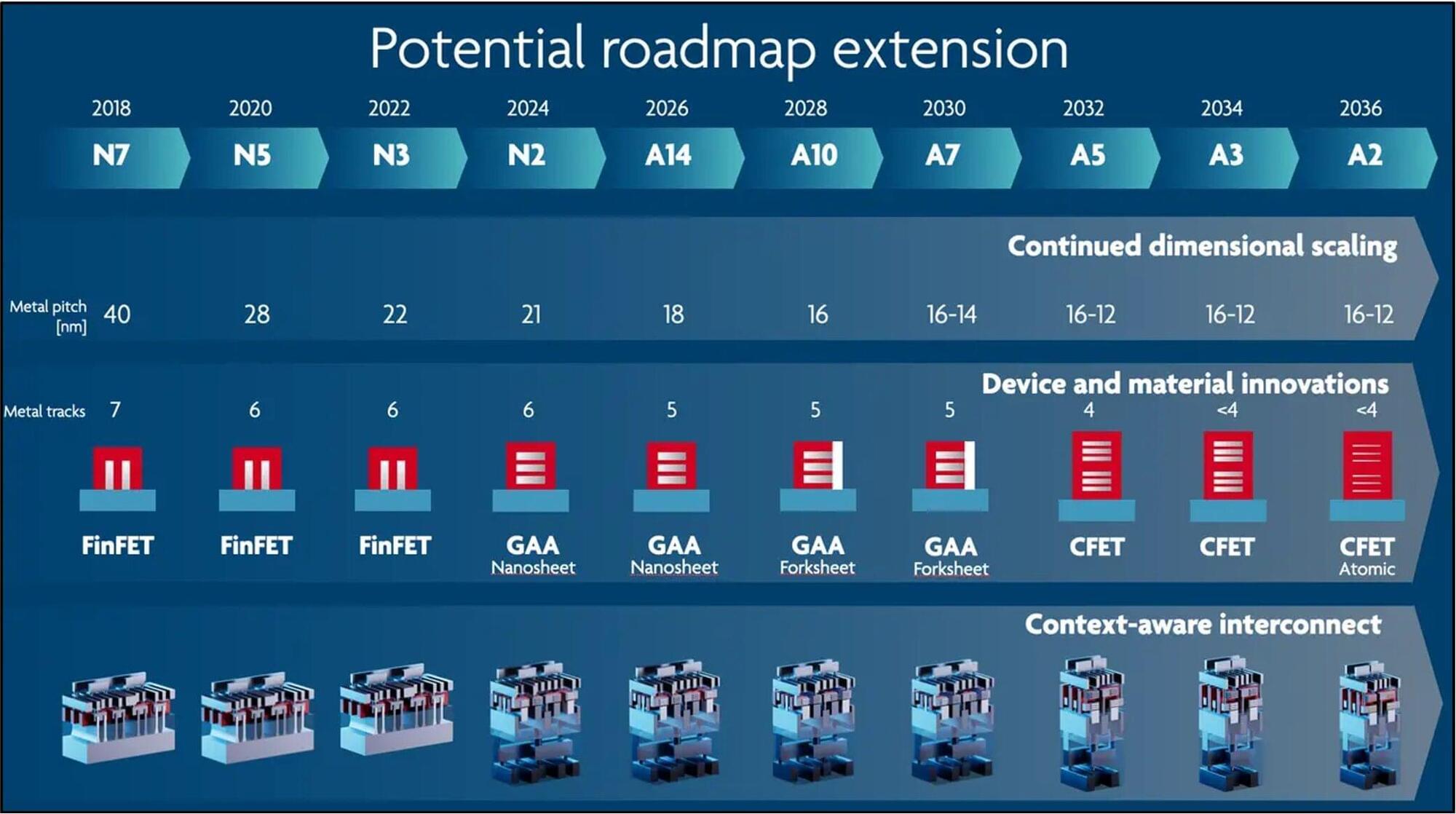
Over 60% of new CVEs are exploited within 48 hours—automation now defines who wins the cyber race.



Robots aren’t always the most delicate of machines when handling fragile objects. They don’t have the lightness of touch of humans. But that could be about to change thanks to a new development in smart materials.
Researchers have developed a method for weaving flexible fibers that can be controlled by magnetic fields. Not only can this be used for robot hands to pick up objects like soft fruits, potato chips and worms, but it can also be used in a range of other applications. These include gloves that provide a realistic touch in virtual reality and breathable fabrics.
Artificial intelligence and transhumanism.
Follow Closer To Truth on Instagram for daily videos, updates, and announcements: https://www.instagram.com/closertotruth/
Humanity’s future is now framed by artificial intelligence (AI) and increasing interventions in the human body to cure and to enhance, i.e., transhumanism. Considering the stakes and the dangers, a philosophical perspective is imperative.
Make a tax-deductible donation of any amount to help support Closer To Truth continue making content like this: https://shorturl.at/OnyRq.
Terrence William Deacon is an American neuroanthropologist. He taught at Harvard for eight years, relocated to Boston University in 1992, and is currently Professor of Anthropology and member of the Cognitive Science Faculty at the University of California, Berkeley.


In terms of objects, human touch has typically been understood to be limited to physical touch, where we detect objects through contact with our skin.
However, recent findings in animal have challenged this view. It is known that certain wading birds such as sandpipers and plovers, for example, use a form of ‘remote touch’ to detect prey hidden beneath the sand using their beaks.
Remote touch allows the detection of objects buried under granular materials, such as sand or soil, through subtle mechanical signals transmitted through the material when pressure is applied nearby.
The new study, published in IEEE International Conference on Development and Learning (ICDL), investigated whether humans share a similar capability to touch objects remotely.
The researchers asked 12 participants to move their fingers gently through sand to locate a hidden cube before physically touching it.
Remarkably, the results revealed a comparable ability to that seen in wading birds, despite humans lacking the specialised beak structures that enable this sense in birds.
By modelling the physical aspects of the remote touch phenomenon, the study found that human hands are remarkably sensitive, detecting the presence of buried objects by perceiving small displacements in the sand surrounding them with 70% precision within the expected detectable range.


Can an AI persona detect when a human is lying—and should we trust it if it can?
Artificial intelligence, or AI, has had many recent advances and continues to evolve in scope and capability. A new Michigan State University-led study is diving deeper into how well AI can understand humans by using it to detect human deception.
In the study, published in the Journal of Communication, researchers from MSU and the University of Oklahoma conducted 12 experiments with over 19,000 AI participants to examine how well AI personas were able to detect deception and truth from human subjects.