According to Gates, tech such as VR goggles and motion-capture gloves would be needed to accurately capture a user’s body language and expressions.
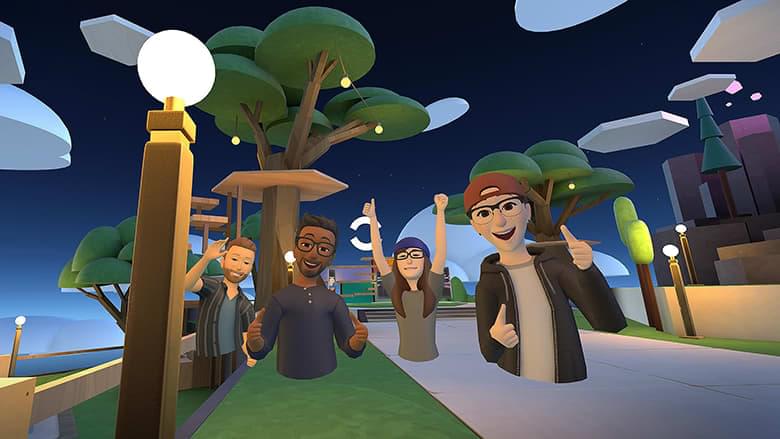



Facebook on Thursday announced that it is opening up Horizon Worlds, its virtual reality world of avatars, to anyone 18 and older in the U.S. and Canada.
Horizon Worlds launched in beta last year to select Oculus VR users, who answered invitations to join the virtual world. With the announcement on Thursday, users will no longer need to be invited.
The broader launch of Horizon Worlds is an important step for Facebook, which officially changed its name to Meta in October. The company adopted the new moniker, based on the sci-fi term metaverse, to describe its vision for working and playing in a virtual world.

Virtual environments have also shown promise for activists resisting digital authoritarianism. On Minecraft, Reporters Without Borders has sponsored an Uncensored Library where users could see content by dissident writers that had been censored in countries like Saudi Arabia, Russia and Vietnam. It’s possible that the metaverse may bring new promise for freedom and transparency across borders.
But the metaverse’s consequences may be even more radical.
If it becomes as all-encompassing as some predict, the metaverse may foster virtual communities, networks and economies that transcend borders and national identities. Individuals might one day identify primarily with metaverse-based decentralized autonomous organizations with their own quasi-foreign policies. Such a transition could mandate the reconceptualization of geopolitical affairs from the ground up.
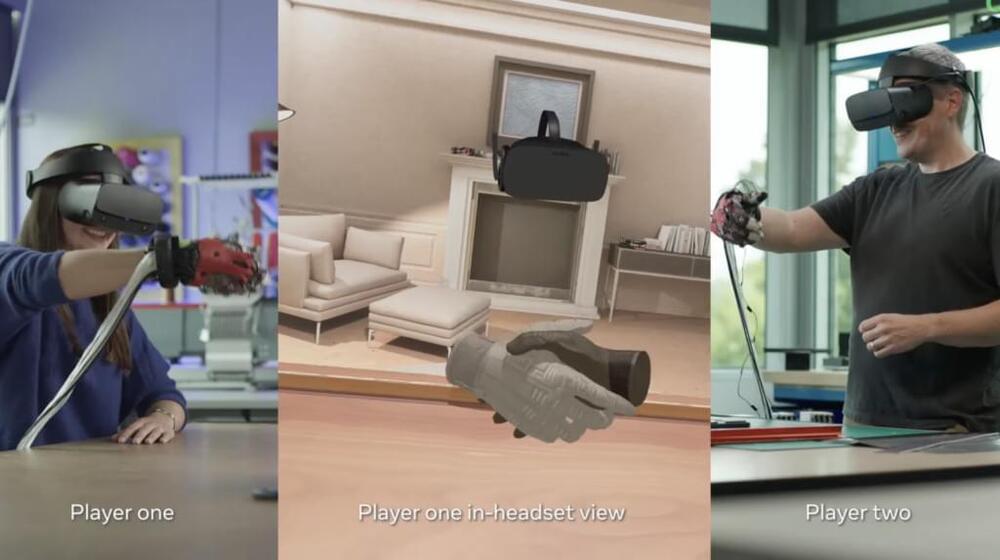

In the novel-turned-movie Ready Player One by Ernest Cline, the protagonist escapes to an online realm aptly called OASIS. Instrumental to the OASIS experience is his haptic (relating to sense of touch) bodysuit, which enables him to move through and interact with the virtual world with his body. He can even activate tactile sensations to feel every gut punch, or a kiss from a badass online girl.
While no such technology is commercially available yet, the platform Meta, formerly known as Facebook, is in the early stages of creating haptic gloves to bring the virtual world to our fingertips. These gloves have been in the works for the past seven years, the company recently said, and there’s still a few more to go.
