New research has found a way to power spacecraft with lasers generated using solar energy alone.

The International Renewable Energy Agency says breakthroughs like this, along with others such as solar panels that work at night or China’s flywheel energy storage project, are key to cutting back on dirty energy use and creating stronger and more reliable power systems.
“Further international cooperation is vital to deliver fit-for-purpose grids, sufficient energy storage and faster electrification, which are integral to move clean energy transitions quickly and securely,” Executive Director of the International Energy Agency Fatih Birol said in an IEA report.
This new way of storing energy could deliver cleaner, more affordable energy to cities, businesses, and homes. Researchers at Rice University believe it could be widely available in five to 10 years, making renewable energy more practical and accessible.

DOI: Abstract We are living in a historical period in respect to the deterioration in public health, as we experience the rise of the catastrophic obesity epidemic and mental health crisis in recent decades, despite the great efforts from the scientific and medical community to seek health solutions and to try to find cures to the enormous human suffering and economic costs resulting by this collapse in public health. This trend has reached such a critical level that it jeopardizes society when over 40% of the population is obese in the United States, suffering grave medical health conditions, even as the expenditure on public health is rising exponentially to over 20% of gross domestic product. This should point to a monumental failure in our fundamental understanding of basic human biology and health. This article suggests that our current Western reductionist scientific paradigm in both biology and medicine has proved impotent and failed us completely. Therefore, the current cultural health crises require a more holistic approach to human biology and health in terms of chronobiological trends. The emerging neuroscience of brain energy metabolism will be considered as a holistic model for understanding how solar cycles affect our civilization and drive our sex and growth hormones and neurotransmitters that shape both our physical and mental health.

A new solar cell process using Sn(II)-perovskite oxide material offers a promising pathway for green hydrogen production through water splitting, advancing sustainable energy technologies.
Experts in nanoscale chemistry have made significant progress toward sustainable and efficient hydrogen production from water using solar power.
An international collaborative study led by Flinders University, involving researchers from South Australia, the US, and Germany, has uncovered a novel solar cell process that could play a key role in future technologies for photocatalytic water splitting—a critical step in green hydrogen production.
The researchers produced new materials with perovskite crystal structures and compared them with existing materials at the cell level, concluding that high efficiencies can only be achieved with lead perovskites. They then fabricated highly efficient demonstrators, such as a perovskite silicon tandem solar cell of more than 100 sq cm with screen-printed metallization.
The project also included the development of a scalable perovskite-silicon tandem solar cell that achieved a 31.6% power conversion efficiency, first announced in September. The Fraunhofer researchers used a combination of vapor deposition and wet-chemical deposition to ensure an even deposition of the perovskite layer on the textured silicon surface. “Close industrial cooperation is the next step in establishing this future technology in Europe,” said Professor Andreas Bett, coordinator of the project.

Researchers at the University of Reading and University College London have developed a new artificial intelligence model that can predict how atoms arrange themselves in crystal structures. Called CrystaLLM, the technology works similarly to AI chatbots, by learning the “language” of crystals by studying millions of existing crystal structures. It could lead to faster discovery of new materials for everything from solar panels to computer chips.
Envision a settlement where the sunlight that beams across Australia buoy on its vast outback powers millions of homes and industries across Southeast Asia. This is how the Australia-Asia PowerLink (AAPowerLink) is being realized: the longest sub-sea cable in the world, linking northern Australia to Singapore, presently is one of the all-time break-through renewable energy developments. By virtue of this mammoth solar farm with its advanced energy transmission technology, this ambitious vision will shape the future energy systems around the world while addressing some critical climate issues.
Taking enormous advantage from its plentiful sunlight, northern Australia houses the world’s biggest Solar Precinct in its Northern Territory gathering between 17–20 GW peak electricity, a size surpassing that of Australia’s largest coal-fired power station.
The project incorporates advanced storage of 36–42 GWh, supplying 800 MW to Darwin and 1.75 GW to Singapore. In addition to reducing emissions and electricity prices for the Darwin region, it creates a renewable energy export marketplace for the region and demonstrates the use of the solar-rich area to meet 15 percent of Singapore’s electricity demand.
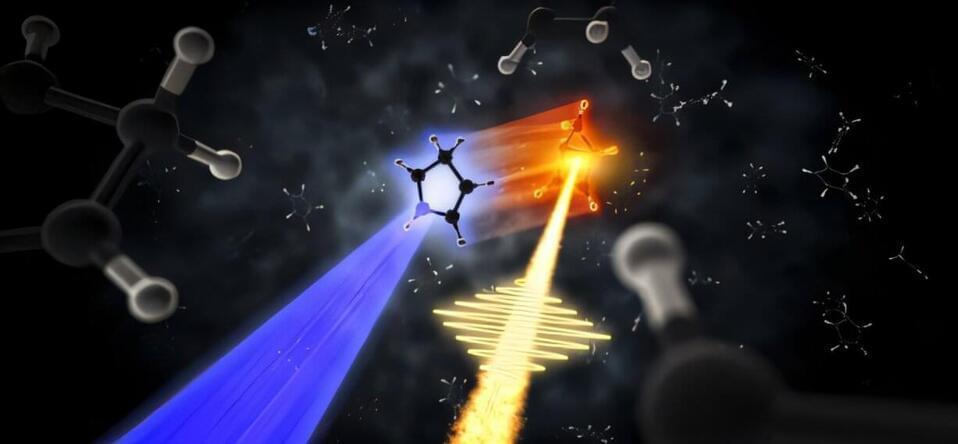
When molecules interact with ultraviolet (UV) light, they can change shape quickly, producing strain—stress in a molecule’s chemical structure due to an increase in the molecule’s internal energy. These processes typically take just tens of picoseconds (one millionth of a millionth of a second). Advanced capabilities at X-ray free electron laser (XFEL) facilities now enable scientists to create images of these ultrafast structural changes.
In work appearing in The Journal of Physical Chemistry A, researchers found structural evidence of a strained bicyclic molecule (a molecule consisting of two joined rings) that emerges from the chemical reaction that occurs when a cyclopentadiene molecule absorbs UV light. Cyclopentadiene is a good sample chemical for studying a range of reactions, and these findings have broad implications for chemistry.
Highly strained molecules have a variety of interesting applications in solar energy and pharmaceuticals. However, strain doesn’t typically occur naturally—energy must be added to a molecular system to create the strain. Identifying processes that produce molecules with strained rings is a challenge of broad interest in physical chemistry.
A new design principle has been identified that could eliminate the use of toxic chemicals in solar cell manufacturing.
The standard manufacturing process of organic cells involves toxic solvents. This environmental concern has hindered the widespread adoption of organic solar cells.
Researchers at Linköping University (LiU) have revealed a new design principle for eco-friendly, high-efficiency organic solar cells.