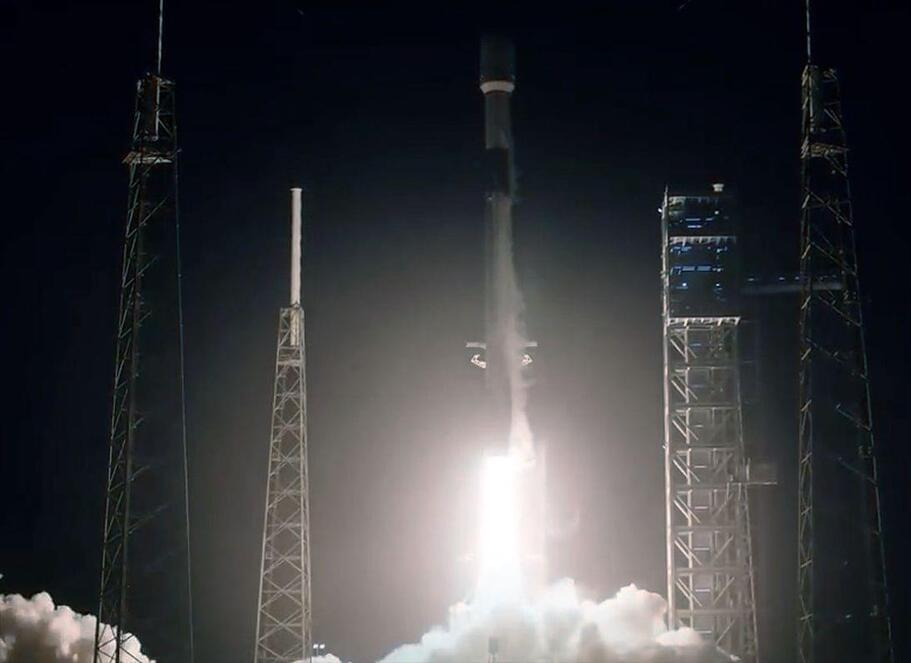
Liftoff occurred at 12:33 a.m. EST on Saturday (Dec. 23).
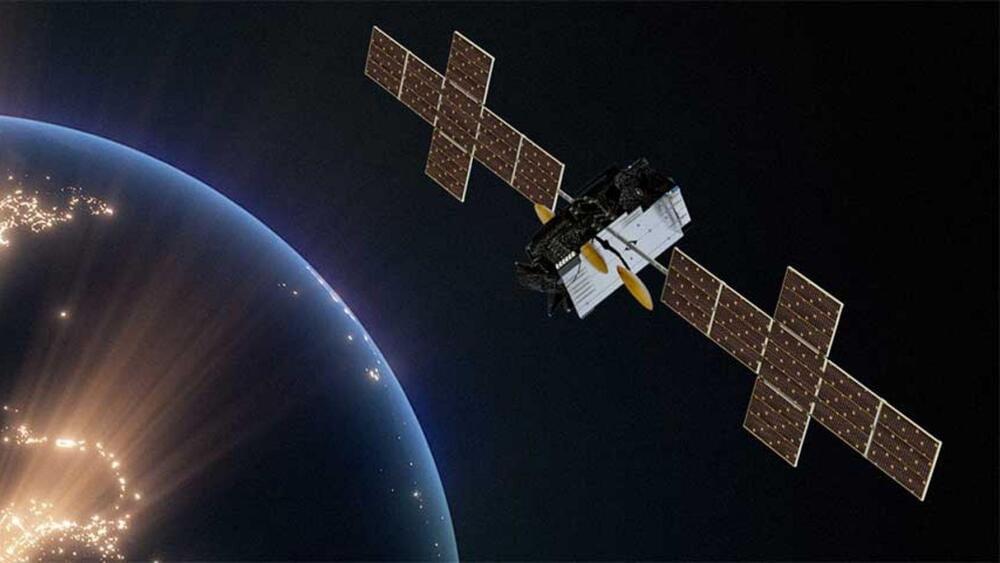



HughesNet’s move to offer 100 Mbps speeds brings it closer to its industry rival, SpaceX’s Starlink, which ranges between 25 to 220 Mbps.