These gloves would allow the wearer to not only interact with and control the virtual world, but experience it in a way similar to how one experiences the physical world. The wearer would use the gloves in tandem with a headset for AR or VR. A video posted by Meta in a blog shows two users having a remote thumb-wrestling match. In their VR headsets, they see a pair of disembodied hands reflecting the motions that their own hands are making. In their gloves, they feel every squeeze and twitch of their partner’s hand—at least that’s the idea.
Subscribe at the link below for new content every Thursday!
Kaleidoscope Presents: We Are Stars.
We Are Stars is the most immersive science documentary in the Universe! This 360°, 3D, high frame rate experience seeks to answer some of the biggest questions of all time. What are we made of? Where did it all come from? Explore the secrets of our cosmic chemistry and our explosive origins.
We join the Time Master narrated by Hollywood superstar Andy Serkis, a Victorian gent with his very own time tent who whisks us off on a 13.8 billion year adventure.
Check out the Creators.
https://www.instagram.com/nsccreative/
https://www.facebook.com/NSCcreative/
https://twitter.com/NSCcreative.
Masterpiece Studio (formerly MasterpieceVR) today announced it’s releasing a free edition of its latest professional VR creator suite, Masterpiece Studio Pro. The free software license is targeting individuals looking to use the suite for non-commercial use.
The free version is said to contain the entire set of features of Masterpiece Studio Pro, which is a subscription-based service aimed at freelancers, teams, and educators using its creation tools for work.
Like its original 2019-era Masterpiece Studio, Masterpiece Studio Pro lets users create 3D assets within VR, letting you use motion controllers to draw, sculpt, texture, optimize, rig, skin, and animate things like characters or objects. The Pro version was launched back in April 2021.
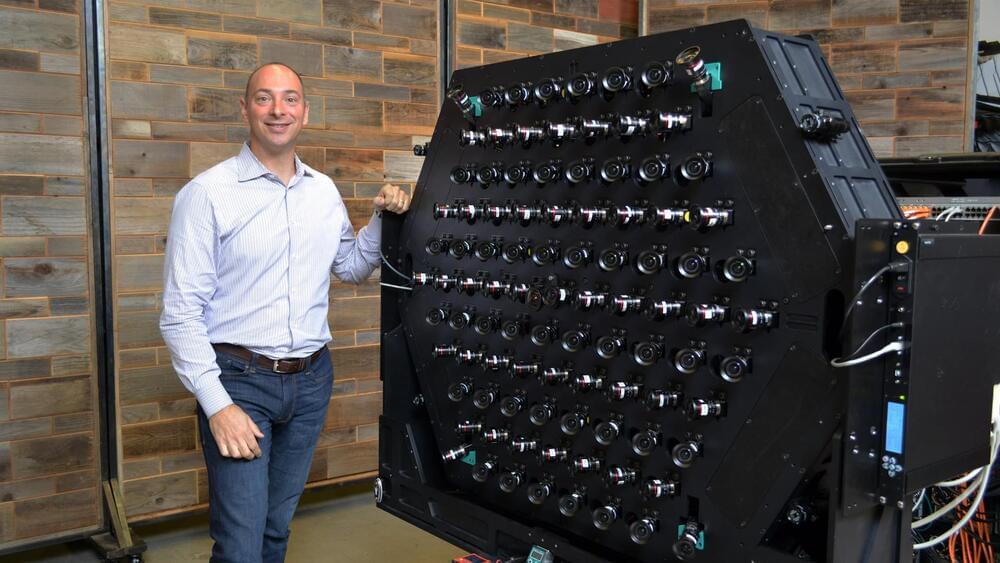

Lytro’s Immerge light-field camera is meant for professional high-end VR productions. It may be a beast of a rig, but it’s capable of capturing some of the best looking volumetric video that I’ve had my eyes on yet. The company has revealed a major update to the camera, the Immerge 2.0, which, through a few smart tweaks, makes for much more efficient production and higher quality output.
Light-field specialist Lytro, which picked up a $60 million Series D investment earlier this year, is making impressive strides in its light-field capture and playback technology. The company is approaching light-field from both live-action and synthetic ends; last month Lytro announced Volume Tracer, a software which generates light-fields from pre-rendered CG content, enabling ultra-high fidelity VR imagery that retains immersive 6DOF viewing.
Immerge 2.0
On the live-action end, the company has been building a high-end light-field camera which they call Immerge. Designed for high-end productions, the camera is actually a huge array of individual lenses which all work in unison to capture light-fields of the real world.
Gesture interface company Leap Motion is announcing an ambitious, but still very early, plan for an augmented reality platform based on its hand tracking system. The system is called Project North Star, and it includes a design for a headset that Leap Motion claims costs less than $100 at large-scale production. The headset would be equipped with a Leap Motion sensor, so users could precisely manipulate objects with their hands — something the company has previously offered for desktop and VR displays.
