Our everyday electronic devices, such as living room lights, washing machines, and televisions, operate thanks to electrical currents. Similarly, the functioning of computers is based on the manipulation of information by small charge carriers known as electrons. Spintronics, on the other hand, introduces a unique approach to this process.
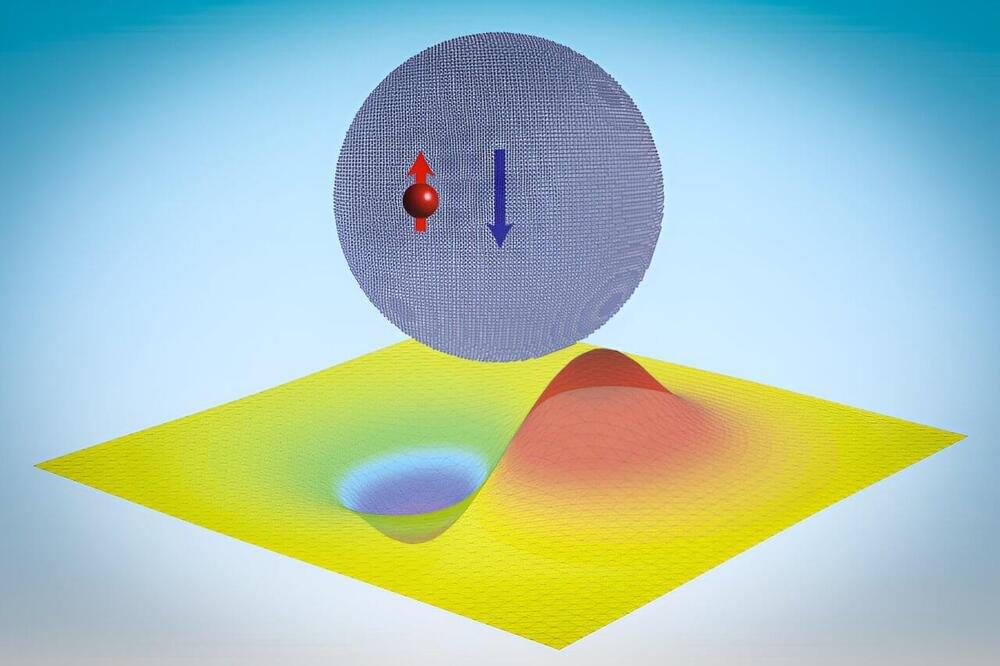
Instead of the charge of electrons, the spintronic approach is to exploit their magnetic moment, in other words, their spin, to store and process information – aiming to make the computers of the future more compact, fast, and sustainable. One way of processing information based on this approach is to use the magnetic vortices called skyrmions or, alternatively, their still little understood and rarer cousins called ‘merons’. Both are collective topological structures formed of numerous individual spins. Merons have to date only been observed in natural antiferromagnets, where they are difficult to both analyze and manipulate.