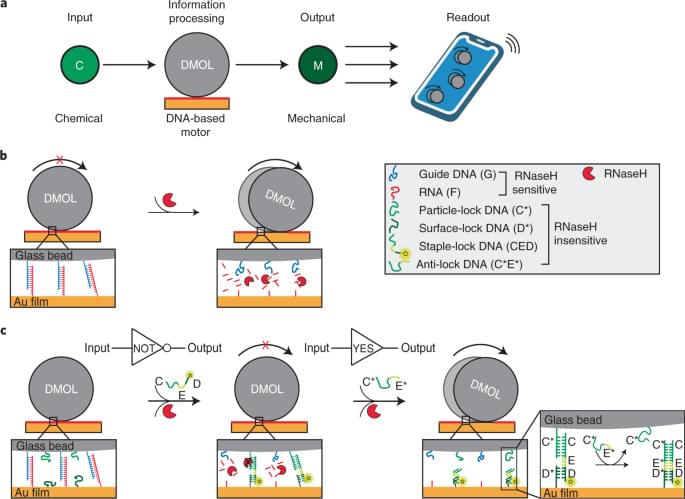
Current DNA computation techniques are slow in generating chemical outputs in response to chemical inputs and rely heavily on fluorescence readouts. Here, the authors introduce a new paradigm for DNA computation where the chemical input is processed and transduced into a mechanical output in the form of macroscopic locomotion using dynamic DNA-based motors.