New theoretical research finds that it’s impossible to form a black hole with the energy of light particles alone, poking a hole in Einstein’s theory of general relativity.
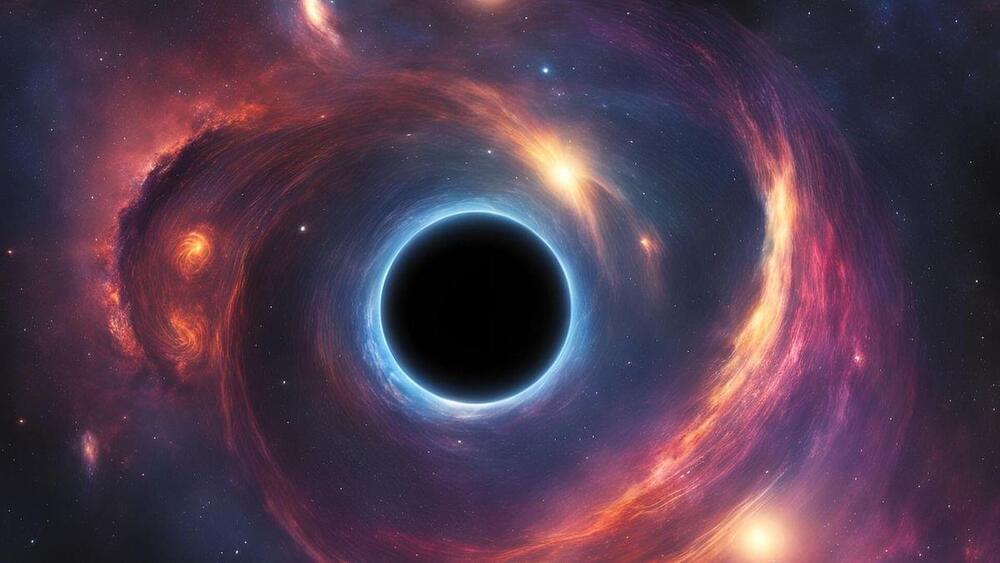


When two black holes collide, space and time shake and energy spreads out like ripples in a pond. These gravitational waves, predicted by Einstein in 1916, were observed for the first time by the Laser Interferometer Gravitational-Wave Observatory (LIGO) telescope in September 2015.

Is nature really as strange as quantum theory says — or are there simpler explanations? Neutron measurements prove: It doesn’t work without the strange properties of quantum theory.
Quantum theory allows particles to exist in superposition states, defying classical realism. The Leggett-Garg inequality tests this by comparing quantum behavior against classical expectations. Recent neutron beam experiments at TU Wien confirmed that particles do violate this inequality, reinforcing the validity of quantum theory over classical explanations.


