Opinion: The average big construction project is overdue and over budget. A dose of automation could help.



Next month, however, a team of MIT researchers will be presenting a so-called “Proxyless neural architecture search” algorithm that can speed up the AI-optimized AI design process by 240 times or more. That would put faster and more accurate AI within practical reach for a broad class of image recognition algorithms and other related applications.
“There are all kinds of tradeoffs between model size, inference latency, accuracy, and model capacity,” says Song Han, assistant professor of electrical engineering and computer science at MIT. Han adds that:
“[These] all add up to a giant design space. Previously people had designed neural networks based on heuristics. Neural architecture search tried to free this labor intensive, human heuristic-based exploration [by turning it] into a learning-based, AI-based design space exploration. Just like AI can [learn to] play a Go game, AI can [learn how to] design a neural network.”
A fringe group of scientists and tech moguls think they’re closing in on the fountain of youth. Here’s everything you need to know:
What is biohacking? Silicon Valley is built on the idea that technology can optimize, or “hack,” any aspect of our lives — so why not the human life span? Until recently, anyone hawking pills or treatments that promised to restore youthfulness was considered a quack, yet a growing number of “transhumanists” are convinced that, in time, human beings can be transformed through bioengineering, and that aging will be curable just like any other malady.
In light of rapid gains in gene editing, nanotechnology, and robotics, some futurists expect this generation’s biohackers to double their life spans. Aubrey de Grey, a regenerative medicine researcher backed by tech mogul Peter Thiel, insists that someone alive today will live to be 1,000. “It’s extraordinary to me that it’s such an incendiary claim,” de Grey says. Korean physician and financier Joon Yun has offered two $500,000 prizes to anyone who can restore a test animal’s youthful heart rate and extend its lifespan by 50 percent. For humans, the mortality rate at age 20 is 0.001 percent, Yun figures, “so if you could maintain the homeostatic capacity of that age throughout your life, your average life span would be 1,000.”
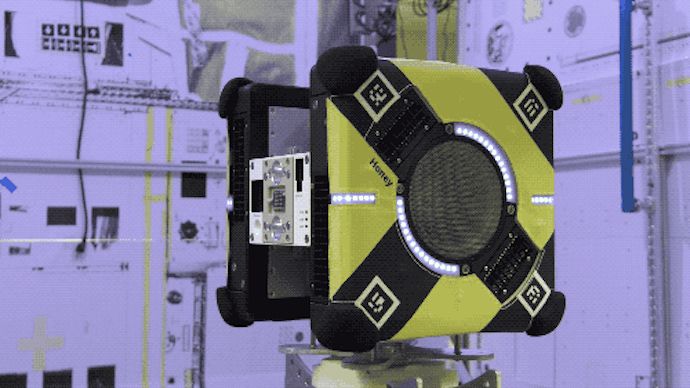
NASA’s newest International Space Station crew members are creating quite the buzz.
The agency is sending three Astrobee robots to the orbiting outpost.
The cube-shaped devices will stay “as busy as a bee” flying around the station, assisting with routine tasks like maintenance and inventory tracking.
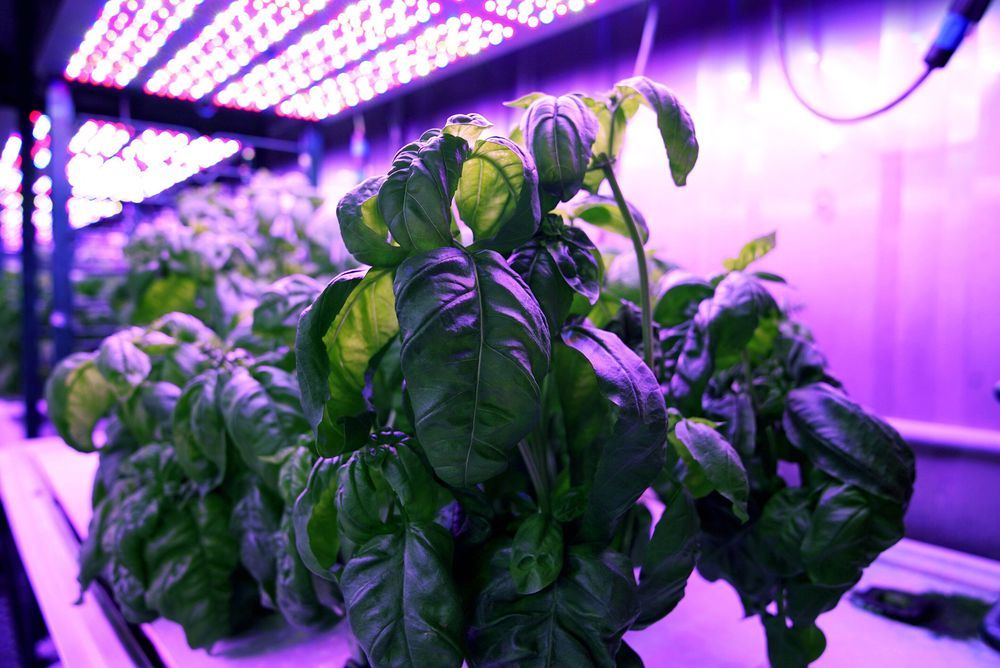

