New mathematical models of our Milky Way Galaxy are helping a team of Argentine, Chilean and Spanish astrophysicists trace the origins of our galaxy back through time.


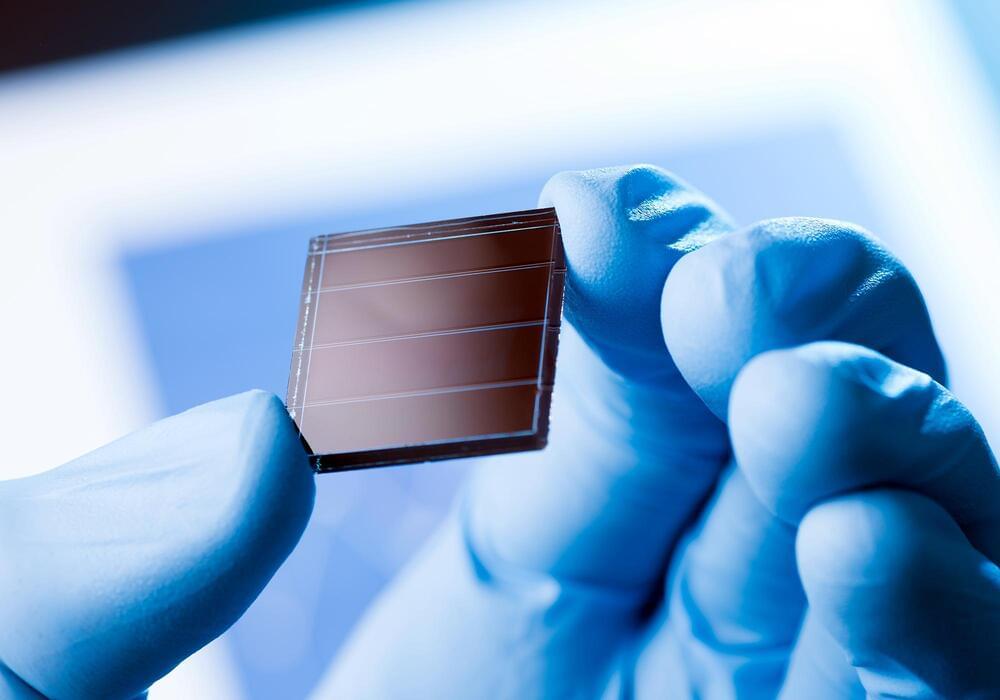
Physicists at Paderborn University have enhanced solar cell efficiency significantly using tetracene, an organic material, based on complex computer simulations. They discovered that defects at the tetracene-silicon interface boost energy transfer, promising a new solar cell design with drastically improved performance.
Physicists at Paderborn University have used complex computer simulations to create a novel solar cell design that boasts substantially higher efficiency than existing options. The enhancement in performance is attributed to a slender coating of an organic compound named tetracene. The results have recently been published in the renowned journal Physical Review Letters.
“The annual energy of solar radiation on Earth amounts to over one trillion kilowatt-hours and thus exceeds the global energy demand by more than 5,000 times. Photovoltaics, i.e. the generation of electricity from sunlight, therefore offers a large and still largely untapped potential for the supply of clean and renewable energy. Silicon solar cells used for this purpose currently dominate the market, but have efficiency limits,” explains Prof Dr Wolf Gero Schmidt, physicist and Dean of the Faculty of Natural Sciences at Paderborn University. One reason for this is that some of the energy from short-wave radiation is not converted into electricity, but into unwanted heat.

Supernovae–stellar explosions as bright as an entire galaxy–have fascinated us since time immemorial. Yet, there are more hydrogen-poor supernovae than astrophysicists can explain. Now, a new Assistant Professor at the Institute of Science and Technology Austria (ISTA) has played a pivotal role in identifying the missing precursor star population. The results, now published in Science, go back to a conversation the involved professors had many years ago as junior scientists.
The Enigma of Hydrogen-Poor Supernovae
Some stars do not simply die down, but explode in a stellar blast that could outshine entire galaxies. These cosmic phenomena, called supernovae, spread light, elements, energy, and radiation in space and send galactic shock waves that could compress gas clouds and generate new stars. In other words, supernovae shape our universe. Among these, hydrogen-poor supernovae from exploding massive stars have long puzzled astrophysicists. The reason: scientists have not been able to put their finger on their precursor stars. It is almost as if these supernovae appeared out of nowhere.

