😗😁
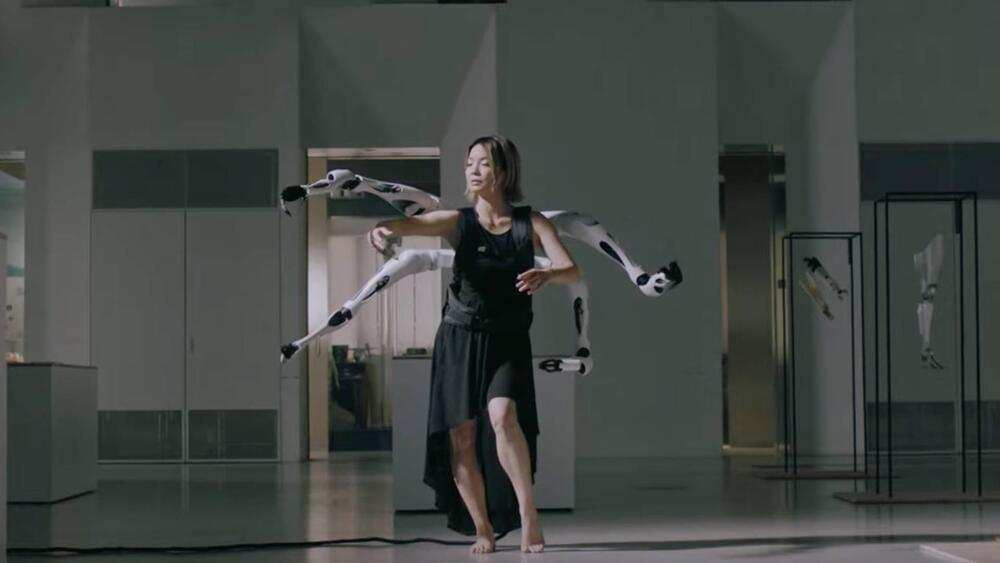
Jizai Arms.
“Half a century since the concept of a cyborg was introduced, Jizai-bodies (digital cyborgs), enabled by the spread of wearable robotics, are the focus of much research in recent times,” states the company’s website.
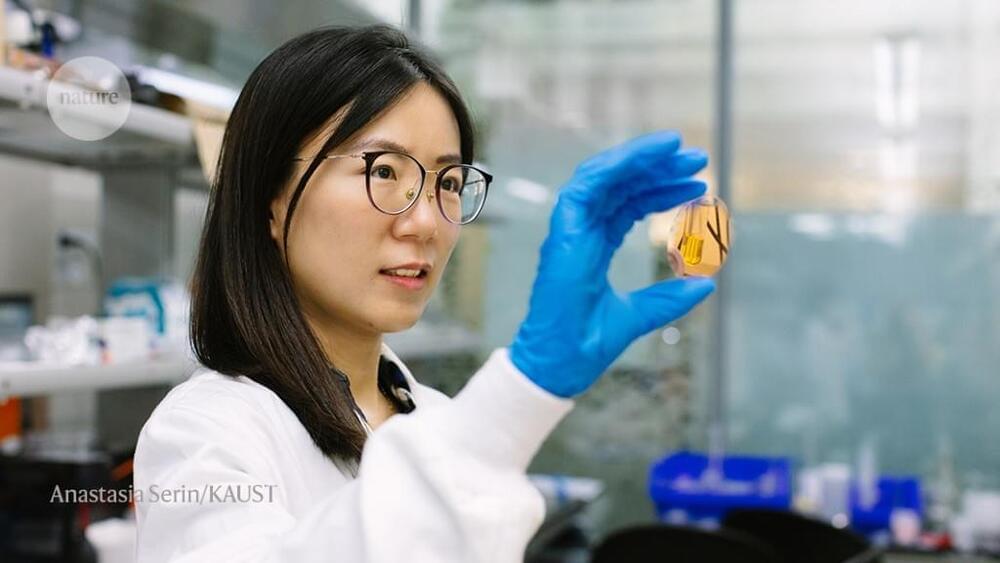
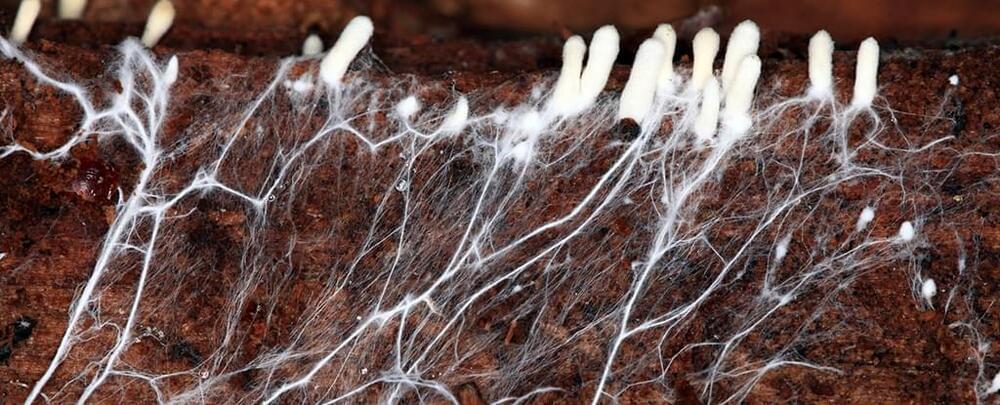



A team from Newcastle University and Northumbria University in the UK has found that the thin, root-like threads produced by many fungi can potentially be used as a biodegradable, wearable material that’s also able to repair itself.
