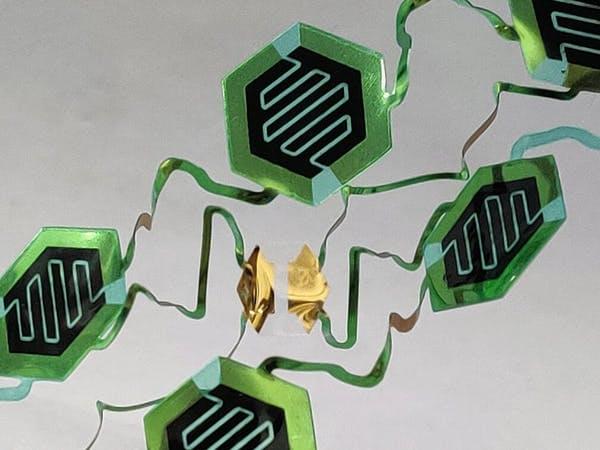
UC Berkeley engineers have come up a new technique for creating wearable sensor prototypes.
The geopolitical tension surrounding.

No he does not respond to the resveratrol challenges. Important here are the chapters concerning Resetting the Ageing Clock and Repeatable Ageing Reversal.
In the final episode of this season, Dr. David Sinclair and Matthew LaPlante focus on current and near-future technologies relevant to health and aging. In addition to discussing the utility of wearable sensors and biological age measurements, they highlight innovative research aimed at reversing biological age. The societal effects of therapies that successfully extend healthspan and/or lifespan are also considered.
#DavidSinclair #Longevity #Aging.
Thank you to our sponsors:
Levels — https://levels.link/sinclair.
Athletic Greens — https://athleticgreens.com/sinclair.
InsideTracker — https://insidetracker.com/sinclair.
Our Patreon page:
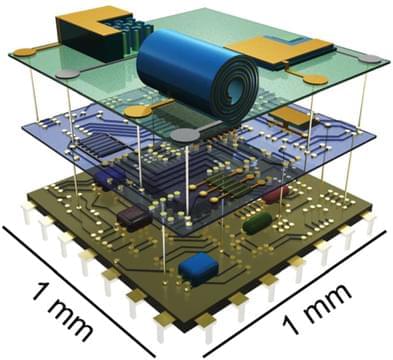
And it’s the size of a grain of dust. Energy storage might have been revolutionized thanks to a common dessert dish.
Advances in microelectronics have enabled the use of miniaturized computers for autonomous intelligence at the size of a dust particle less than one square millimeter across and a few hundred micrometers thick, creating an environment for ubiquitous computing. However, the size mismatch between microbatteries and microelectronics has emerged as a fundamental barrier against the take-off of tiny intelligent systems requiring power anytime anywhere. Mainstream microbattery structures include stacked thin films on the chip or electrode pillars and on-chip interdigitated microelectrodes. Nevertheless, available technologies cannot shrink the footprint area of batteries while maintaining adequate energy storage. Alternatively, the on-chip self-assembly process known as micro-origami is capable of winding stacked thin films into Swiss-roll structures to reduce the footprint area, which exactly mimics the manufacture of the most successful full-sized batteries—cylinder batteries. In addition to discussing in detail the technical difficulties of reducing the size of on-chip microbatteries with various structures and potential solutions, this Perspective highlights the following two basic requirements for eventual integration in microcomputers: minimum energy density of 100 microwatt-hour per square centimeter and monolithic integration with other functional electric circuits on the chip.
