NVIDIA has unveiled ‘Grace’ – its first data centre CPU, which will deliver a 10x performance leap for systems training AI models, using energy-efficient ARM cores. The company also revealed plans for a 20 exaflop supercomputer.


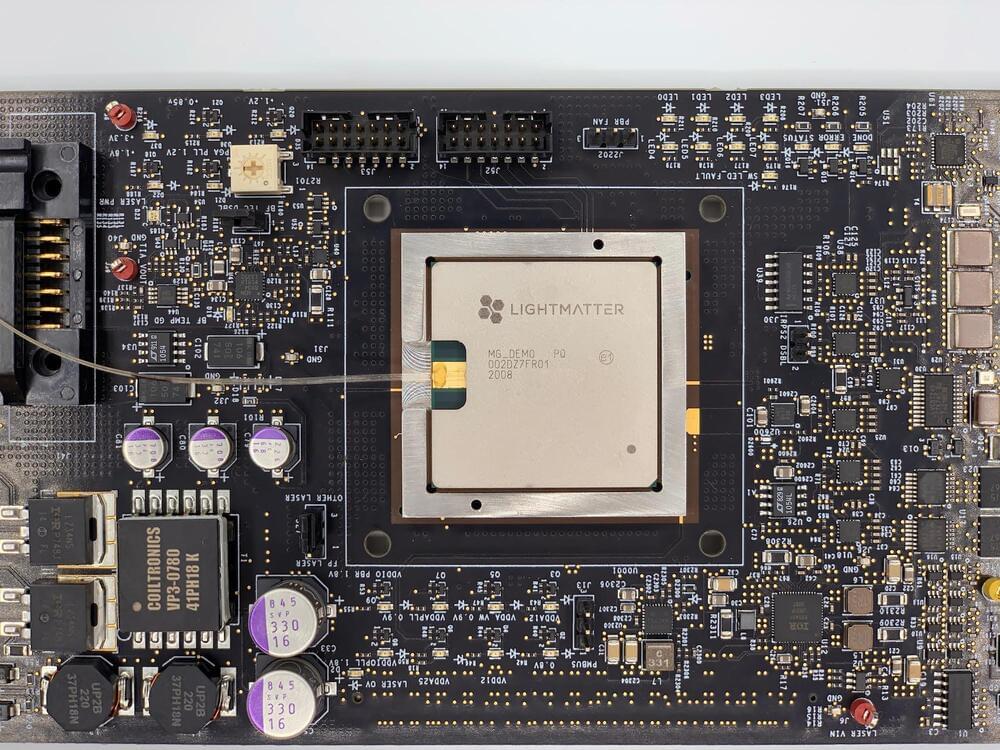
The Lightmatter photonic computer is 10 times faster than the fastest NVIDIA artificial intelligence GPU while using far less energy. And it has a runway for boosting that massive advantage by a factor of 100, according to CEO Nicholas Harris.
In the process, it may just restart a moribund Moore’s Law.
Or completely blow it up.
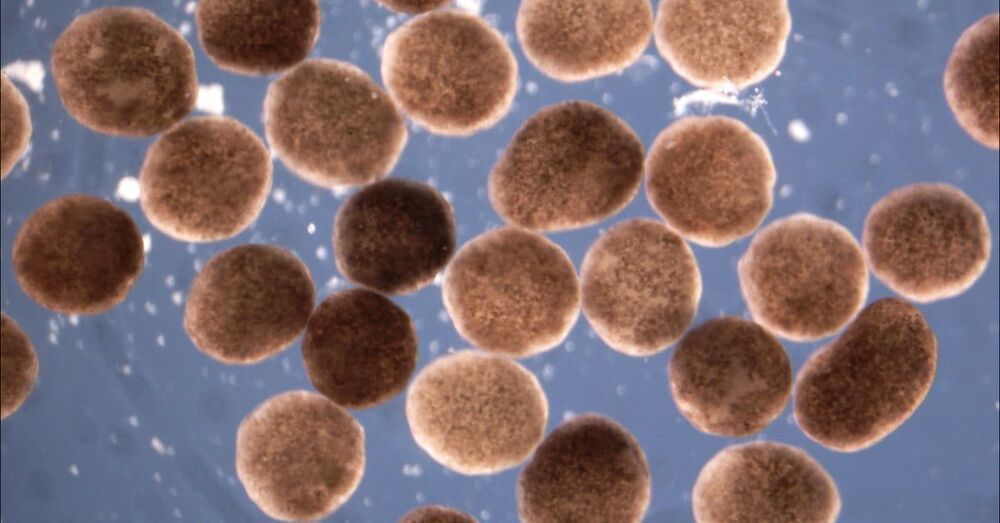
As the Tufts scientists were creating the physical xenobot organisms, researchers working in parallel at the University of Vermont used a supercomputer to run simulations to try and find ways of assembling these living robots in order to perform useful tasks.
Scientists at Tufts University have created a strange new hybrid biological/mechanical organism that’s made of living cells, but operates like a robot.
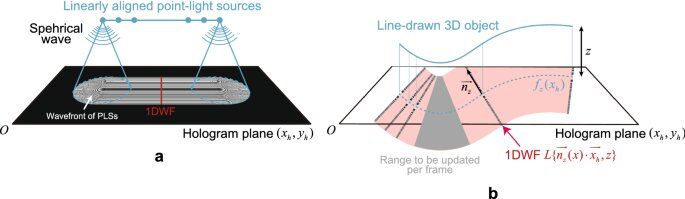
Researchers from Tokyo Metropolitan University have devised and implemented a simplified algorithm for turning freely drawn lines into holograms on a standard desktop CPU. They dramatically cut down the computational cost and power consumption of algorithms that require dedicated hardware. It is fast enough to convert writing into lines in real time, and makes crisp, clear images that meet industry standards. Potential applications include hand-written remote instructions superimposed on landscapes and workbenches.
T potential applications of holography include important enhancements to vital, practical tasks, including remote instructions for surgical procedures, electronic assembly on circuit boards, or directions projected on landscapes for navigation. Making holograms available in a wide range of settings is vital to bringing this technology out of the lab and into daily life.
One of the major drawbacks of this state-of-the-art technology is the computational load of hologram generation. The kind of quality we’ve come to expect in our 2D displays is prohibitive in 3D, requiring supercomputing levels of number crunching to achieve. There is also the issue of power consumption. More widely available hardware like GPUs in gaming rigs might be able to overcome some of these issues with raw power, but the amount of electricity they use is a major impediment to mobile applications. Despite improvements to available hardware, the solution can’t be achieved by brute force.