In their tests, the researchers focused on the Ganoderma lucidum fungus, producing a skin from branching filaments known as hyphae, which together weave into a structure called a mycelium.
With a little more work the fragile skins could serve as a substitute for leather, satisfying vegan, environmental, and fashion tastes, though the process of its creation also needs to be sped and scaled up before it can be transformed into next season’s jacket.
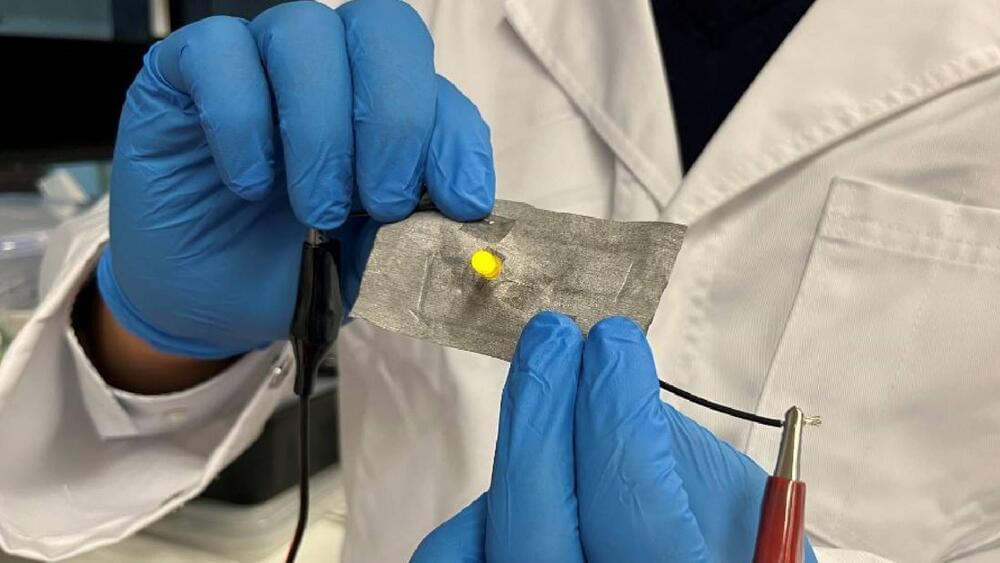

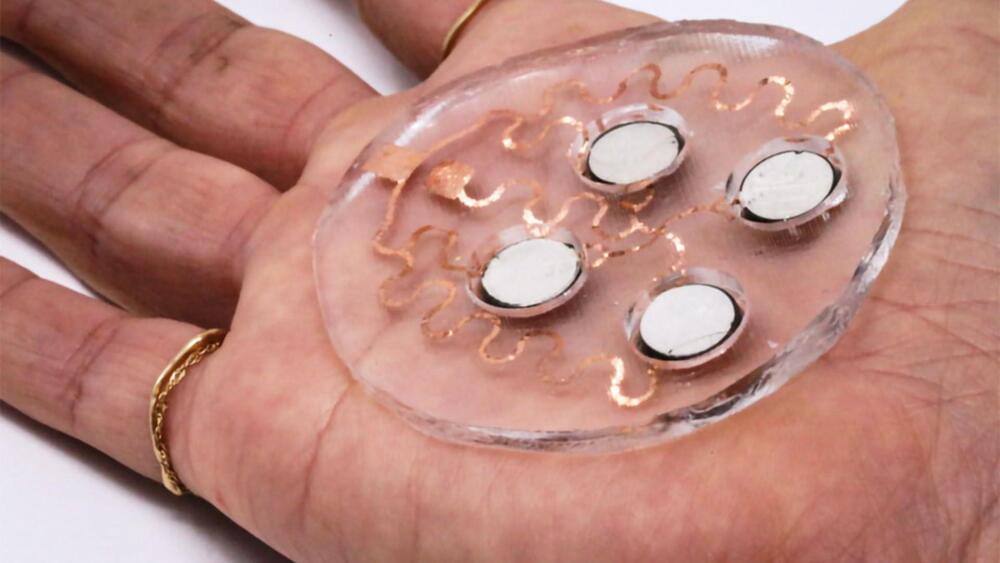
Scientists have invented a simple metallic coating treatment for clothing or wearable textiles, which can repair itself, repel bacteria, and even monitor a person’s electrocardiogram (ECG) heart signals.
