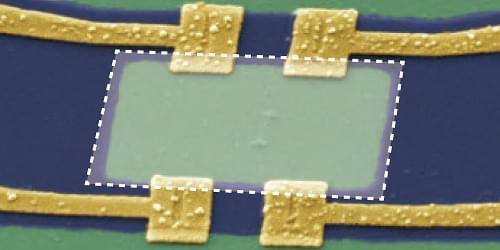
A circuit containing four superconducting devices called Josephson junctions can be finely tuned for various technological applications.

A pair of physicists at the University of Crete has found that some types of biological magnetoreceptors used by various creatures to navigate, operate at or near the quantum limit. In their paper published in the journal PRX Life, I. K. Kominis and E. Gkoudinakis describe how they worked the problem of magnetic sensing in tiny animals in reverse by putting bounds on unknown quantum boundaries, and what it showed about the navigation abilities of certain animals.
Prior research has shown that many creatures use the Earth’s magnetic field as a navigation aid. Some sharks, fish and birds, for example, use it to help them traverse long distances. Different animals also have different types of magnetic sensors, including radical-pair, induction and magnetite mechanisms.
Radical-pair works by sensing correlations between unpaired electrons attached to certain molecules. Induction works by turning energy in the magnetic field into electricity and then sensing the electrical charge. And magnetite-based magnetoreception involves sensing the movement or orientation of tiny iron crystals in the body, similar to a human-made compass.

A team of physicists affiliated with multiple institutions in China has measured a pulse of light in 37 dimensions. In their paper published in Science Advances, the group explains that their experiment was meant to demonstrate that quantum mechanics is more nonclassical than thought.
Quantum mechanics involves how things work at the subatomic level, while general relativity describes classical theory, which has aspects of what physicists call local realism, where things happen around us in the ways that we expect them to happen and in the order we expect.
Physicists have tried and failed to unite the two theories for decades. The problem has only grown more difficult in recent years as research efforts have shown that the differences between them are greater than thought. In this new effort, the researchers in China sought to see how far nonclassical quantum mechanics differs from classical theory by carrying out an experiment to demonstrate the Greenberger–Horne–Zeilinger (GHZ) paradox.

Emmy Noether was hailed as a mathematical genius in her own time. And her theorem on symmetry is still driving new discoveries in particle physics and quantum computing today.
By John Gribbin and Mary Gribbin.
The term “nanoscale” refers to dimensions that are measured in nanometers (nm), with one nanometer equaling one-billionth of a meter. This scale encompasses sizes from approximately 1 to 100 nanometers, where unique physical, chemical, and biological properties emerge that are not present in bulk materials. At the nanoscale, materials exhibit phenomena such as quantum effects and increased surface area to volume ratios, which can significantly alter their optical, electrical, and magnetic behaviors. These characteristics make nanoscale materials highly valuable for a wide range of applications, including electronics, medicine, and materials science.
A transcript of our conversation:
Dr. Flavio Lanfranconi: Good to see you. Great. I was just trying to keep up with everything you’ve posted recently. It’s difficult, but…
Matt Segall: Sorry about that.

“While some may suggest that a standalone quantum computer is still years away, the commercial opportunities from this breakthrough are here and now,” said Dr. Thomas Ehmer from the Healthcare business sector of Merck KGaA, Darmstadt, Germany. “The generation of meaningful synthetic data, specifically when you do not have many training data, is nontrivial and we see it as a new era for AI unlocked by quantum technologies. The Helios system, launching later this year will hopefully enable AI to be used in unprecedented ways and unlocking transformative potential across industries.”
Gen QAI leverages the unique capabilities of quantum computing to explore data complexities far beyond what classical computing systems and GPUs can handle. Quantinuum is collaborating with industry partners on Generative AI projects that harness the power of quantum computing in sectors such as automotive, pharmaceuticals and materials science. In the coming months, Quantinuum will share results from ongoing collaborations, showcasing the groundbreaking potential of quantum-driven advancements in Generative AI.
Physicists have performed a simulation they say sheds new light on an elusive phenomenon that could determine the ultimate fate of the universe.
Pioneering research in quantum field theory around 50 years ago proposed that the universe may be trapped in a false vacuum —meaning it appears stable but in fact could be on the verge of transitioning to an even more stable, true vacuum state.
While this process could trigger a catastrophic change in the universe’s structure, experts agree that predicting the timeline is challenging, but it is likely to occur over an astronomically long period, potentially spanning millions of years.
