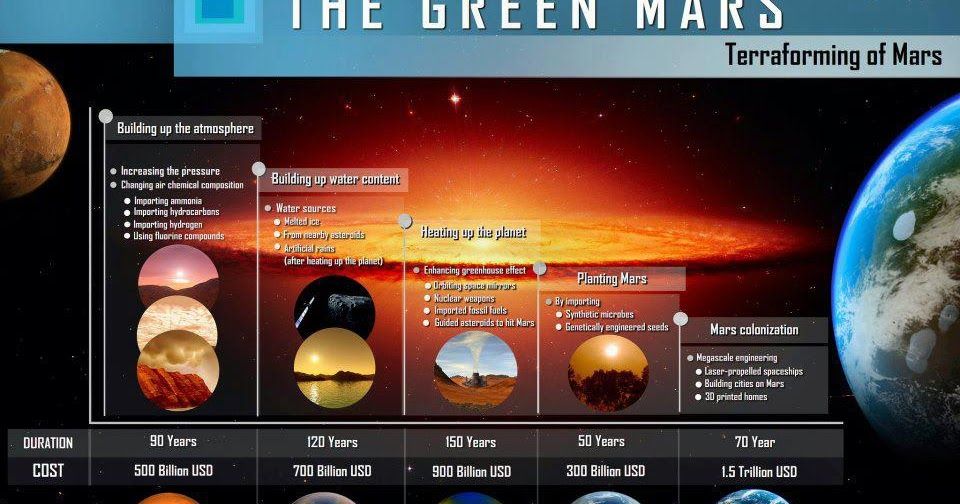
If all the solar incident on Mars were to be captured with 100% efficiency, then Mars would warm to Earth-like temperatures in about 10 years. However, the efficiency of the greenhouse effect is plausibly about 10%, thus the time it would take to warm Mars would be ~100 years. This assumes, of course, adequate production of super greenhouse gases over that entire time. The super greenhouse gases desired for use on Mars would be per fluorinated compounds (PFCs) as these are not toxic, do not destroy ozone, will resist degradation by ultraviolet life, and are composed of elements (C, S, and F) that are present on Mars. Fluorine has been detected on Mars by Curiosity.
The Warming Phase of a terraforming project on Mars results in a planet with a thick CO2 atmosphere. The thickness is determined by the total releasable CO2 present on Mars.
The temperatures would become well above freezing and liquid water is common. An Earth-like hydrological cycle is maintained. Photosynthetic organisms can be introduced as conditions warm and organic biomass is thus produced. A rich flora and fauna are present. A natural result of this is the biological consumption of the nitrate and perchlorate in the.