This i share with pleasure H/T Ulla Mattfolk.
Physical insights drawn from the real world are inexplicably useful for solving abstruse problems in mathematics.

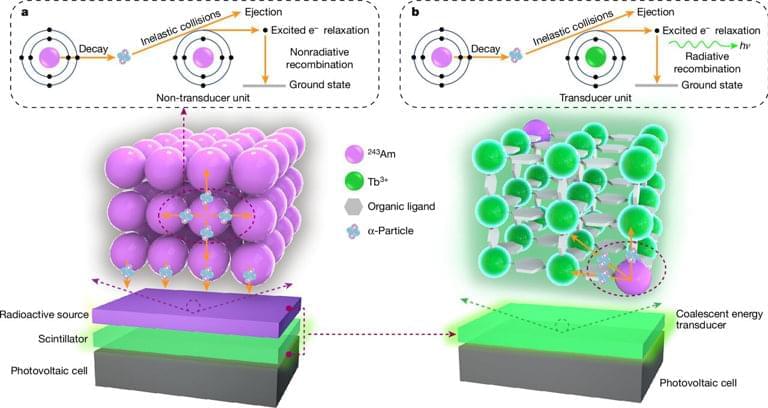
Sara Imari Walker is a professor of physics at Arizona State University and the author of a new book Life as No One Knows It: The Physics of Life’s Emergence. As I wrote in my review of the book, I’m a big fan of Walker’s work (full disclosure, we have collaborated before on a paper and a proposal).
The subject of her work and the new book is what might be called the “Physics of Life.” This is different from biophysics, which tries to account for specific physics aspects of biological processes. Instead, the Physics of Life has a more ambitious goal: to understand what separates living from non-living systems.
Along with her collaborators, Walker developed Assembly Theory, which focuses on “selection” and is a fundamental physics account for the difference between life and non-life. Assembly Theory quantifies complexity by measuring how many unique steps are needed to build a molecular structure. By identifying complex patterns that signify biological processes, this framework could help scientists detect life forms on other worlds — even those that may not look like anything we’re familiar with on Earth.
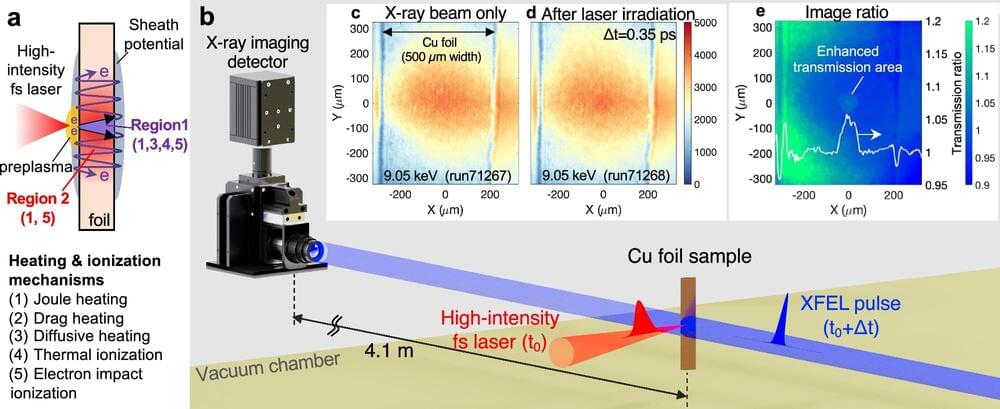
In a few picoseconds (trillionths of a second), a small, thin piece of copper momentarily becomes dense plasma, specifically a state called warm dense matter, warm being a relative term—the metal is nearly 200,000 degrees Fahrenheit. With the short duration of a high-powered laser pulse, copper shifts from a solid state to a plasma state in an instant before it explodes. Understanding the progression of heat in the copper is an exciting breakthrough in physics relevant to the interior of giant planets and laser fusion fuel cores.