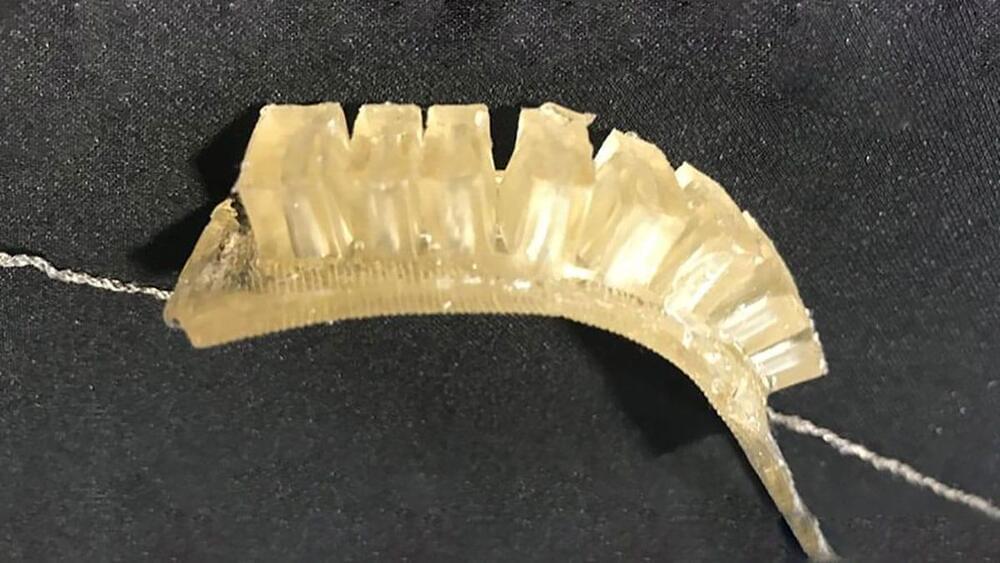

Soft sensing technologies have the potential to revolutionize wearable devices, haptic interfaces, and robotic systems. However, most soft sensing technologies aren’t durable and consume high amounts of energy.
Now, researchers at the University of Cambridge have developed self-healing, biodegradable, 3D-printed materials that could be used in the development of realistic artificial hands and other soft robotics applications. The low-cost jelly-like materials can sense strain, temperature, and humidity. And unlike earlier self-healing robots, they can also partially repair themselves at room temperature.
“Incorporating soft sensors into robotics allows us to get a lot more information from them, like how strain on our muscles allows our brains to get information about the state of our bodies,” said David Hardman from Cambridge’s Department of Engineering the paper’s first author.
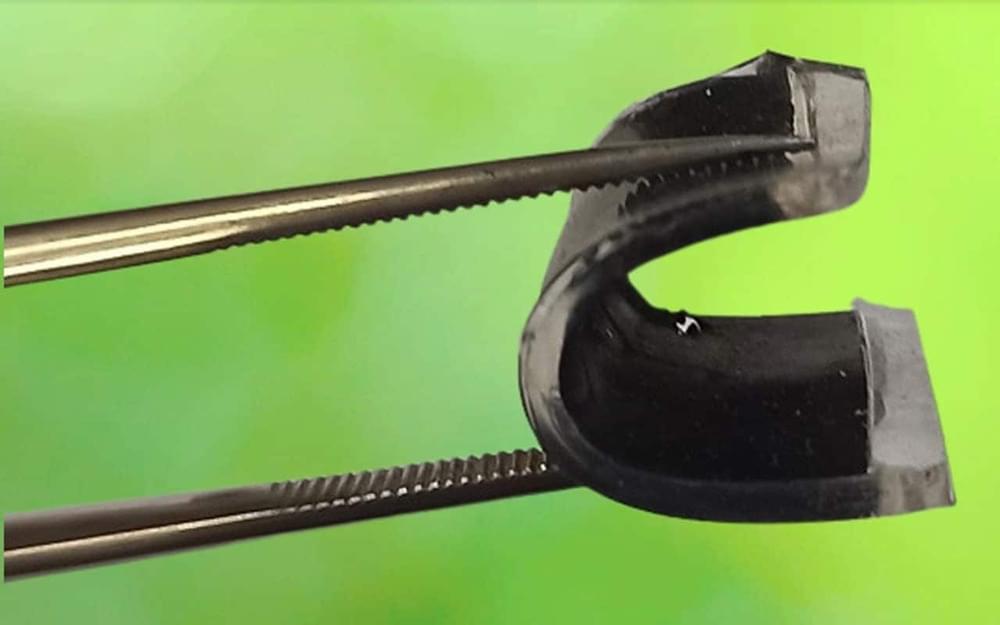

A team of researchers from the University of Surrey’s Advanced Technology Institute (ATI) and the Federal University of Pelotas (UFPel), Brazil, has developed a new type of supercapacitor that can be integrated into footwear or clothing, an advance with applications in wearables and IoT (Internet of Things) devices.
