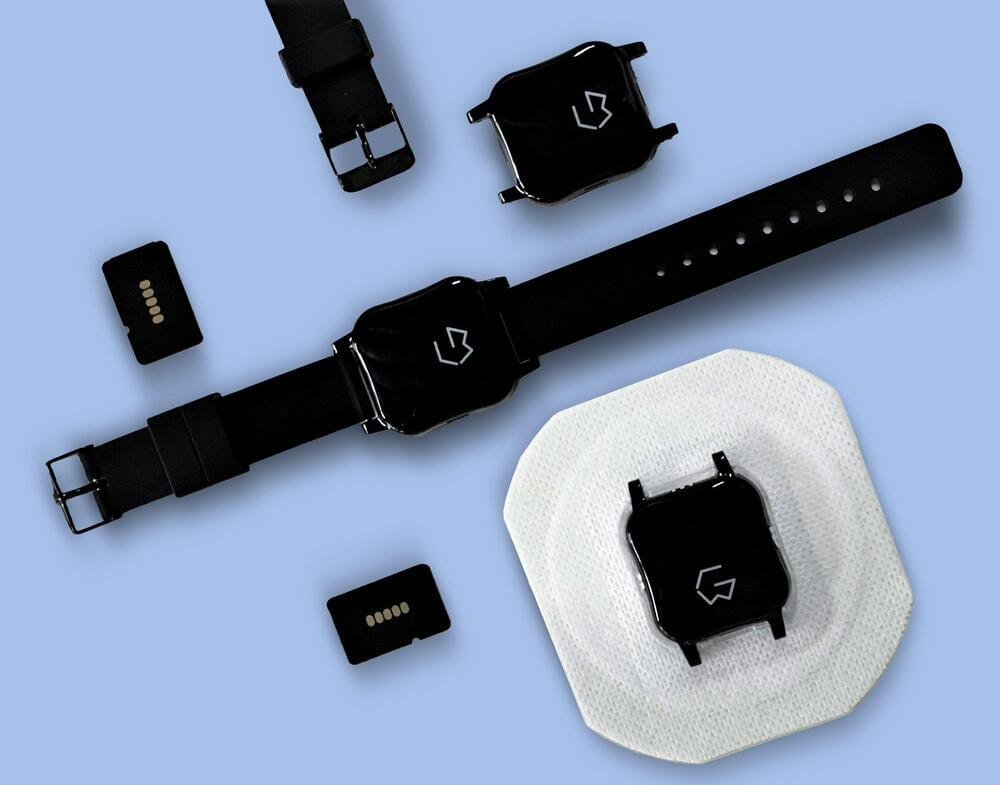
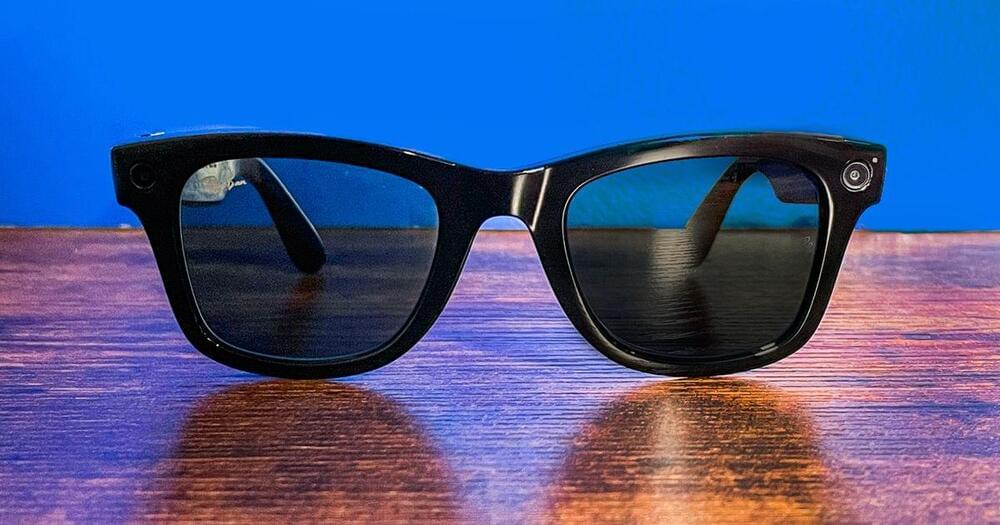
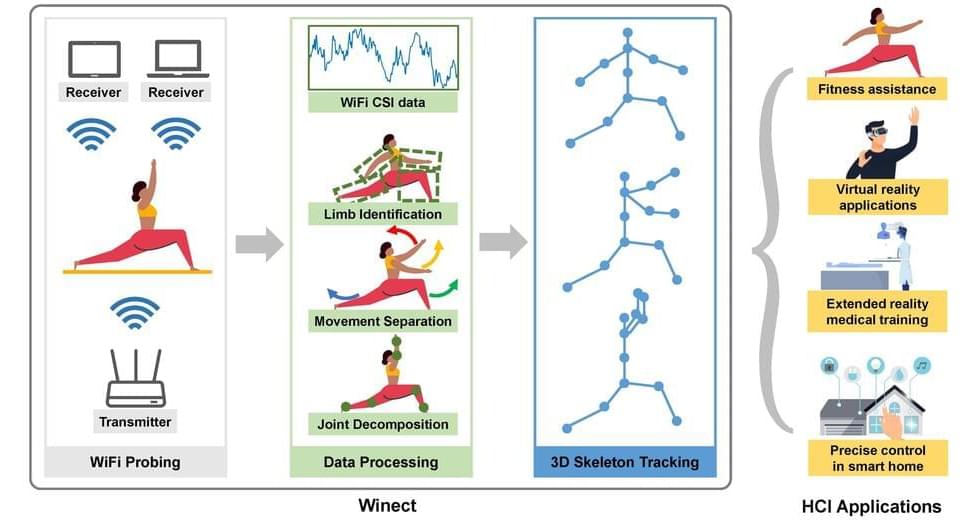
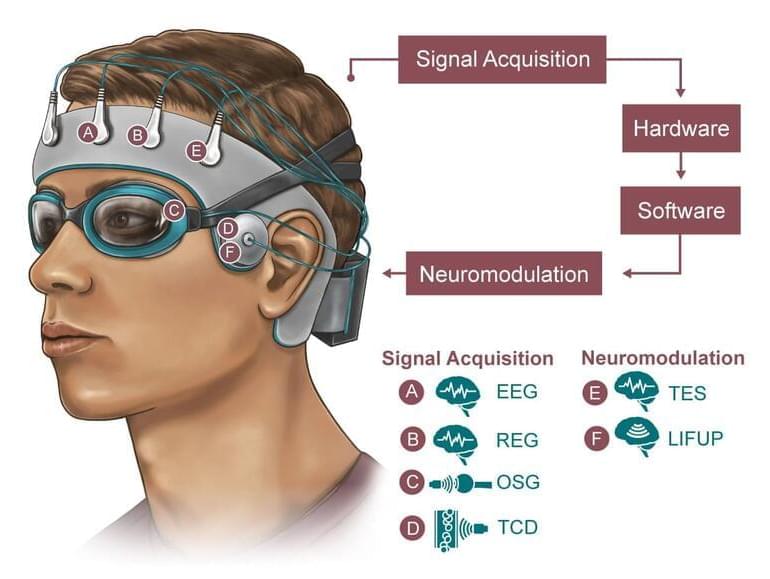
The team has set an internal deadline of 2025.
In a move that could peg it against electric vehicle market leader, Tesla, Apple has begun working aggressively on its fully autonomous electric car, Bloomberg reported. Developing a car has been on Apple’s agenda since 2014 but recent moves within the company signal a push towards making an Apple car a reality.
Given Apple’s history of taking regularly used products and transforming them into their must-have versions using excellent design, it is hardly a surprise. With Steve Jobs at the helm of affairs, Apple made the iPod even when music players were ubiquitous. Then the company revealed the iPhone when Nokia was still selling resistive touch screens as its premium product. And recently, the Apple Watch has become the “it” wearable even though there are other smartwatch options in the market. During a time where electric vehicles are in a surge, it only seems natural that the electric car is Apple’s next target.