What can carbon deposits on Mars tell scientists about whether life could have once existed on the Red Planet? This is what a recent study published in Sci | Space
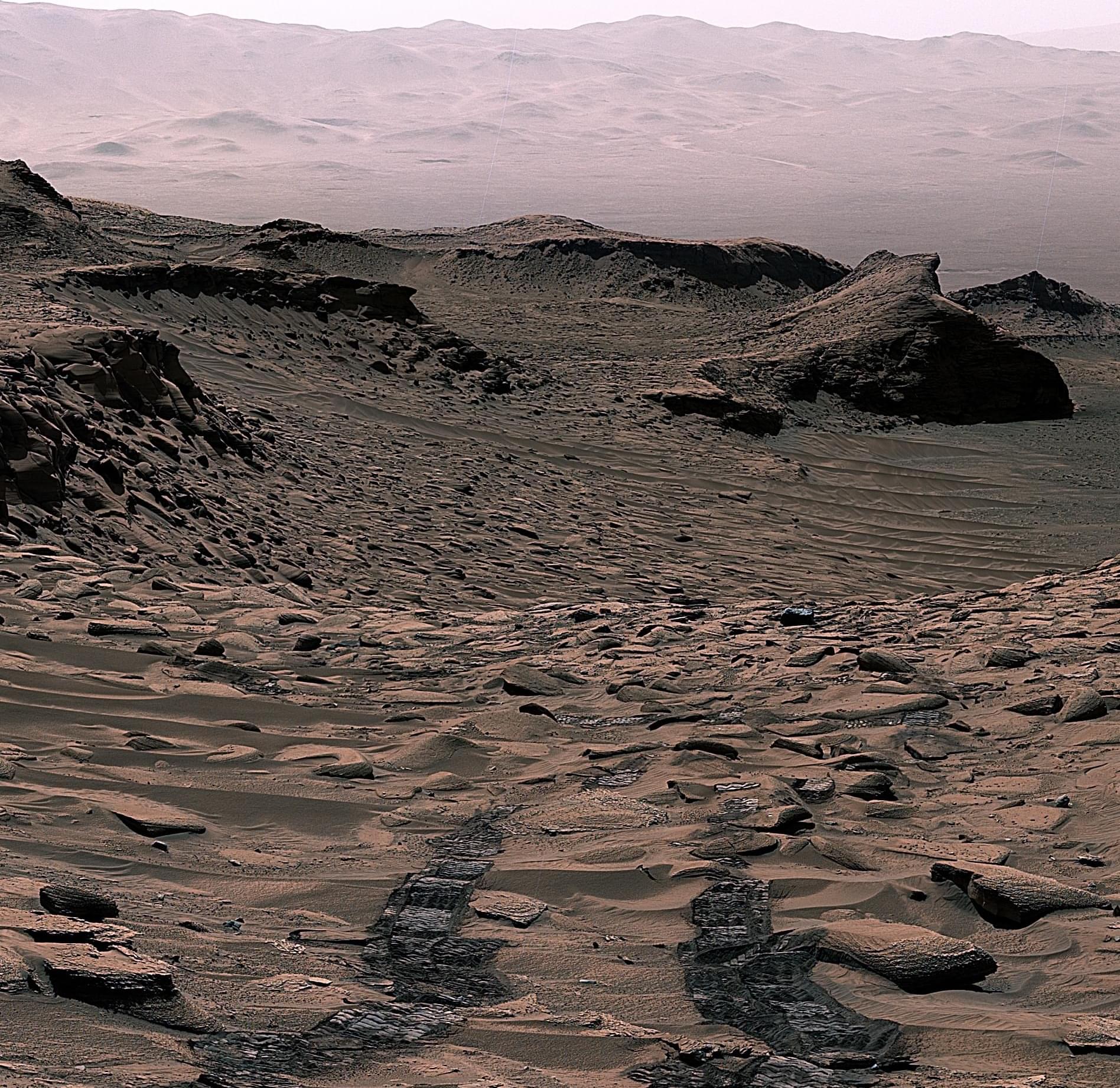



NASA’s Lucy mission is about to fly past asteroid Donaldjohanson, a strange, elongated rock in the main belt. While this three-mile-wide object isn’t one of Lucy’s primary targets, the April 20 flyby serves as a full dress rehearsal before the spacecraft heads toward the Trojan asteroids near Jup

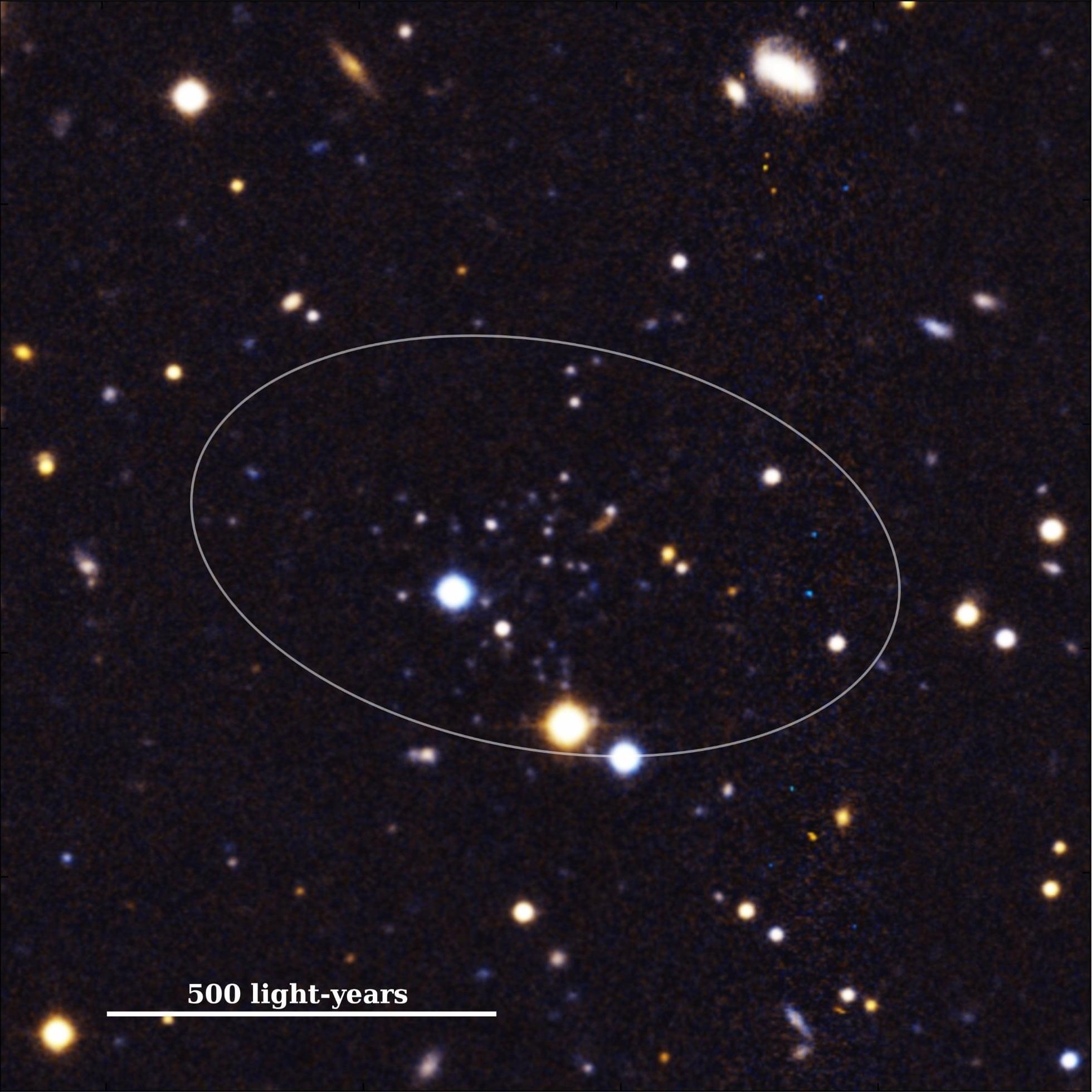
Astronomers have detected the most promising signs yet of a possible biosignature outside the solar system, although they remain cautious.
Using data from the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST), the astronomers, led by the University of Cambridge, have detected the chemical fingerprints of dimethyl sulfide (DMS) and/or dimethyl disulfide (DMDS), in the atmosphere of the exoplanet K2-18b, which orbits its star in the habitable zone.
On Earth, DMS and DMDS are only produced by life, primarily microbial life such as marine phytoplankton. While an unknown chemical process may be the source of these molecules in K2-18b’s atmosphere, the results are the strongest evidence yet that life may exist on a planet outside our solar system.
Subsurface ocean on Mars suggested by new data and long organic molecules found too. See why these suggest life may be on Mars today!GoldBacks from Galactic/.…
At the same time, he noted, there was still a 0.3% chance that their observation was a statistical fluke. “We need to be open and continue exploring other scenarios,” he added.
K2-18b is part of the “sub-Neptune” class of nearly 6,000 exoplanets that have been discovered beyond the solar system since the 1990s.
