Researchers have developed a quantum gas microscope that can pinpoint the horizontal and vertical positions of atoms arranged in a lattice.


Physicists successfully measure gravity in the quantum world, detecting weak gravitational pull on a tiny particle with a new technique that uses levitating magnets, putting scientists closer to solving mysteries of the universe.
Scientists are a step closer to unraveling the mysterious forces of the universe after working out how to measure gravity on a microscopic level.
Experts have never fully understood how the force discovered by Isaac Newton works in the tiny quantum world.
Scientists at the DOE’s Brookhaven National Laboratory have discovered that coating tantalum with magnesium significantly enhances its properties as a superconducting material for quantum computing. This coating prevents oxidation, increases purity, and improves the superconducting transition temperature of tantalum, offering promising advancements for the development of qubits and the future of quantum computing.
Scientists at the U.S. Department of Energy’s (DOE) Brookhaven National Laboratory have discovered that adding a layer of magnesium improves the properties of tantalum, a superconducting material that shows great promise for building qubits, the basis of quantum computers.
As described in a paper just published in the journal Advanced Materials, a thin layer of magnesium keeps tantalum from oxidizing, improves its purity, and raises the temperature at which it operates as a superconductor. All three may increase tantalum’s ability to hold onto quantum information in qubits.

A new study by researchers at Lanzhou University and Hubei University proposes a quantum battery (QB) charging scheme based on a rectangular hollow metal waveguide. This approach allows them to overcome environment-induced decoherence and charging distance limitations. The findings are published in Physical Review Letters.
The demand and supply for batteries continue to grow with a focus on enhancing energy storage, longevity, and charging capabilities. On this front, scientists are now developing quantum batteries that leverage principles of quantum mechanics to store and supply energy.
The aim is to use fundamental principles of quantum mechanics such as entanglement and coherence to overcome the constraints of classical physics, thereby achieving stronger charging power, higher charging capacity, and larger work extraction compared to classical counterparts.
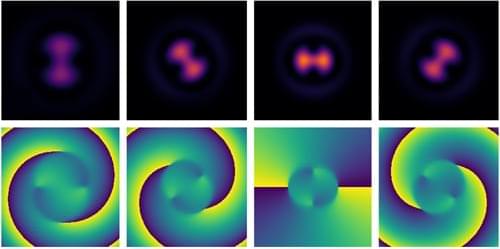
In Nature Physics, the LSU Quantum Photonics Group offers fresh insights into the fundamental traits of surface plasmons, challenging the existing understanding. Based on experimental and theoretical investigations conducted in Associate Professor Omar Magaña-Loaiza’s laboratory, these novel findings mark a significant advancement in quantum plasmonics, possibly the most noteworthy in the past decade.
While prior research in the field has predominantly focused on the collective behaviors of plasmonic systems, the LSU group adopted a distinct approach. By viewing plasmonic waves as a puzzle, they were able to isolate multiparticle subsystems, or break down the puzzle into pieces. This allowed the team to see how different pieces work together and revealed a different picture, or in this case, new behaviors for surface plasmons.
Plasmons are waves that move along the surface of metals when light is coupled to charge oscillations. Much like tossing pebbles into water generates ripples, plasmons are “ripples” traveling along metal surfaces. These minute waves operate on a nanometer scale, rendering them crucial in fields such as nanotechnology and optics.
A holographic universe where spacetime is built from quantum bits. In this interview, we hear all about how the concept of entanglement entropy, a measure of quantum information between regions is related to the structure of spacetime. What can we learn from entanglement and entropy about gravity, and what has gravity to say about quantum physics? We find out in this video.
Tadashi Takayanagi is a prominent Japanese researcher most known for his research on holographic entanglement entropy for which he won the 2015 New Horizon award. Tadashi did his Ph.D. at Tokyo University and has obtained postdoc positions at Harvard and Kavli Institute of Theoretical Physics at the University of California. He is currently a professor at Kyoto University and holds a visiting position at Kavli Institute. A well-known hobby of Tadashi is his mineral collection from which he draws inspiration for his research work.
A recent study conducted at Tel Aviv University has devised a large mechanical system that operates under dynamical rules akin to those found in quantum systems. The dynamics of quantum systems, composed of microscopic particles like atoms or electrons, are notoriously difficult, if not impossible, to observe directly.
However, this new system allows researchers to visualize phenomena occurring in specialized “topological” materials through the movement of a system of coupled pendula.
The research is a collaboration between Dr. Izhar Neder of the Soreq Nuclear Research Center, Chaviva Sirote-Katz of the Department of Biomedical Engineering, Dr. Meital Geva and Prof. Yair Shokef of the School of Mechanical Engineering, and Prof. Yoav Lahini and Prof. Roni Ilan of the School of Physics and Astronomy at Tel Aviv University and was recently published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
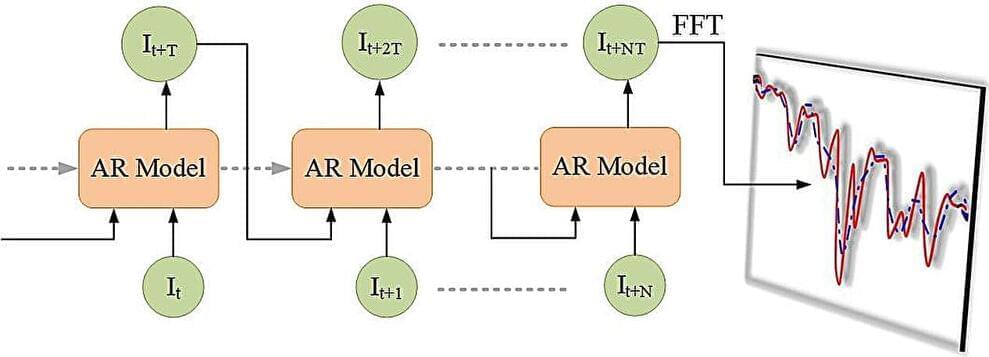
A recent study conducted at Tel Aviv University has devised a large mechanical system that operates under dynamical rules akin to those found in quantum systems. The dynamics of quantum systems, composed of microscopic particles like atoms or electrons, are notoriously difficult, if not impossible, to observe directly.
However, this new system allows researchers to visualize phenomena occurring in specialized “topological” materials through the movement of a system of coupled pendula.
The research is a collaboration between Dr. Izhar Neder of the Soreq Nuclear Research Center, Chaviva Sirote-Katz of the Department of Biomedical Engineering, Dr. Meital Geva and Prof. Yair Shokef of the School of Mechanical Engineering, and Prof. Yoav Lahini and Prof. Roni Ilan of the School of Physics and Astronomy at Tel Aviv University and was recently published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
A recent study conducted at Tel Aviv University has devised a large mechanical system that operates under dynamical rules akin to those found in quantum systems. The dynamics of quantum systems, composed of microscopic particles like atoms or electrons, are notoriously difficult, if not impossible, to observe directly.
However, this new system allows researchers to visualize phenomena occurring in specialized “topological” materials through the movement of a system of coupled pendula.
The research is a collaboration between Dr. Izhar Neder of the Soreq Nuclear Research Center, Chaviva Sirote-Katz of the Department of Biomedical Engineering, Dr. Meital Geva and Prof. Yair Shokef of the School of Mechanical Engineering, and Prof. Yoav Lahini and Prof. Roni Ilan of the School of Physics and Astronomy at Tel Aviv University and was recently published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.