A new AI model that harnesses the power of the world’s fastest supercomputer, Fugaku, can rapidly predict tsunami flooding in coastal areas before the tsunami reaches land.
The development of the new technology was announced as part of a joint project between the International Research Institute of Disaster Science (IREDeS) at Tohoku University, the Earthquake Research Institute at the University of Tokyo, and Fujitsu Laboratories.
The 2011 Great East Japan Earthquake and subsequent tsunami highlighted the shortcomings in disaster mitigation and the need to utilize information for efficient and safe evacuations.
Holograms deliver an exceptional representation of 3D world around us. Plus, they’re beautiful. (Go ahead — check out the holographic dove on your Visa card.) Holograms offer a shifting perspective based on the viewer’s position, and they allow the eye to adjust focal depth to alternately focus on foreground and background.
Researchers have long sought to make computer-generated holograms, but the process has traditionally required a supercomputer to churn through physics simulations, which is time-consuming and can yield less-than-photorealistic results. Now, MIT researchers have developed a new way to produce holograms almost instantly — and the deep learning-based method is so efficient that it can run on a laptop in the blink of an eye, the researchers say.
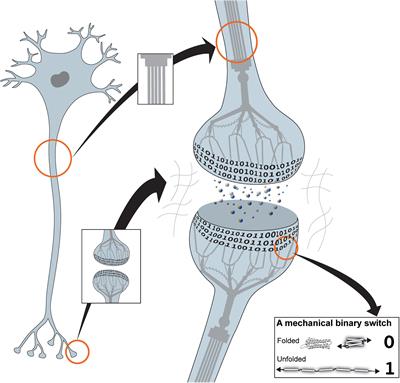
One of the major unsolved mysteries of biological science concerns the question of where and in what form information is stored in the brain. I propose that memory is stored in the brain in a mechanically encoded binary format written into the conformations of proteins found in the cell-extracellular matrix (ECM) adhesions that organise each and every synapse. The MeshCODE framework outlined here represents a unifying theory of data storage in animals, providing read-write storage of both dynamic and persistent information in a binary format. Mechanosensitive proteins that contain force-dependent switches can store information persistently, which can be written or updated using small changes in mechanical force. These mechanosensitive proteins, such as talin, scaffold each synapse, creating a meshwork of switches that together form a code, the so-called MeshCODE. Large signalling complexes assemble on these scaffolds as a function of the switch patterns and these complexes would both stabilise the patterns and coordinate synaptic regulators to dynamically tune synaptic activity. Synaptic transmission and action potential spike trains would operate the cytoskeletal machinery to write and update the synaptic MeshCODEs, thereby propagating this coding throughout the organism. Based on established biophysical principles, such a mechanical basis for memory would provide a physical location for data storage in the brain, with the binary patterns, encoded in the information-storing mechanosensitive molecules in the synaptic scaffolds, and the complexes that form on them, representing the physical location of engrams. Furthermore, the conversion and storage of sensory and temporal inputs into a binary format would constitute an addressable read-write memory system, supporting the view of the mind as an organic supercomputer.
I would like to propose here a unifying theory of rewritable data storage in animals. This theory is based around the realisation that mechanosensitive proteins, which contain force-dependent binary switches, can store information persistently in a binary format, with the information stored in each molecule able to be written and/or updated via small changes in mechanical force. The protein talin contains 13 of these switches (Yao et al., 2016; Goult et al., 2018; Wang et al., 2019), and, as I argue here, it is my assertion that talin is the memory molecule of animals. These mechanosensitive proteins scaffold each and every synapse (Kilinc, 2018; Lilja and Ivaska, 2018; Dourlen et al., 2019) and have been considered mainly structural. However, these synaptic scaffolds also represent a meshwork of binary switches that I propose form a code, the so-called MeshCODE.

Canadian startup Xanadu says their quantum computer is cloud-accessible, Python programmable, and ready to scale.
Quantum computers based on photons may have some advantages over electron-based machines, including operating at room temperature and not temperatures colder than that of deep space. Now, say scientists at quantum computing startup Xanadu, add one more advantage to the photon side of the ledger. Their photonic quantum computer, they say, could scale up to rival or even beat the fastest classical supercomputers—at least at some tasks.
Whereas conventional computers switch transistors either on or off to symbolize data as ones and zeroes, quantum computers use quantum bits or “qubits” that, because of the bizarre nature of quantum physics, can exist in a state known as superposition where they can act as both 1 and 0. This essentially lets each qubit perform multiple calculations at once.
The more qubits are quantum-mechanically connected entangled together, the more calculations they can simultaneously perform. A quantum computer with enough qubits could in theory achieve a “quantum advantage” enabling it to grapple with problems no classical computer could ever solve. For instance, a quantum computer with 300 mutually-entangled qubits could theoretically perform more calculations in an instant than there are atoms in the visible universe.