HughesNet’s Jupiter 3 satellite, although geostationary and considerably farther away, rivals Starlink with its size and capacity. The ultra-high-density satellite operates in Ka-band frequencies with 300 spot beams, efficiently allocating and directing signals for better coverage.
Hughes, a pioneer in satellite-delivered internet service since the 1990s, continues to earn recognition.
The company launched 23 of its Starlink internet satellites on a Falcon 9 rocket that had flown 18 times before, breaking its own record for the most flights by a single booster.
SpaceX has achieved a new milestone in its quest to reuse rockets and reduce the cost of spaceflight. The company launched 23 Starlink internet satellites on a Falcon 9 rocket that had flown 18 times before, breaking its record for the most flights by a single booster.
Falcon 9’s first stage has landed on the Just Read the Instructions droneship, completing the first 19th launch and landing of a booster pic.twitter.com/WoVx0R0Esj — SpaceX (@SpaceX) December 23, 2023
The historic launch occurred from Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida on Saturday (December 23) at 12:33 am EST (0533 GMT). The Falcon 9’s first stage, which debuted in May 2020 on the Demo-2 Crew Dragon mission that carried astronauts for the first time, still bore the faded NASA ‘worm’ logo from that occasion.
SpaceX is aiming to launch another batch of Starlink v2 Mini satellites from the Space Launch Complex 40 launchpad. This Booster, B1058, will try to launch and land for a record-breaking 19th time.\
\
Window Opens: December 22nd at 11PM EST (04:00 UTC on the 23rd)\
Window Closes: December 23rd at 3:31AM EST (08:31 UTC)\
Primary T0: December 22nd at 11:00PM EST (04:00 UTC on the 23rd)\
\
Mission: F9 launch of 23 Starlink v2 Mini satellites \
Target orbit: 285km perigee, 293km apogee, 43 degree inclination.\
Booster: B1058-19; 49d 3h 22min 40s turnaround\
