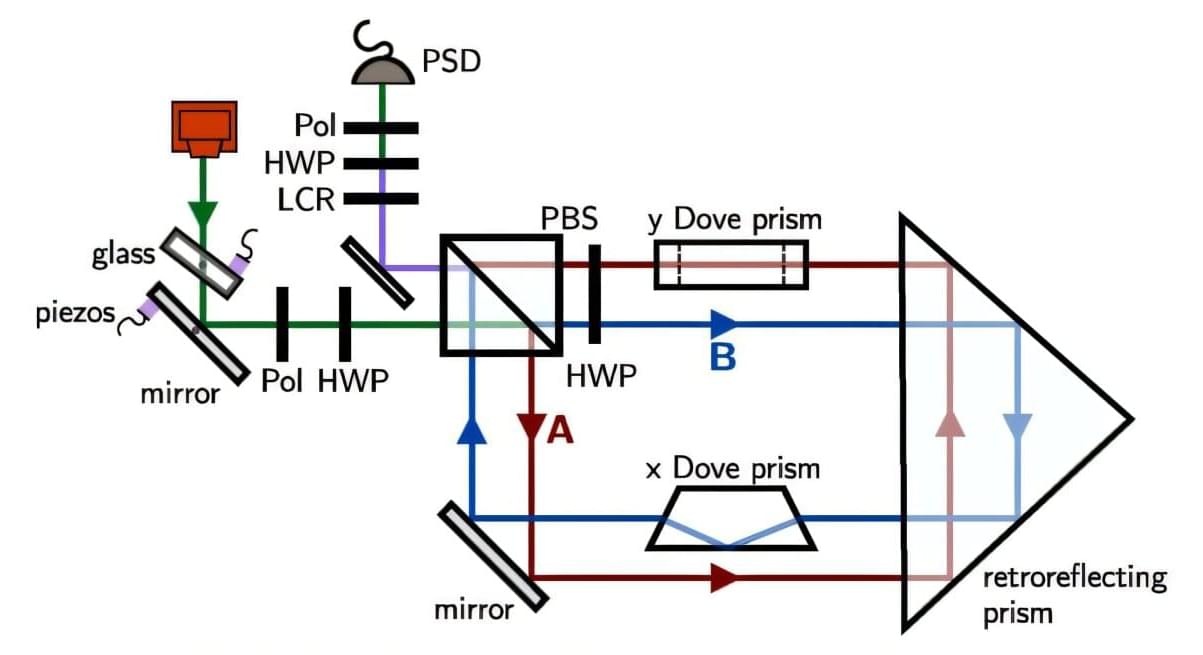
A quantum trick based on interferometric measurements allows a team of researchers at LMU to detect even the smallest movements of a laser beam with extreme sensitivity.
Precisely measuring minute shifts or slight tilts of a laser beam is crucial in many scientific and technological applications, such as atomic force microscopy. So-called weak value amplification (WVA), a method that grew out of thinking about the foundations of quantum mechanics, has already shown that under certain conditions the output signal of an interferometer changes markedly when the beams inside it are altered only minimally. An interferometer is a measuring device that can detect such tiny differences by comparing overlapping light waves.
LMU physicist Carlotta Versmold and her colleagues, all members of the MCQST Cluster of Excellence, working together with researchers at Tel Aviv University, have now extended this type of measurement. The team recently developed a trick that also amplifies changes in the incoming beam. This makes it possible to carry out far more precise measurements that were previously difficult to achieve. A laser beam reflected from a distant window, for example, could pick up vibrations in the glass caused by conversations inside the building, allowing those conversations to be overheard.