Team develops simulator with 256 qubits, largest of its kind ever created.
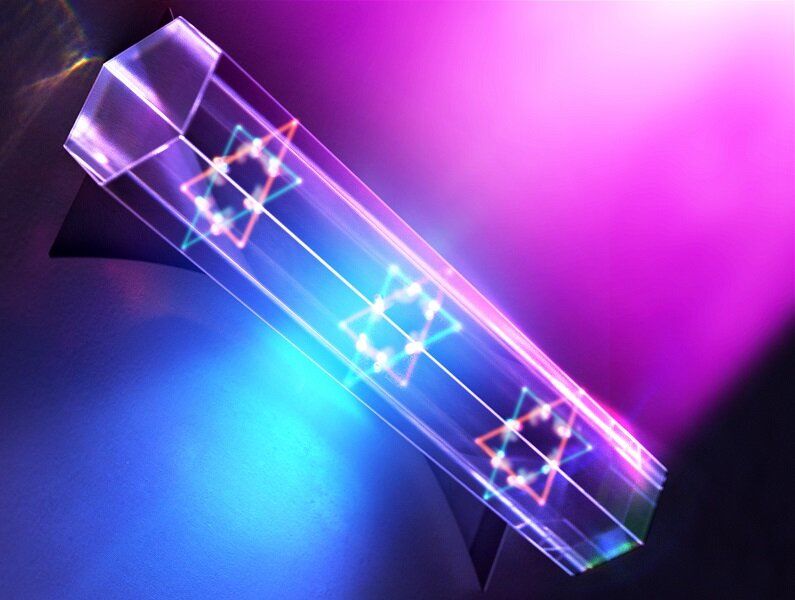
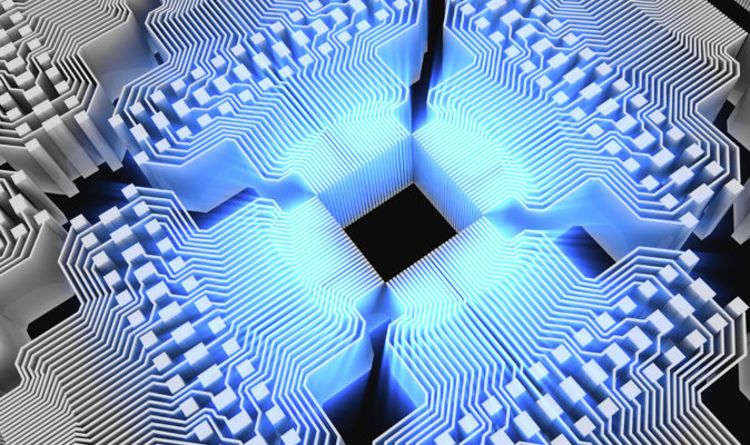
A team of physicists from the Harvard-MIT Center for Ultracold Atoms and other universities has developed a special type of quantum computer known as a programmable quantum simulator capable of operating with 256 quantum bits, or “qubits.”
The system marks a major step toward building large-scale quantum machines that could be used to shed light on a host of complex quantum processes and eventually help bring about real-world breakthroughs in material science, communication technologies, finance, and many other fields, overcoming research hurdles that are beyond the capabilities of even the fastest supercomputers today. Qubits are the fundamental building blocks on which quantum computers run and the source of their massive processing power.