Booster history: Demo-2, Anasis II, SL v1.0–12, CRS-21, Transporter-1, SL v1.0–20, SL v1.0–23, SL v1.0–26, SL 4–1, Transporter-3, SL 4–8, SL 4–17, SL 4–21, SL 4–2, SL 4–37, SL 6–5, SL 6–17, SL 6–26.\
Booster recovery: Droneship Just Read The Instructions (JRIT) located 629km downrange\
Fairing recovery: Bob\
Rocket trajectory: Southeast passing north of Bahamas\
Stubby nozzle: NO\
Stats: \
· SpaceX’s 95th launch of the year and the 6th launch of the month\
· 262nd Falcon orbital launch since Amos 6, F9’s 282nd orbital flight.\
· SpaceX’s 161st launch from SLC-40\
· 71st landing on JRTI out of 72 attempts\
· 181st successful landing since the last failed one\
· 55th launch dedicated to Starlink Gen 2 and 129th launch dedicated to Starlink overall.\
· First Falcon booster to fly for a 19th time\
\
Forum: https://forum.nasaspaceflight.com/ind…\
\
⚡ Become a member of NASASpaceflight’s channel for exclusive discord access, fast turnaround clips, and other exclusive benefits. Your support helps us continue our 24/7 coverage. ⚡\
\
🔍 If you are interested in using footage captured by this stream, please review our content use policy: https://www.nasaspaceflight.com/conte…
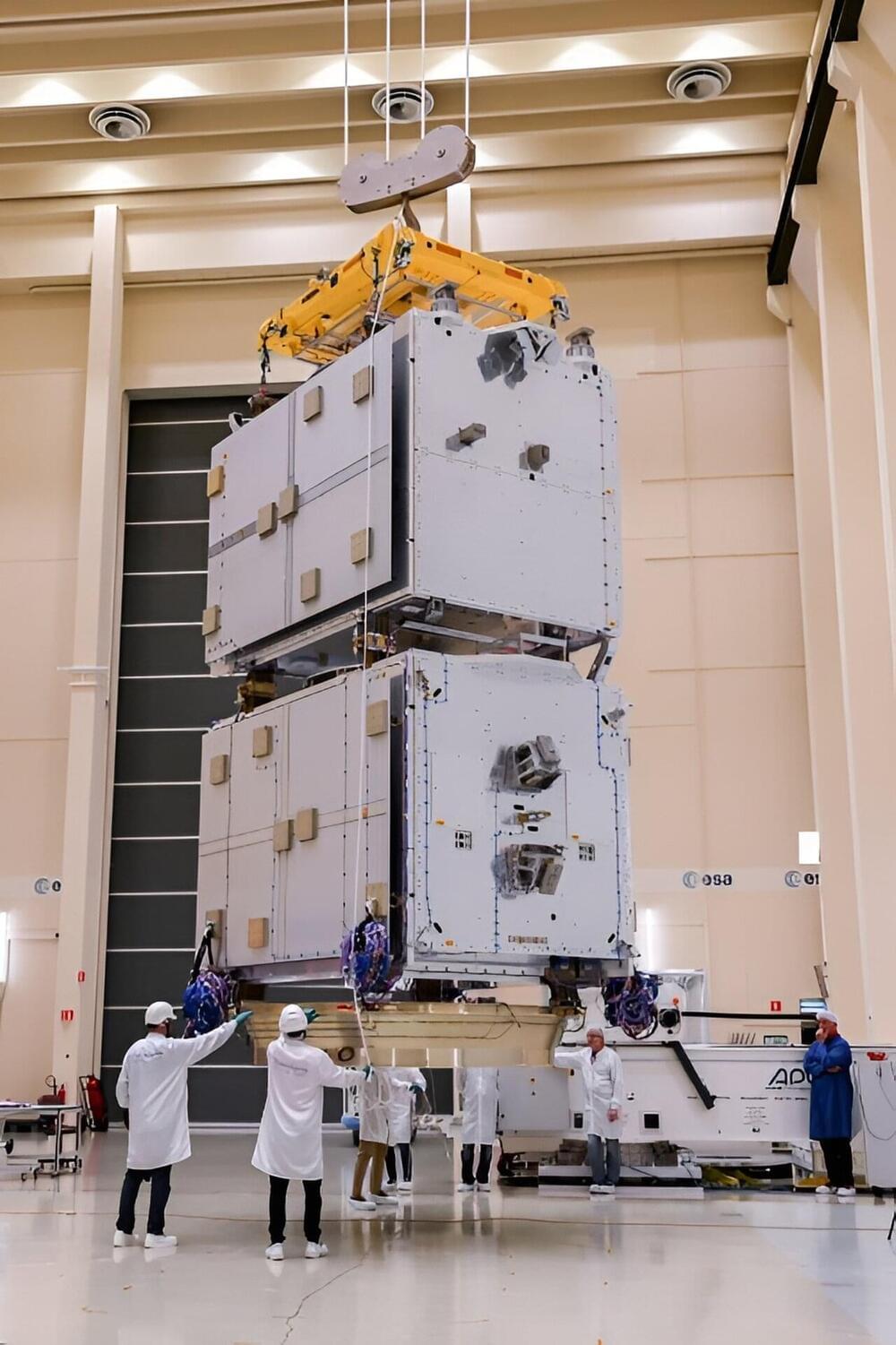

The new Galileo satellite model from Thales Alenia Space underwent mechanical and signal performance testing this summer at ESA’s ESTEC Test Center. Structural models resisted launch-like noise and vibrations while an electrical model proved its ability to send Galileo signals—a major milestone in the development of Galileo’s Second Generation.
Europe’s Galileo is the world’s most precise satellite navigation system, providing meter-level accuracy to more than 4 billion users worldwide. It currently comprises 28 satellites in orbit and 10 more are due to be launched, after which a new generation of satellites, the Galileo Second Generation or G2, will revolutionize the fleet with enhanced capabilities.