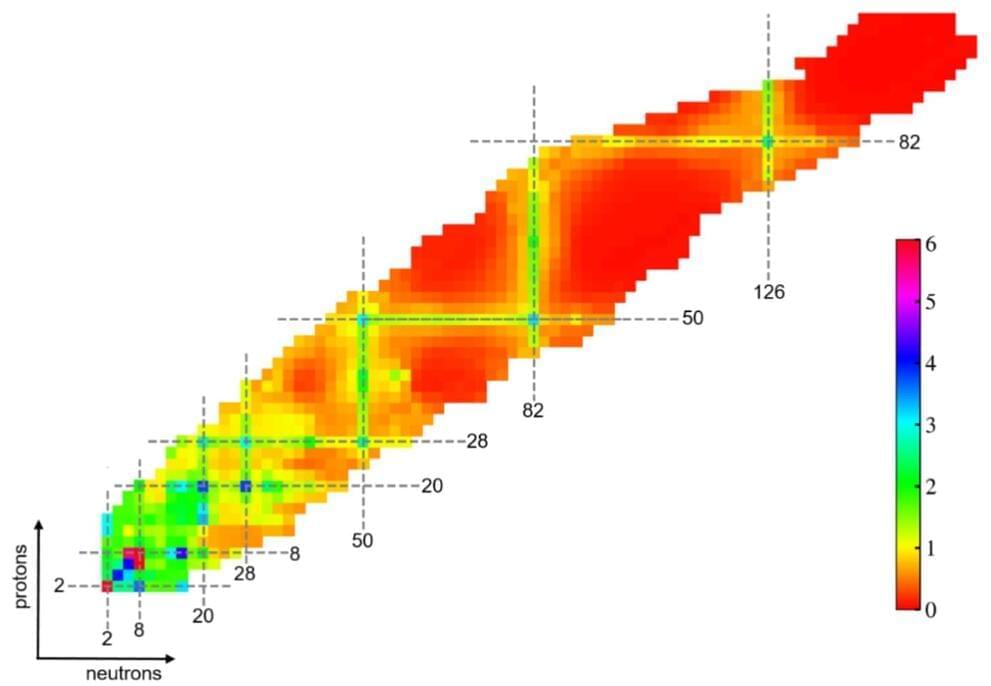
A research team has used a machine learning approach to investigate the evolution of shell structure for nuclei far from the stability valley. The study, published in Physics Letters B and conducted by researchers from the Institute of Modern Physics (IMP) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, Huzhou University, and the University of Paris-Saclay, reveals the double-magic nature of tin-100 and the disappearance of the magic number 20 in oxygen-28.
When you cool light photons to absolute zero, things get really weird.
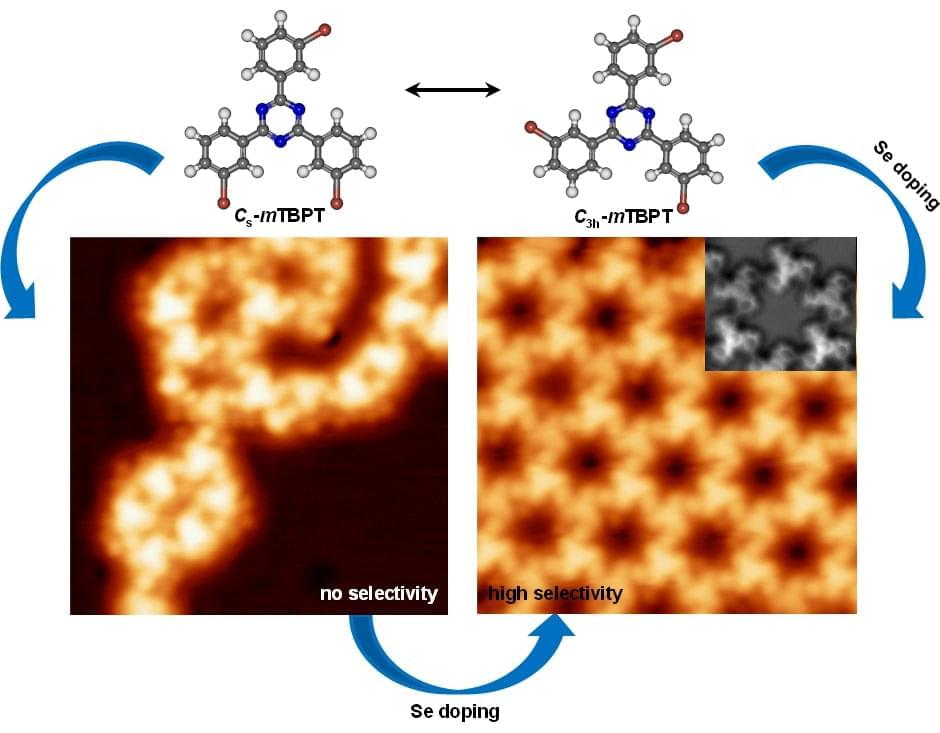
Physicists from the National University of Singapore (NUS) have achieved controlled conformational arrangements in nanostructures using a flexible precursor and selenium doping, enhancing material properties and structural homogeneity. Their method advances on-surface synthesis for the design and development of engineered nanomaterials.
