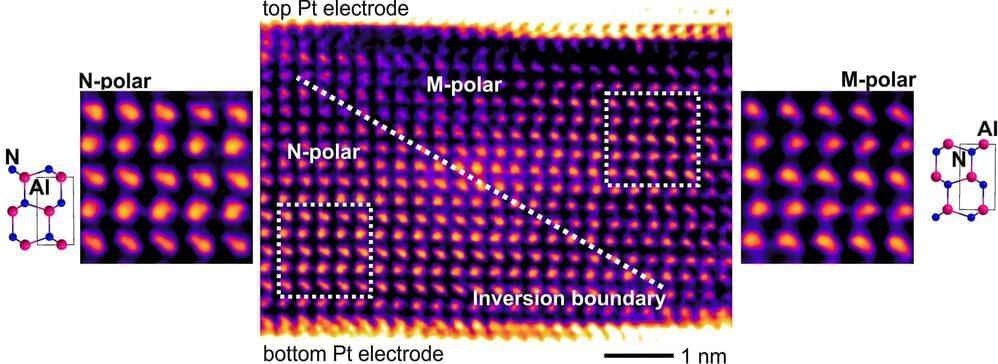
Materials scientists at Kiel University and the Fraunhofer Institute for Silicon Technology in Itzehoe (ISIT) have cleared another hurdle in the development and structuring of new materials for next-generation semiconductor devices, such as novel memory cells.
They have shown that ferroelectric aluminum scandium nitride can be scaled down to a few nanometers and can store different states, making it suitable as a nanoswitch. In addition, they have proved aluminum scandium nitride to be a particularly stable and powerful semiconductor material for current technologies based on silicon, silicon carbide and gallium nitride. In contrast to today’s microelectronics, the material can withstand extreme temperatures of up to 1,000°C.
This opens up applications such as information storage or sensors for combustion processes in engines or turbines in both the chemical industry and in the steel industry. The results were published in the journal Advanced Science. The study was part of a research project that brings together basic research in materials development and applications in microelectronics.