“G2 satellites will be much larger than those of the First Generation, use electric propulsion, host a more powerful navigation antenna, carry more and even better atomic clocks on board and have fully digital payloads,” explains ESA’s Galileo Second Generation Project Manager Miguel Manteiga Bautista. “The modular architecture will offer a high degree of flexibility to accommodate more equipment and inter-satellite links will be enabled,” he adds.
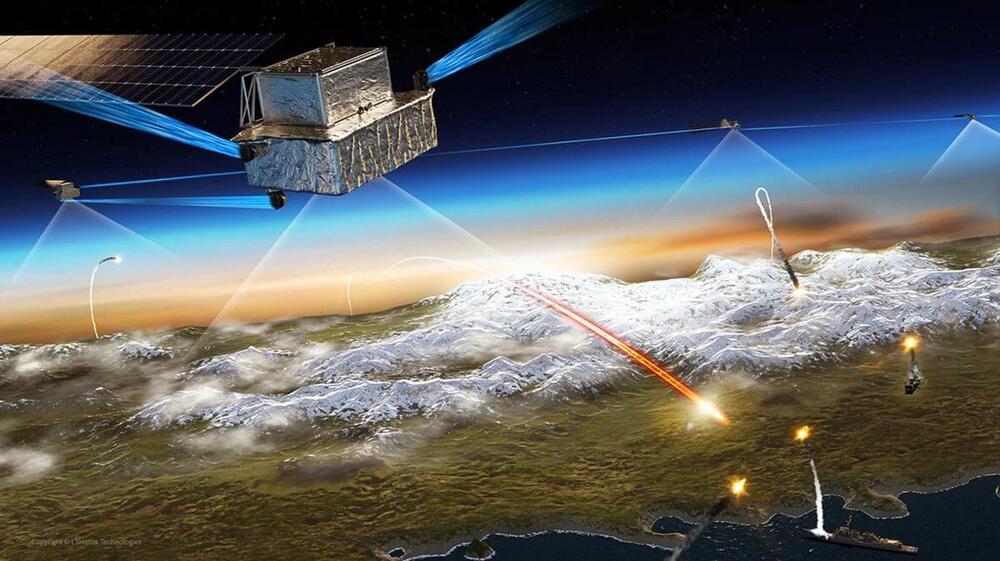

WASHINGTON — Defense contractor L3Harris announced Dec. 20 it has received approval from the Space Development Agency to move into production on 16 satellites designed to detect and monitor hypersonic missiles aimed at the U.S. or its allies.
L3Harris said its satellites cleared a critical design review and a production readiness review.
The Space Development Agency (SDA) is a U.S. Space Force organization building a layered network of satellites known as the Proliferated Warfighter Space Architecture. It includes a Transport Layer of interconnected communications satellites that will transmit data collected by the Tracking Layer of sensor satellites.
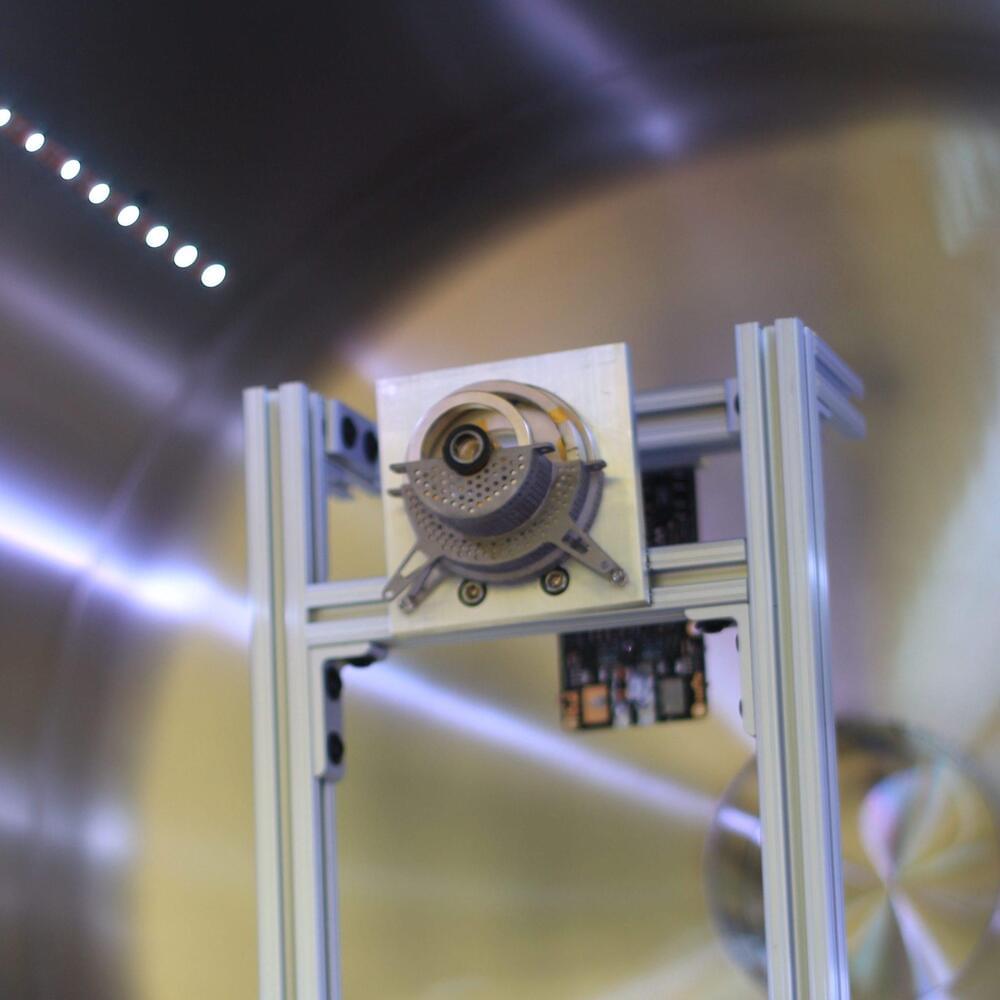
For its latest Hyperspace Challenge accelerator, the U.S. Space Force selected three startups specializing in satellite propulsion, picks reflecting the military’s growing interest in nimble satellites that can maneuver to outplay adversaries.
This marks a shift for the Pentagon, which traditionally has launched satellites into orbit and restricted their movements to conserve fuel. But with rivals fielding maneuverable spacecraft, U.S. officials are calling for a shift to “dynamic space operations,” enabled by autonomous refueling and other in-orbit services.