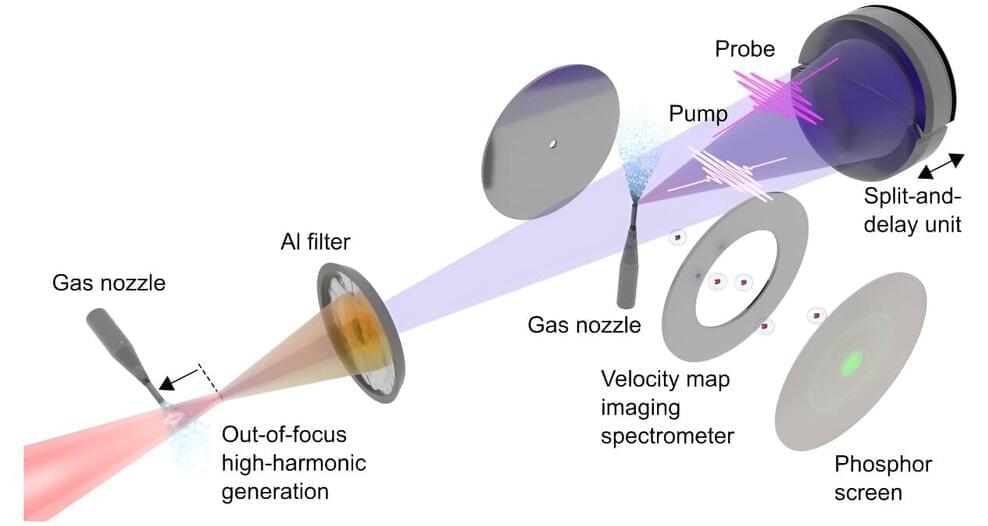
A team of researchers from the Max Born Institute in Berlin has, for the first time, demonstrated attosecond-pump attosecond-probe spectroscopy (APAPS) at a repetition rate of 1 kilohertz. This became possible by the development of a compact, intense attosecond source using an out-of-focus generation geometry. The approach opens new avenues for the investigation of extremely fast electron dynamics in the attosecond regime.
The first generation of attosecond pulses (1 attosecond corresponds to 10-18 seconds) at the turn of this century has enabled unprecedented insights into the world of electrons. For their pioneering work, first leading to the demonstration of attosecond pulses in 2001, Anne L’Huillier, Pierre Agostini, and Ferenc Krausz were awarded the Nobel Prize in Physics in 2023.
Current attosecond techniques, however, come with an important drawback: To be able to record a movie in a pump-probe experiment, an attosecond pulse typically has to be combined with a femtosecond pulse (1 femtosecond corresponds to 10-15 seconds) whose optical cycles (a few femtoseconds long) is used as a clock with attosecond resolution. This constitutes a limitation for the investigation of electron dynamics on attosecond timescales.
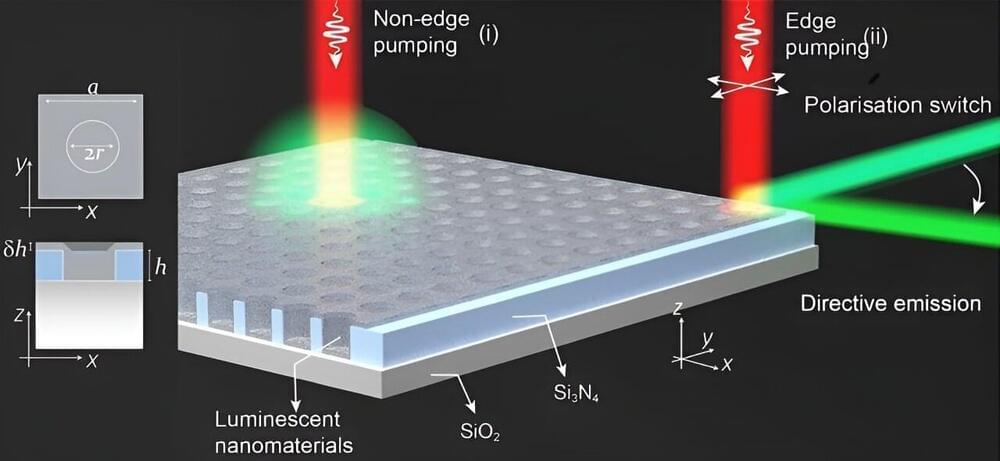
National University of Singapore researchers and their collaborators have unveiled a novel concept termed “supercritical coupling” that enables a several-fold increase in photon upconversion efficiency. This discovery not only challenges existing paradigms, but also opens a new direction in the control of light emission.
Photon upconversion, the process of converting low-energy photons into higher-energy ones, is a crucial technique with broad applications, ranging from super-resolution imaging to advanced photonic devices. Despite considerable progress, the quest for efficient photon upconversion has faced challenges due to inherent limitations in the irradiance of lanthanide-doped nanoparticles and the critical coupling conditions of optical resonances.
The concept of “supercritical coupling” plays a pivotal role in addressing these challenges. This fundamentally new approach, proposed by a research team led by Professor Liu Xiaogang from the Department of Chemistry, NUS and his collaborator, Dr. Gianluigi Zito from the National Research Council of Italy leverages on the physics of “bound states in the continuum” (BICs).

