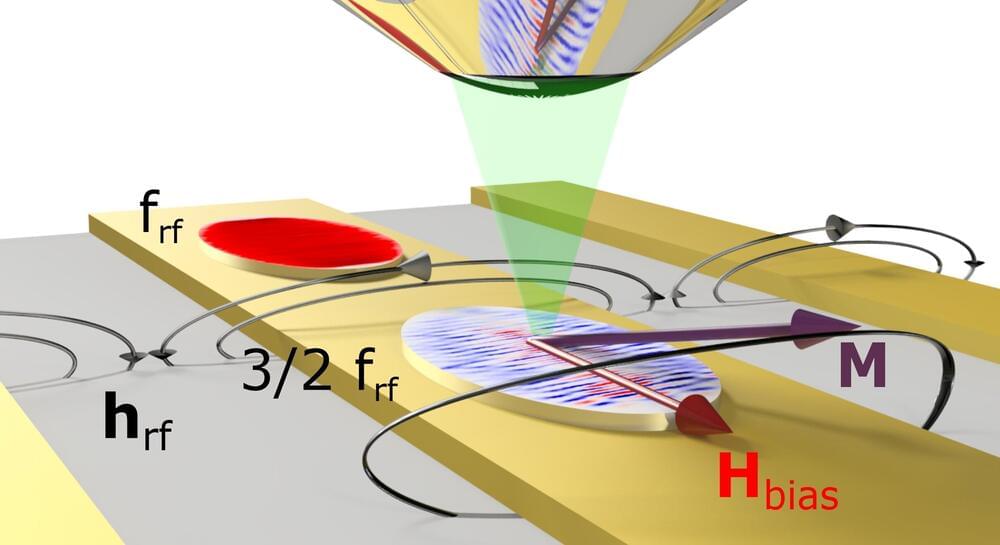
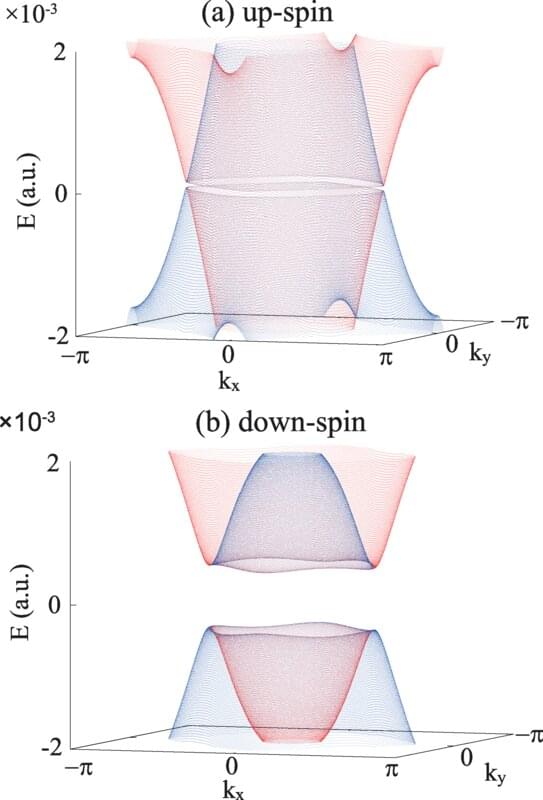
Strong alternating magnetic fields can be used to generate a new type of spin wave that was previously just theoretically predicted. This was achieved for the first time by a team of physicists from Martin Luther University Halle-Wittenberg (MLU). They report on their work in Nature Communications and provide the first microscopic images of these spin waves.
The basic idea of spintronics is to use a special property of electrons—spin—for various electronic applications such as data and information technology. The spin is the intrinsic angular momentum of electrons that produces a magnetic moment. Coupling these magnetic moments creates the magnetism that could ultimately be used in information processing. When these coupled magnetic moments are locally excited by a magnetic field pulse, this dynamic can spread like waves throughout the material. These are referred to as spin waves or magnons.
A special type of those waves is at the heart of the work of the physicists from Halle. Normally, the non-linear excitation of magnons produces integers of the output frequency—1,000 megahertz becomes 2,000 or 3,000, for example.