A supercapacitor is an electricity storage device, similar to a battery, but it stores and releases electricity much faster.
The researchers have devised a novel method for the development of flexible supercapacitors based on carbon nanomaterials. The new method, which is cheaper and less time-consuming to fabricate, involves transferring aligned carbon nanotube (CNT) arrays from a silicon wafer to a polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) matrix. This is then coated in a material called polyaniline (PANI), which stores energy through a mechanism known as pseudocapacitance, offering outstanding energy storage properties with exceptional mechanical integrity.
Parents Use AI To See One Last Message From Their Deceased Son ‘…what’s to keep me from showing face, Man?’
Feel Virtual Reality In Mid-Air! ‘…a pressure on the lips — warm and soft, moist and sweet.’ — Frederick Pohl, 1965.
Via Virtual Reality, Mother Encounters Deceased Daughter ‘But that barrier was going to melt away someday soon. The transhumanists had promised…’ — Stephen Baxter, 2008.
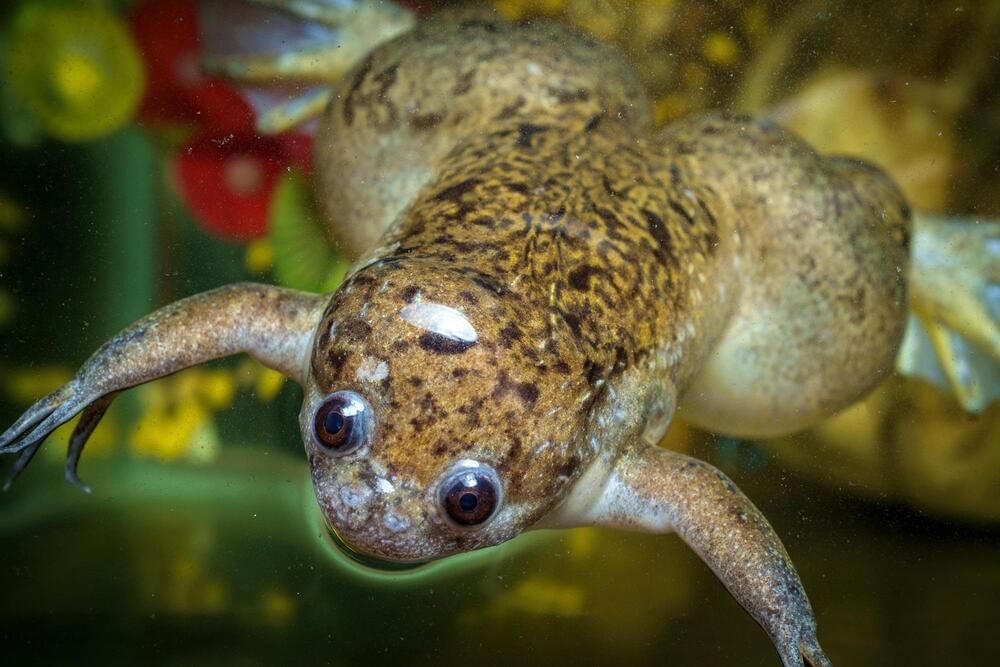

Frogs briefly treated with a five-drug cocktail administered by a wearable bioreactor on the stump were able to regrow a functional, nearly complete limb.
For millions of patients who have lost limbs for reasons ranging from diabetes to trauma, the possibility of regaining function through natural regeneration remains out of reach. Regrowth of legs and arms remains the province of salamanders and superheroes.
But in a study published in the journal Science Advances, scientists at Tufts University and Harvard University’s Wyss Institute have brought us a step closer to the goal of regenerative medicine.
