Oil and gas giant submits plans for up to 500MW of solar and battery storage to supply renewable power to industrial customers — including its own LNG operations — in WA Pilbara region.
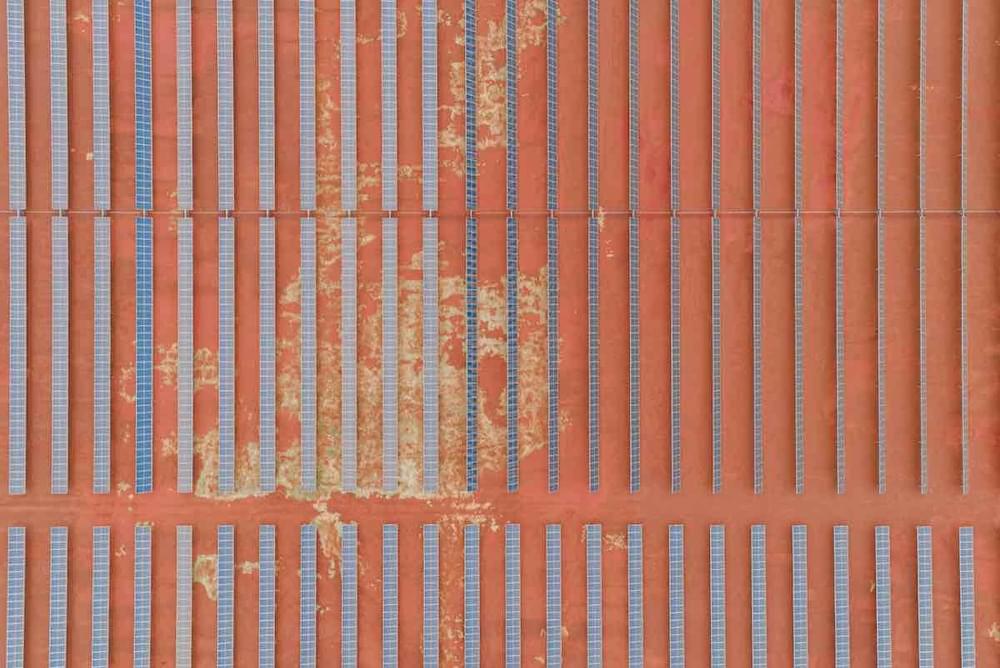
Oil and gas giant Woodside has kicked off the new year by firming up plans to develop a massive solar and battery project in Western Australia’s Pilbara region, to supply renewable electricity to local industrial customers, including its own Pluto LNG facility.
In a submission to the W.A. Environmental Protection Authority on Monday, the company proposed the Woodside Solar Facility to be built in 100MW phases to a total capacity of up to 500MW, ultimately comprising around 1,000,000 solar panels and including battery energy storage infrastructure of up to 400MWh.
Woodside confirmed in its proposal that the solar farm and battery would deliver solar power to customers on the Burrup Peninsula, including at the Maitland Industrial Park, and likely including the company’s own onshore Pluto gas processing plant.