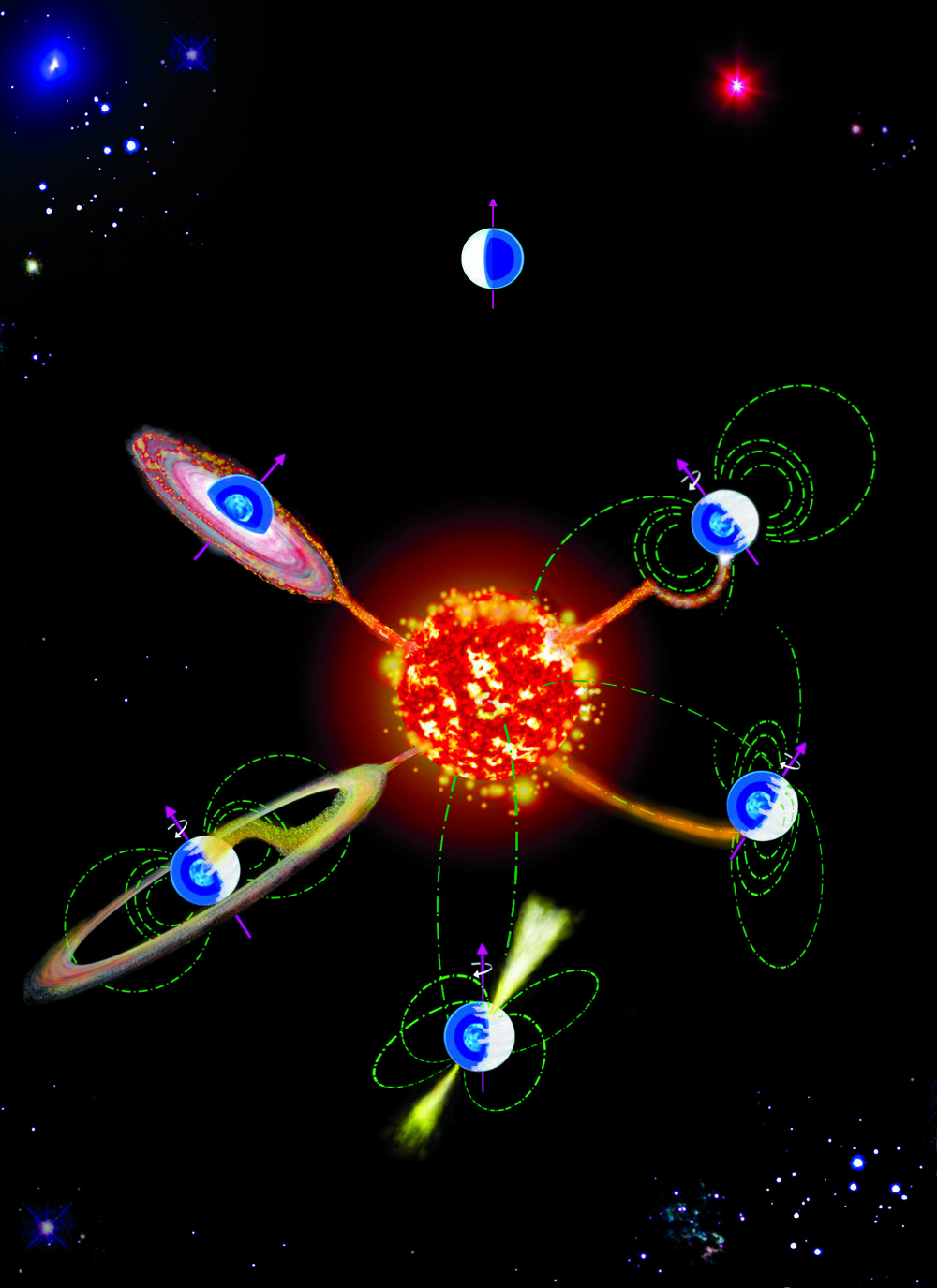
A team of international scientists, led by the Galician Institute of High Energy Physics (IGFAE) and the ARC Centre of Excellence for Gravitational Wave Discovery (OzGrav), has proposed a simple and novel method to bring the accuracy of the Hubble constant measurements down to 2% using a single observation of a pair of merging neutron stars.
The universe is in continuous expansion. Because of this, distant objects such as galaxies are moving away from us. In fact, the further away they are, the faster they move. Scientists describe this expansion through a famous number known as the Hubble constant, which tells us how fast objects in the universe recede from us depending on their distance to us. By measuring the Hubble constant in a precise way, we can also determine some of the most fundamental properties of the universe, including its age.
For decades, scientists have measured Hubble’s constant with increasing accuracy, collecting electromagnetic signals emitted throughout the universe but arriving at a challenging result: the two current best measurements give inconsistent results. Since 2015, scientists have tried to tackle this challenge with the science of gravitational waves, ripples in the fabric of space-time that travel at the speed of light. Gravitational waves are generated in the most violent cosmic events and provide a new channel of information about the universe. They’re emitted during the collision of two neutron stars —the dense cores of collapsed stars —and can help scientists dig deeper into the Hubble constant mystery.