On-surface synthesis has been extensively investigated over the past decades for its ability to create diverse nanostructures. Various complex nanostructures have been achieved through the smart design of precursors, choice of substrates and precise control of experimental parameters such as molecular concentration, electrical stimulation and thermal treatment.
Among these methods, the Ullmann coupling is notable for efficiently linking precursors through dehalogenation and covalent bonding. While most research has focused on conformationally rigid precursors, exploring conformationally flexible precursors offers significant potential for developing complex functional nanomaterials with engineered structures and properties.
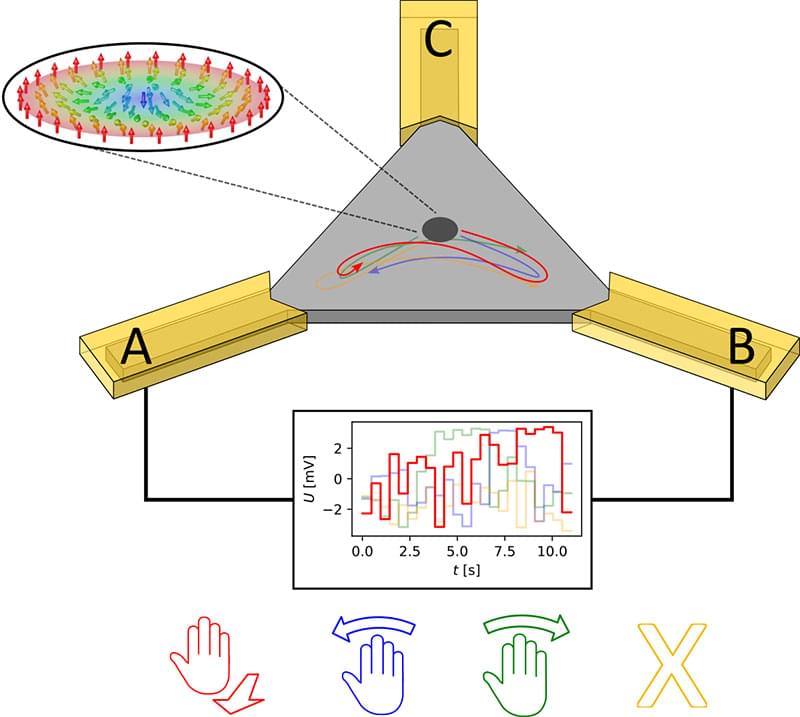
Researchers at Johannes Gutenberg University Mainz (JGU) have managed to enhance the framework of Brownian reservoir computing by recording and transferring hand gestures to the system which then used skyrmions to detect these individual gestures.
“We were impressed to see that our hardware approach and concept worked so well – and even better than energy-intensive software solutions that employ neural networks,” said Grischa Beneke, a member of Professor Mathias Kläui’s research group at the JGU Institute of Physics.
In collaboration with other experimental and theoretical physicists, Beneke was able to demonstrate that simple hand gestures can be recognized by means of Brownian reservoir computing with a relatively high degree of precision.
Have you ever wondered if our universe is more mysterious than we could ever imagine? Some scientists believe that we might be living inside a black hole! This mind-bending idea challenges everything we know about space, time, and the very fabric of reality. Join us as we dive deep into the groundbreaking theories and explore the evidence suggesting that our universe could be the interior of a massive black hole. Learn about the fascinating connection between black holes and the Big Bang, the nature of singularities, and the surprising ways in which physics supports this extraordinary concept. Could the secret to understanding our universe lie within these cosmic giants? Watch now to find out!