In this first article in a series on philosophy and science, we take a look at materialism and why it is fundamental to science.
A short disclaimer before we read further: I’m a materialist. Materialism is a branch of philosophy to which the sciences, particularly the physical and life sciences, owe a lot. Materialism posits that the material world — matter — exists, and everything in the Universe, including consciousness, is made from or is a product of matter. An objective reality exists and we can understand it. Without materialism, physics, chemistry, and biology as we know it wouldn’t exist.
Another branch of philosophy, idealism, is in direct contradiction to materialism. Idealism states that, instead of matter, the mind and consciousness are fundamental to reality; that they are immaterial and therefore independent of the material world.

“A spinning black hole is like a rocket on the launch pad,” said Dr. Biny Sebastian. “Once material gets close enough, it’s like someone has fueled the rocket and hit the ‘launch’ button.”
The center of our Milky Way Galaxy is exhibiting spinning behavior while warping the spacetime environment, according to a recent study published in the Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society. A team of international researchers led by Penn State University investigated the spinning patterns of the supermassive black hole at the center of the Milky Way, Sagittarius A* (Sgr A•, which is located approximately 26,000 light-years from Earth, and holds the potential to help astrophysicists better understand the behavior of black holes throughout the cosmos.
“A spinning black hole is like a rocket on the launch pad,” said Dr. Biny Sebastian, who is a researcher in the Department of Physics & Astronomy at the University of Manitoba and a co-author on the study. “Once material gets close enough, it’s like someone has fueled the rocket and hit the ‘launch’ button.”
For the study, the researchers analyzed data sets from six archival observations obtained by the Chandra X-Ray Observatory, which has been using its powerful instruments to study the cosmos since its launch in July 1999. Using a method that was developed in a 2019 study by the current study’s lead author, Dr. Ruth Daly, the researchers determined that Sagittarius A* was spinning in such a manner that it is warping the surrounding spacetime environment into a football shape, which becomes flatter as the spin increases and is driven by the surrounding matter and the black hole’s magnetic field. The researchers concluded that if the amount of this matter and magnetic field’s strength change in the future, this could alter the amount of energy the spin exerts out into space.
In an extremely cosmic–brain take, University of Rochester astrophysics professor Adam Frank suggests that a civilization could advance so much that it could eventually tinker with the fundamental laws of physics.
It’s a mind-bending proposition that ventures far beyond the conventional framework of scientific understanding, a reminder that perhaps we should dare to think outside the box — especially as we continue our search for extraterrestrial civilizations.
If a civilization were to be able to change the laws of physics, “the very nature of energy itself, with established rules like energy conservation, would be subject to revision within the scope of engineering,” Frank, who is part of the NASA-sponsored Categorizing Atmospheric Technosignatures program, wrote in an essay for Big Think.