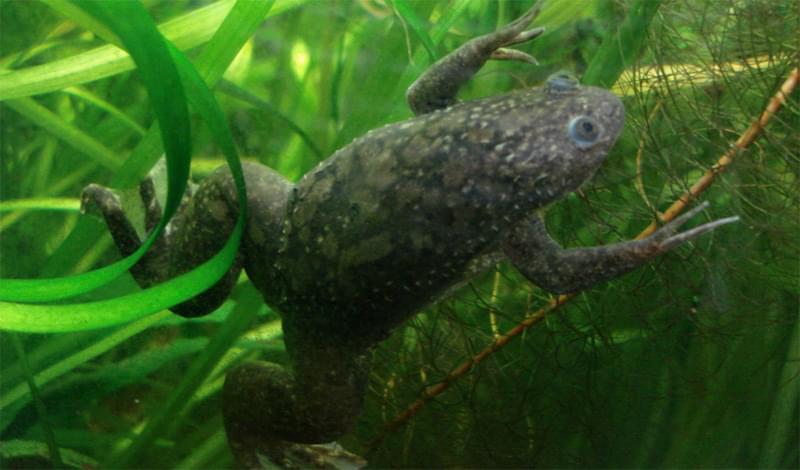

For millions of patients who have lost limbs – for reasons ranging from diabetes to trauma – the possibility of regaining function through natural regeneration remains out of reach. The regrowth of legs and arms remains limited to animals such as salamanders and the realm of science fiction.
However, a new study published in the journal Science Advances, by scientists at Tufts University and Harvard University’s Wyss Institute, has brought us a step closer to the goal of regenerating human limbs.
On adult frogs, which are naturally unable to regenerate limbs, a research team succeeded in triggering regrowth of a lost leg using a five-drug cocktail applied in a silicone wearable bioreactor dome that seals over the stump for just 24 hours. That brief treatment sets in motion an 18-month period of regrowth that eventually restores a functional leg.
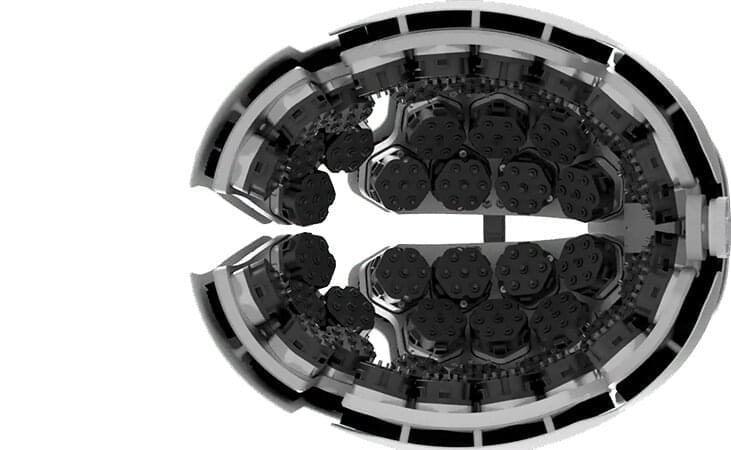

Recent advances in brain imaging techniques facilitate accurate, high-resolution observations of the brain and its functions. For example, functional near-infrared spectroscopy (fNIRS) is a widely used noninvasive imaging technique that employs near-infrared light (wavelength 700 nm) to determine the relative concentration of hemoglobin in the brain, via differences in the light absorption patterns of hemoglobin.
Most noninvasive brain scanning systems use continuous-wave fNIRS, where the tissue is irradiated by a constant stream of photons. However, these systems cannot differentiate between scattered and absorbed photons. A recent advancement to this technique is time-domain (TD)-fNIRS, which uses picosecond pulses of light and fast detectors to estimate photon scattering and absorption in tissues. However, such systems are expensive and complex and have a large form factor, limiting their widespread adoption.
To overcome these challenges, researchers from Kernel, a neurotechnology company, have developed a wearable headset based on TD-fNIRS technology. This device, called “Kernel Flow,” weighs 2.05 kg and contains 52 modules arranged in four plates that fit on either side of the head. The specifications and performance of the Kernel Flow system are reported in the Journal of Biomedical Optics (JBO).