This is according to a press release by Flinders University published last month.
The inventors of the new coating say the conductive circuits created by liquid metal (LM) particles can transform wearable electronics due to the fact that the ‘breathable’ electronic textiles have special connectivity powers to ‘autonomously heal’ themselves even when cut.
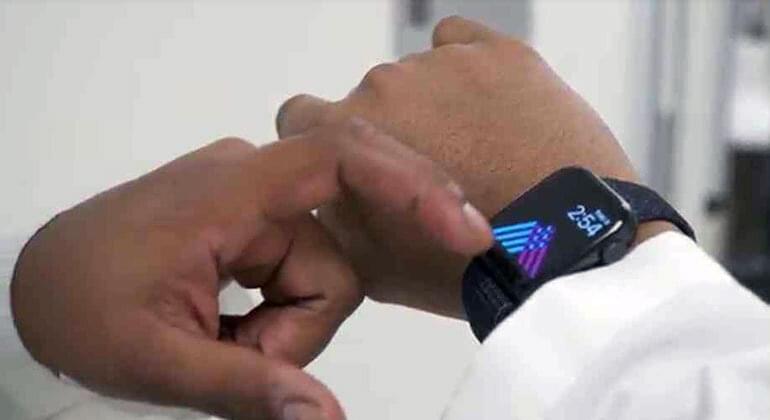

Applying machine learning models, a type of artificial intelligence (AI), to data collected passively from wearable devices can identify a patient’s degree of resilience and well-being, according to investigators at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai in New York.
The findings, reported in the May 2 issue of JAMIA Open, support wearable devices, such as the Apple Watch, as a way to monitor and assess psychological states remotely without requiring the completion of mental health questionnaires.
The paper, titled “A machine learning approach to determine resilience utilizing wearable device data: analysis of an observational cohort,” points out that resilience, or an individual’s ability to overcome difficulty, is an important stress mitigator, reduces morbidity, and improves chronic disease management.
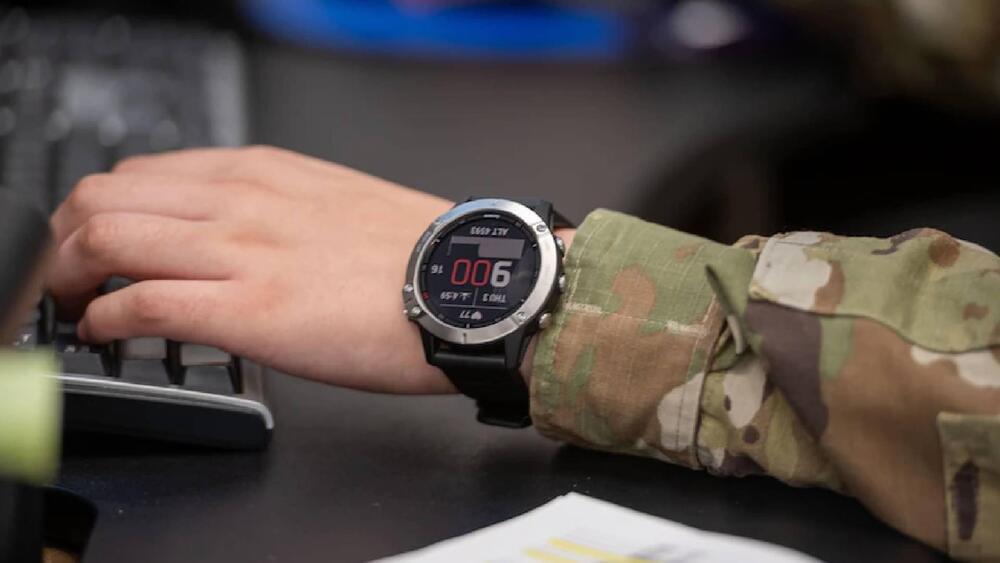

The U.S. Department of Defense (DOD) invented a wearable during the pandemic that was extremely adept at identifying infections.
