A new study has uncovered a surprising and concerning paradox: although Earth’s vegetation cover has expanded dramatically over the past four decades, this widespread “greening” trend is often associated with a decline in soil moisture, particularly in water-scarce regions. The study is published in Communications Earth & Environment.
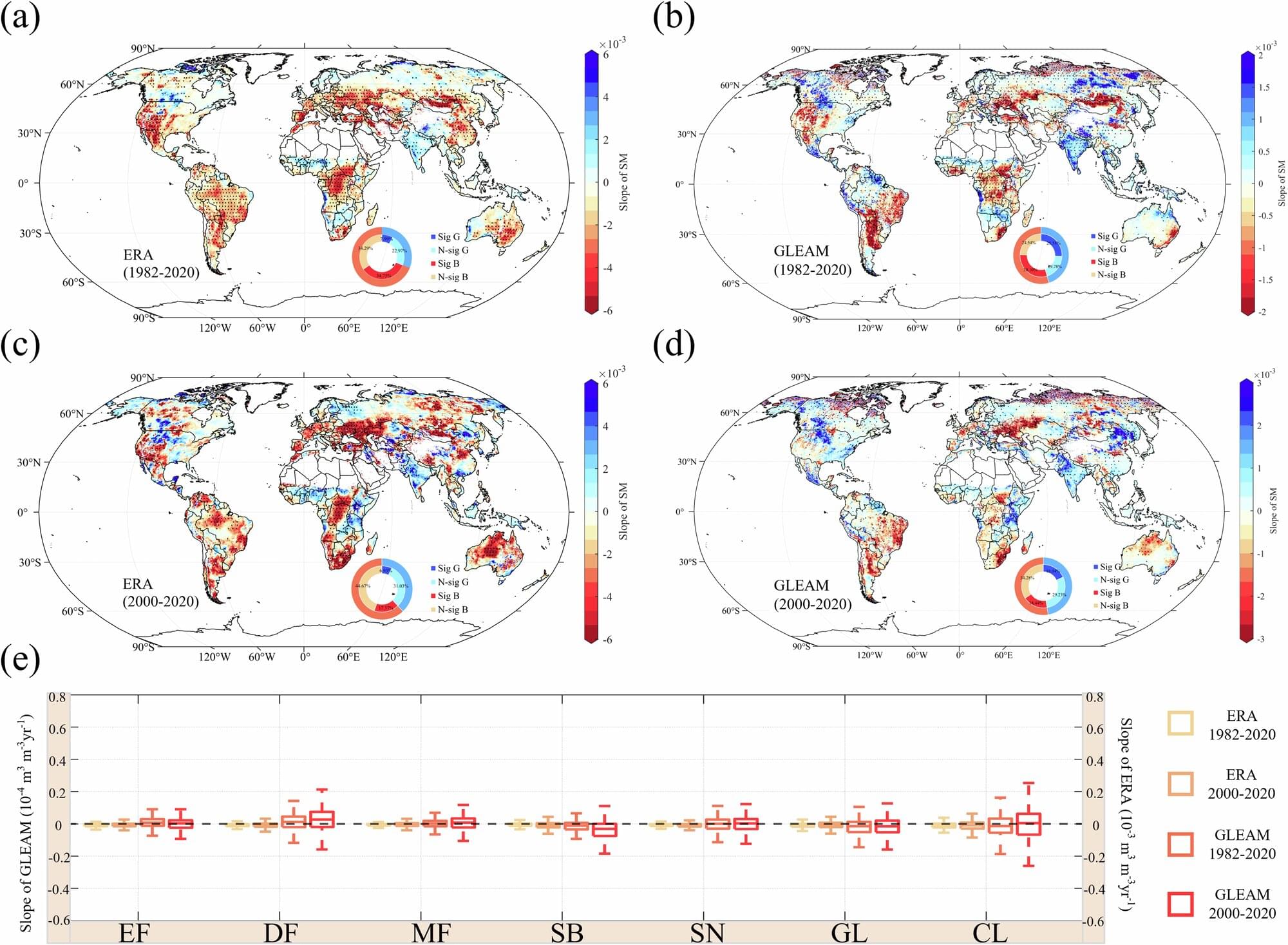
Led by Prof. Chen Yaning from the Xinjiang Institute of Ecology and Geography of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, the researchers employed a multifaceted approach, integrating multi-source satellite observations, reanalysis datasets, and outputs from 12 Earth system models. This comprehensive analysis, spanning the years from 1982 to 2100, enabled researchers to quantitatively assess the causal relationship between vegetation dynamics and soil moisture.
Their findings reveal that while an impressive 65.82% of the global vegetated areas have experienced greening, nearly half of these areas simultaneously witnessed significant soil drying—a “greening-drying” pattern. This detrimental trend is most pronounced in vulnerable regions like Central Africa, Central Asia, eastern Australia, and mid-to-high latitude Europe.