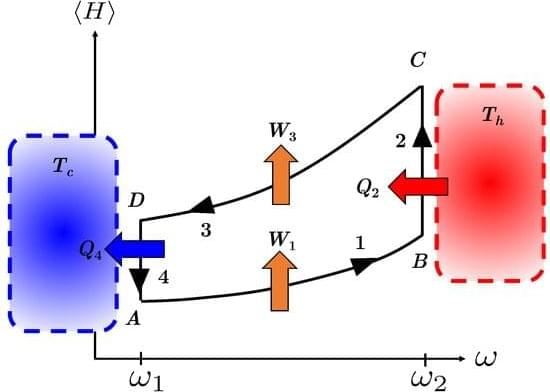
By harnessing quantum phenomena, quantum devices have the potential to outperform their classical counterparts. Here, we examine using wave function symmetry as a resource to enhance the performance of a quantum Otto engine. Previous work has shown that a bosonic working medium can yield better performance than a fermionic medium. We expand upon this work by incorporating a singular interaction that allows the effective symmetry to be tuned between the bosonic and fermionic limits. In this framework, the particles can be treated as anyons subject to Haldane’s generalized exclusion statistics. Solving the dynamics analytically using the framework of “statistical anyons”, we explore the interplay between interparticle interactions and wave function symmetry on engine performance.