Finding evidence of life in the cosmos was the “holy grail” of exoplanet science, Madhusudhan said.

IN A NUTSHELL 🌌 Kokoro Hosogi, an undergraduate student, contributed to a groundbreaking study published in Nature. 🔭 The research utilized observations from the XRISM telescope to explore the dynamics of intergalactic gas. 💫 Discovery revealed the Centaurus cluster gas exhibits a wave-like motion, challenging existing models. 🎓 Hosogi’s involvement highlights the essential role of.
Good space battles can take many forms. They can be oversized, noisy fleet fights involving hundreds of ships or quiet and cerebral tests of wills between two solitary commanders. No matter the scale, great space combat always combines high stakes, clearly explained tactics and superior special effects.
This is the ultimate ranking of the best starship space battles in science fiction movies and television.
🔑 Space Battle Rankings:
1. Battlestar Galactica.
2. Star Trek: Deep Space Nine.
3. Star Wars Episode VI: Return of the Jedi.
4. Babylon 5
5. Star Trek II: The Wrath of Khan.
6. The Orville.
🚀 All Great Battlestar Galactica Battles → • The 4 Most Explosive Space Battles Ev…
🚀 All Great Babylon 5 Battles → • 4 Of Sci-Fi’s Most Explosive Battles…
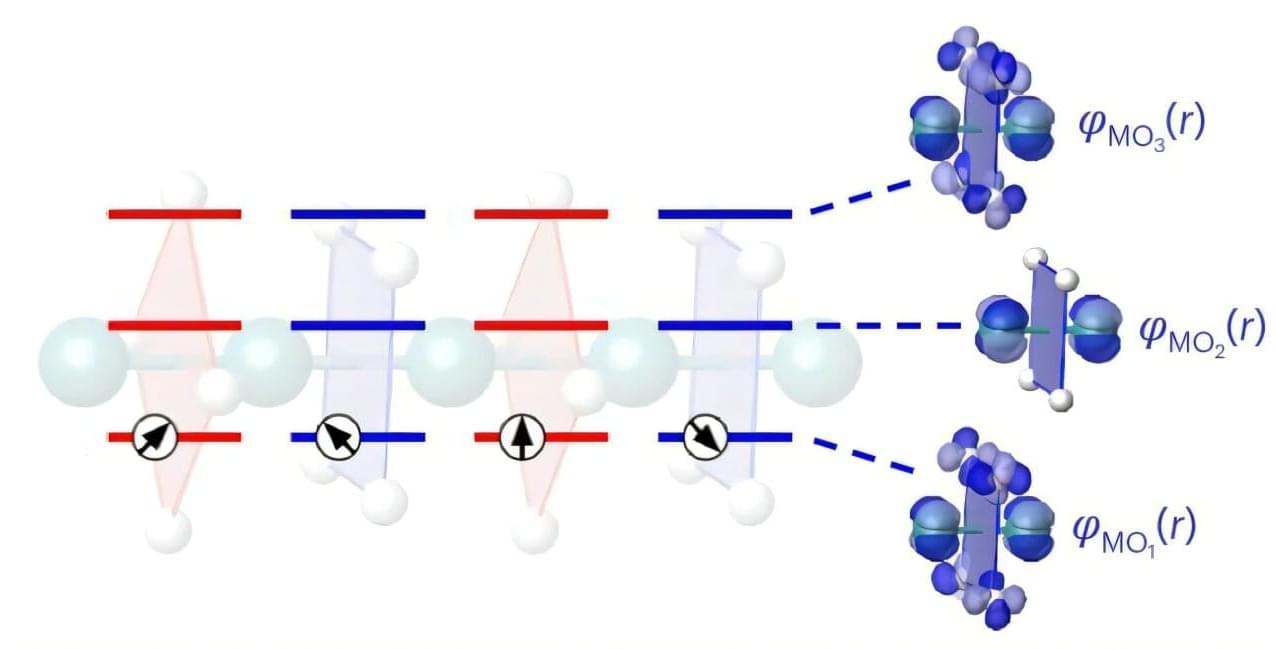
A study by researchers from the University of British Columbia’s Blusson Quantum Matter Institute (UBC Blusson QMI) has found a rare form of one-dimensional quantum magnetism in the metallic compound Ti4MnBi2, offering evidence into a phase space that has remained, until now, largely theoretical.
The study, published in Nature Materials, comes at a time of growing global interest in quantum materials that redefine the boundaries between magnetism, conductivity, and quantum coherence.
“We proved the existence of a new class of quantum materials that are both metallic and one-dimensional magnets, with strong coupling between the magnetic moments and their metallic host,” said UBC Blusson QMI Investigator Prof. Meigan Aronson.