What goes into making plants taste good? For scientists in MIT’s Media Lab, it takes a combination of botany, machine-learning algorithms, and some good old-fashioned chemistry.
Using all of the above, researchers in the Media Lab’s Open Agriculture Initiative report that they have created basil plants that are likely more delicious than any you have ever tasted. No genetic modification is involved: The researchers used computer algorithms to determine the optimal growing conditions to maximize the concentration of flavorful molecules known as volatile compounds.
But that is just the beginning for the new field of “cyber agriculture,” says Caleb Harper, a principal research scientist in MIT’s Media Lab and director of the OpenAg group. His group is now working on enhancing the human disease-fighting properties of herbs, and they also hope to help growers adapt to changing climates by studying how crops grow under different conditions.
When artificial intelligence systems start getting creative, they can create great things – and scary ones. Take, for instance, an AI program that let web users compose music along with a virtual Johann Sebastian Bach by entering notes into a program that generates Bach-like harmonies to match them.
Run by Google, the app drew great praise for being groundbreaking and fun to play with. It also attracted criticism, and raised concerns about AI’s dangers.
My study of how emerging technologies affect people’s lives has taught me that the problems go beyond the admittedly large concern about whether algorithms can really create music or art in general. Some complaints seemed small, but really weren’t, like observations that Google’s AI was breaking basic rules of music composition.
Two new autonomous aircraft concepts that promise to redefine the Air Force’s unmanned fleet are moving forward.
The latest, Skyborg, is an autonomous drone prototyping program underway at the Air Force Research Laboratory. Researchers hope to get the aircraft—expected to be cheaper than other platforms and easily replaceable—combat-ready by the end of 2023.
Air Force Acquisition Executive Will Roper revealed the program, which launched in October, at a conference in Washington last month. Skyborg must be able to autonomously take off and land, fly in bad weather, and avoid other aircraft, terrain, and obstacles, the Air Force said.

(Reuters) — Alphabet Inc’s Google said on Thursday it was dissolving a council it had formed a week earlier to consider ethical issues around artificial intelligence and other emerging technologies.
The council had run into controversy over two of its members, according to online news portal Vox, which first reported the dissolution of the council.
The council, launched on March 26, was meant to provide recommendations for Google and other companies and researchers working in areas such as facial recognition software, a form of automation that has prompted concerns about racial bias and other limitations.

It is a crazy thought, right?! To think that mushrooms could be alien life. But before you dismiss the idea, take a look at some of principles of the theory. The main concept was formulated by the ingenious psychonaut philosopher Terrence McKenna, and goes along following lines.
Like no other form of life on our planet, the spores of mushrooms are almost perfectly suited to space travel. They can survive high vacuum and insanely low temperatures; the casing of a spore is one of the most electron dense materials in nature, to the point where McKenna says it is almost akin to a metal; global currents are even able to form on the quasi-metallic surface of an airborne spore, which then acts as a repellent to the extreme radiation of space. It is a mind boggling thought that something could evolve to be so perfectly suited to explore the universe.
If a civilization is advanced enough, then chances are their concepts and understanding of reality would far outweigh ours. If they were advanced enough to be able to change their very genetic structure, then there would be a lot of merit in changing/evolving into a mushroom. Mushrooms are highly resilient, non-invasive, practically immortal, full of neurotransmitters, and able to weather space. It would be the perfect way to explore and colonize the galaxy. Plus once mushrooms establish themselves, they create an underground neural network of mycelium that highly resembles the neural networks of the human brain or the internet.