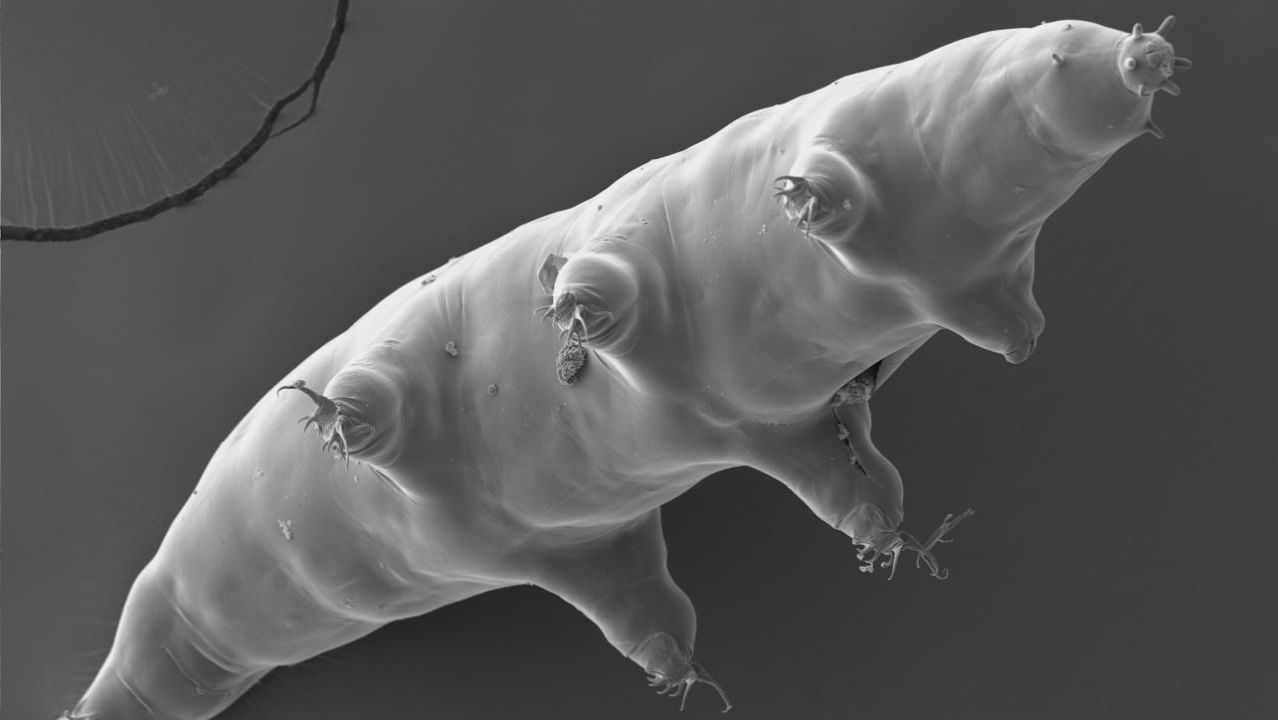
Tardigrades, tiny aquatic creatures found in habitats from backyard ponds to Antarctic glaciers, are tough enough to survive the radiation-fraught perils of space. But for a long time, scientists couldn’t agree on why the animals—also known as water bears—are so hardy. Now, researchers have identified a gene that protects the tardigrades’ DNA from radiation, BBC reports. The gene, called Dsup, showed its importance when researchers inserted it into human DNA strands and blasted them with x-rays. The modified genetic material suffered significantly less damage, they report today in. Scientists hope this finding will help them one day protect another animal—us—against radiation.