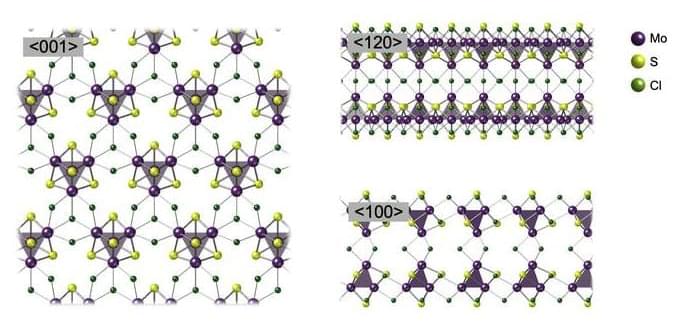
Researchers from Tokyo Metropolitan University have created sheets of transition metal chalcogenide “cubes” connected by chlorine atoms. While sheets of atoms have been widely studied e.g. graphene, the team’s work breaks new ground by using clusters instead. The team succeeded in forming nanoribbons inside carbon nanotubes for structural characterization, while also forming microscale sheets of cubes which could be exfoliated and probed. These were shown to be an excellent catalyst for generating hydrogen.
The findings have been published in Advanced Materials (“Superatomic layer of cubic Mo 4 S 4 clusters connected by Cl cross-linking”).
„ and show the arrangement of the nanosheet when viewed from different directions, respectively. (Image: Tokyo Metropolitan University)
face_with_colon_three steps towards infinity getting much closer to the solution with reinmans hypothesis: D.
Just as molecules are composed of atoms, in math, every natural number can be broken down into its prime factors—those that are divisible only by themselves and 1. Mathematicians want to understand how primes are distributed along the number line, in the hope of revealing an organizing principle for the atoms of arithmetic.
“At first sight, they look pretty random,” says James Maynard, a mathematician at the University of Oxford. “But actually, there’s believed to be this hidden structure within the prime numbers.”
For 165 years, mathematicians seeking that structure have focused on the Riemann hypothesis. Proving it would offer a Rosetta Stone for decoding the primes—as well as a $1 million award from the Clay Mathematics Institute. Now, in a preprint posted online on 31 May, Maynard and Larry Guth of the Massachusetts Institute of Technology have taken a step in this direction by ruling out certain exceptions to the Riemann hypothesis. The result is unlikely to win the cash prize, but it represents the first progress in decades on a major knot in math’s biggest unsolved problem, and it promises to spark new advances throughout number theory.
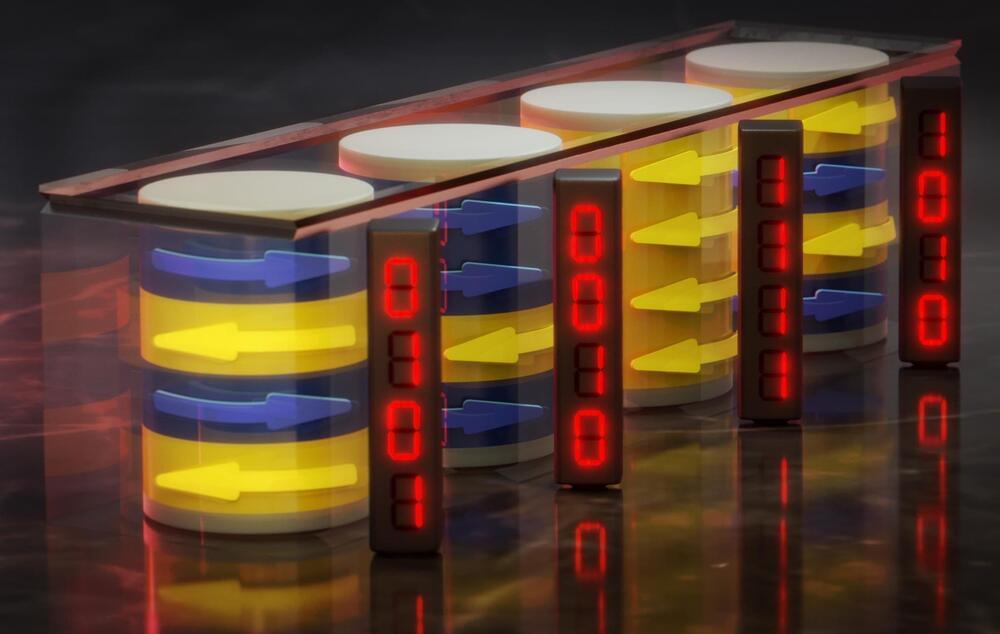
For the first time, researchers have demonstrated that not just individual bits, but entire bit sequences can be stored in cylindrical domains: tiny, cylindrical areas measuring just around 100 nanometers. As the team reports in the journal Advanced Electronic Materials, these findings could pave the way for novel types of data storage and sensors, including even magnetic variants of neural networks.
Groundbreaking Magnetic Storage
“A cylindrical domain, which we physicists also call a bubble domain, is a tiny, cylindrical area in a thin magnetic layer. Its spins, the electrons’ intrinsic angular momentum that generates the magnetic moment in the material, point in a specific direction. This creates a magnetization that differs from the rest of the environment. Imagine a small, cylinder-shaped magnetic bubble floating in a sea of opposite magnetization,” says Prof. Olav Hellwig from Helmholtz-Zentrum Dresden-Rossendorf ’s Institute of Ion Beam Physics and Materials Research, describing the subject of his research. He and his team are confident that such magnetic structures possess a great potential for spintronic applications.

Recent advancements in tachyon theory have addressed past inconsistencies by incorporating both past and future states into the boundary conditions, leading to a new quantum entanglement theory and suggesting a critical role for tachyons in matter formation.
Tachyons are hypothetical particles that travel at speeds greater than the speed of light. These superluminal particles, are the “enfant terrible” of modern physics. Until recently, they were generally regarded as entities that did not fit into the special theory of relativity. However, a paper just published by physicists from the University of Warsaw and the University of Oxford has shown that many of these prejudices were unfounded. Tachyons are not only not ruled out by the theory, but allow us to understand its causal structure better.
Superluminal Motion and Tachyons.