This is according to a press release by the department published on Thursday.
Now the organization is ready to take the next steps in what it calls the Rapid Assessment of Threat Exposure project, also known as the RATE program.
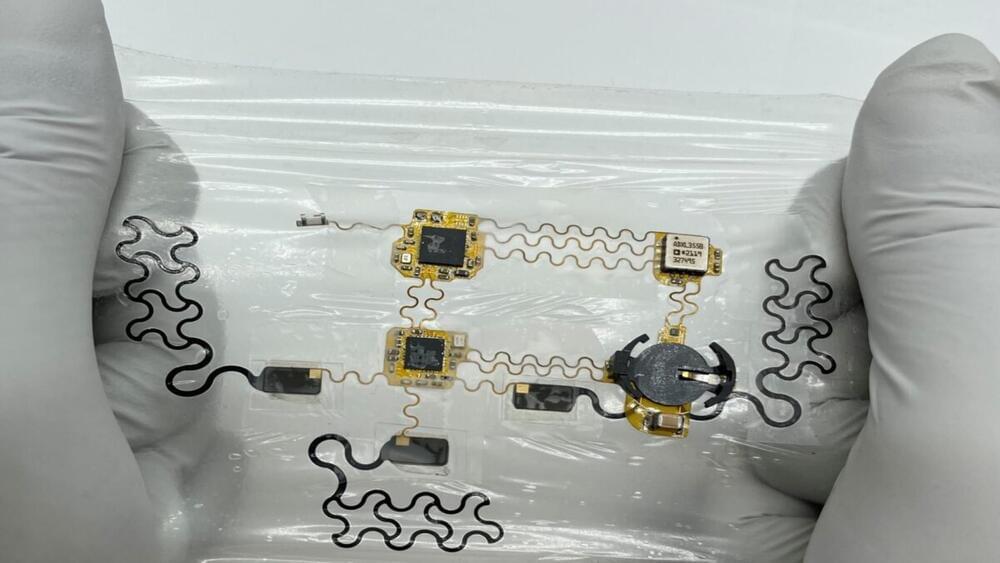

Revolutionizing the process of heart monitoring, researchers have developed a wearable e-tattoo that provides continuous heart monitoring outside of a clinical setting.
A team of researchers from The University of Texas at Austin has created a flexible and wearable medical device that could transform the fight against heart disease. This device called an electronic tattoo or e-tattoo, can be attached to the chest to continuously monitor the heart outside of clinical settings.
The e-tattoo is wireless and mobile, as it has small active circuits and sensors linked by stretchable interconnections. The device weighs just 2.5 grams and can be worn comfortably with a medical dressing.
University of Texas.
AI has just made its next big move! The Humane AI Wearable made its debut on a TED talk. Its coming after iPhones and Android smartphones!
A team of researchers at the U.S. Department of Energy’s Argonne National Laboratory has developed a new scientific tool called Polybot that combines artificial intelligence with robotics. This tool is set to revolutionize polymer electronics research by speeding up the discovery process of materials with multiple applications, from wearable biomedical devices to better batteries, according to a release.
Polymer electronics are the future of flexible electronics. They are efficient and sustainable, used to monitor health and treat certain diseases, among other things. However, the current methods used to prepare these polymers for electronics can take years of intense labor. To achieve targeted performance, there are an overwhelming number of potential tweaks, from spiking the fabrication recipe with different formulations to varying the processing conditions.