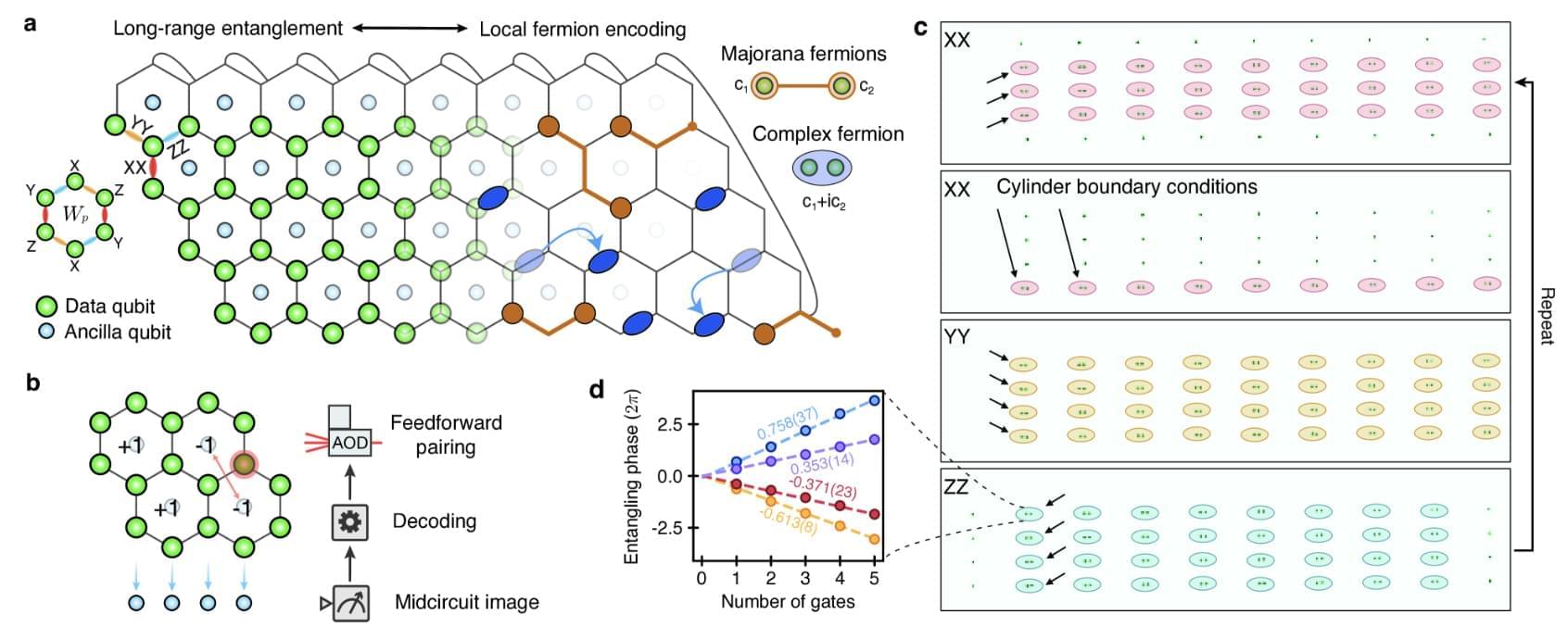
Their work proves that even in isolated quantum systems, disorder naturally grows, aligning quantum mechanics with thermodynamics.
The Paradox of Entropy in Quantum Physics
The second law of thermodynamics is one of the fundamental principles of nature. It states that in a closed system, entropy — the measure of disorder — must always increase over time. This explains why structured systems naturally break down: ice melts into water, and a shattered vase will never reassemble itself. However, quantum physics appears to challenge this rule. Mathematically, entropy in quantum systems seems to remain unchanged, raising a puzzling contradiction.