Project North Star isn’t a new consumer headset, nor will Leap Motion be selling a version to developers at this point. Instead, the company is releasing the necessary hardware specifications and software under an open source license next week. “We hope that these designs will inspire a new generation of experimental AR systems that will shift the conversation from what an AR system should look like, to what an AR experience should feel like,” the company writes.
The headset design uses two fast-refreshing 3.5-inch LCD displays with a resolution of 1600×1440 per eye. The displays reflect their light onto a visor that the user perceives as a transparent overlay. Leap Motion says this offers a field of view that’s 95 degrees high and 70 degrees wide, larger than most AR systems that exist today. The Leap Motion sensor fits above the eyes and tracks hand motion across a far wider field of view, around 180 degrees horizontal and vertical.
iFLY, a leading provider of indoor skydiving facilities, today launched their iFLY VR initiative which combines the company’s indoor skydiving experience with immersive visuals powered by a Gear VR headset. I got to try to experience for myself at the company’s SF Bay location.
Now available at 28 locations in the US, the iFLY VR experience is an optional $20 add-on to the usual indoor flight experience offered by the company (which starts around $70). After training and getting a feel for stable non-VR flying, customers don a purpose-built helmet which incorporates a Gear VR headset. They can choose between several different skydiving locations—like Dubai, Hawaii, or Switzerland—where iFly has recorded real skydives specifically for use in the iFly VR experience.
I went to the company’s SF Bay location to try the iFly VR experience first hand, and came away feeling like I got to experience the ultimate haptic simulation.
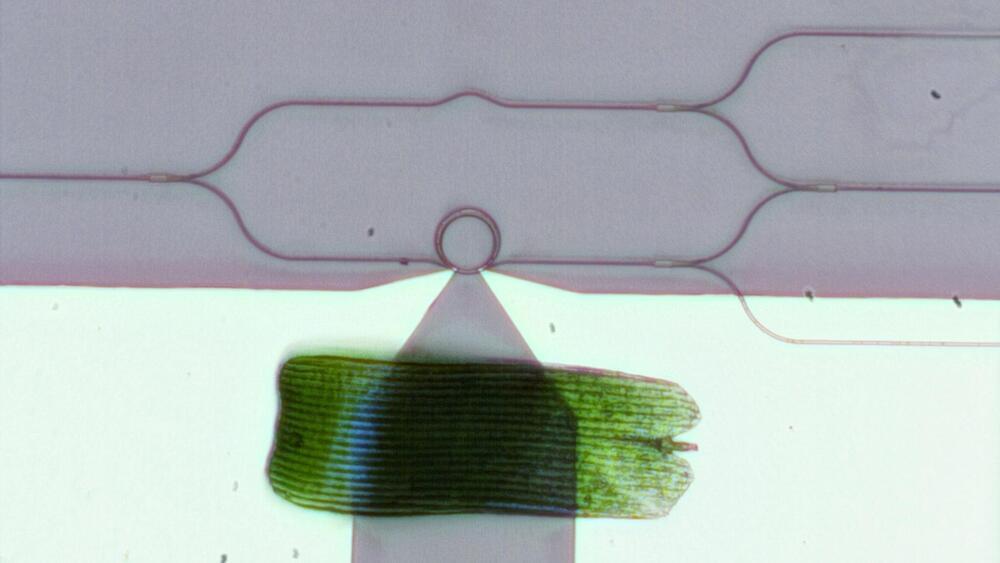
Over the past several decades, researchers have moved from using electric currents to manipulating light waves in the near-infrared range for telecommunications applications such as high-speed 5G networks, biosensors on a chip, and driverless cars. This research area, known as integrated photonics, is fast evolving and investigators are now exploring the shorter—visible—wavelength range to develop a broad variety of emerging applications. These include chip-scale LIDAR (light detection and ranging), AR/VR/MR (augmented/virtual/mixed reality) goggles, holographic displays, quantum information processing chips, and implantable optogenetic probes in the brain.
The one device critical to all these applications in the visible range is an optical phase modulator, which controls the phase of a light wave, similar to how the phase of radio waves is modulated in wireless computer networks. With a phase modulator, researchers can build an on-chip optical switch that channels light into different waveguide ports. With a large network of these optical switches, researchers could create sophisticated integrated optical systems that could control light propagating on a tiny chip or light emission from the chip.
But phase modulators in the visible range are very hard to make: there are no materials that are transparent enough in the visible spectrum while also providing large tunability, either through thermo-optical or electro-optical effects. Currently, the two most suitable materials are silicon nitride and lithium niobate. While both are highly transparent in the visible range, neither one provides very much tunability. Visible-spectrum phase modulators based on these materials are thus not only large but also power-hungry: the length of individual waveguide-based modulators ranges from hundreds of microns to several mm and a single modulator consumes tens of mW for phase tuning. Researchers trying to achieve large-scale integration—embedding thousands of devices on a single microchip—have, up to now, been stymied by these bulky, energy-consuming devices.