“Having the ability to refuel would really open new possibilities,” said John Plumb, assistant secretary of defense for space policy. He said the Pentagon is encouraged to see commercial companies developing technologies for in-orbit logistics that also have significant utility for the military.
In a new breakthrough, researchers have used a novel technique to confirm a previously undetected physics phenomenon that could be used to improve data storage in the next generation of computer devices.
Spintronic memories, utilized in advanced computers and satellites, leverage the magnetic states produced by the intrinsic angular momentum of electrons for data storage and retrieval. Depending on its physical motion, an electron’s spin produces a magnetic current. Known as the “spin Hall effect,” this has key applications for magnetic materials across many different fields, ranging from low-power electronics to fundamental quantum mechanics.
More recently, scientists have found that electrons are also capable of generating electricity through a second kind of movement: orbital angular momentum, similar to how Earth revolves around the sun. This is known as the “orbital Hall effect,” said Roland Kawakami, co-author of the study and a professor in physics at The Ohio State University.
Watch live coverage as SpaceX launches a Falcon 9 rocket with 23 second-generation Starlink internet satellites. Liftoff from pad 40 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station is scheduled for tonight at 11:01 p.m. EST (0401 UTC). The first-stage booster, making its third flight, will land on the drone ship ‘A Shortfall of Gravitas’ about eight and a half minutes into the flight.\
Our live coverage from Cape Canaveral, with commentary by Will Robinson-Smith, will begin about an hour before launch.\
Videos like this are made possible by the support of our members. Join this channel to get access to perks:\