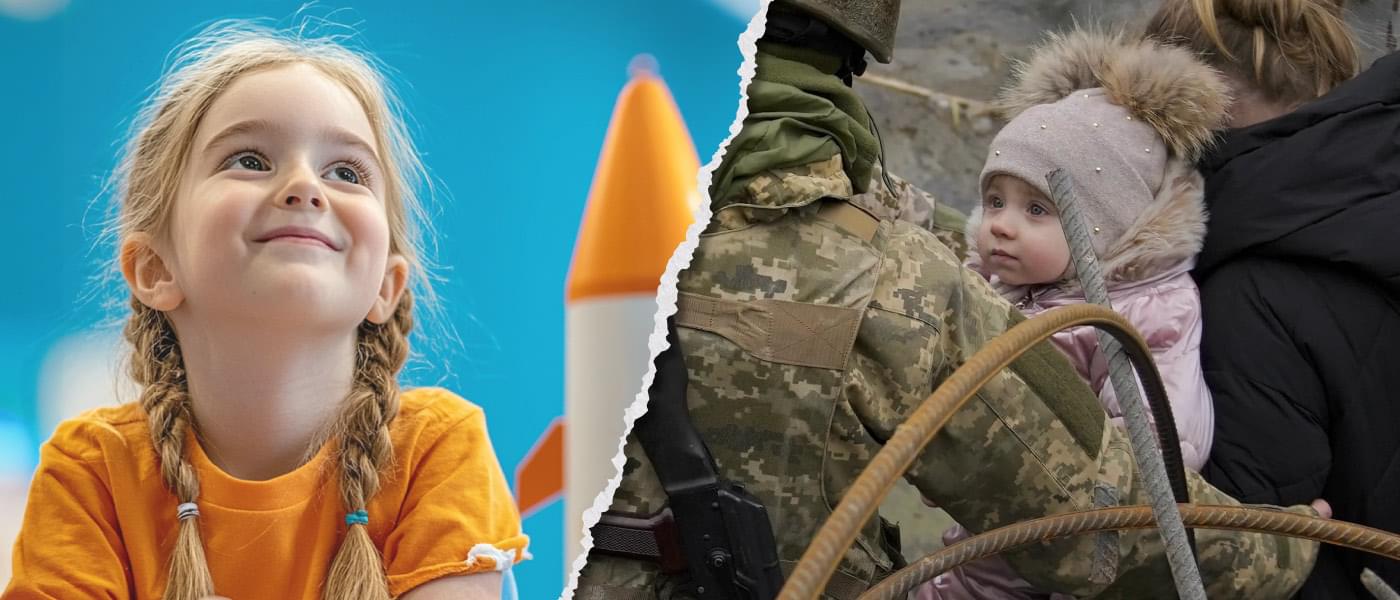
Help us help the kids of Ukraine to dream about the future.
Space, hope, and a great cause on the side of freedom. Follow the links. Make the donation, put a telescope, model rocket or robot in the hands of a kid who very badly needs Permission to Dream!
Space4 Ukraine empowers young Ukrainians whose education has been disrupted by war, giving them access to the tools, training, and opportunities they need to rebuild their future—and ours. Because no human potential should ever be wasted.