Erbium and similar elements provide a wide range of electronic “handles” for manipulating atoms in many-body quantum experiments.
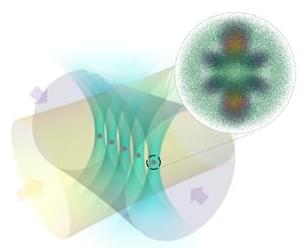

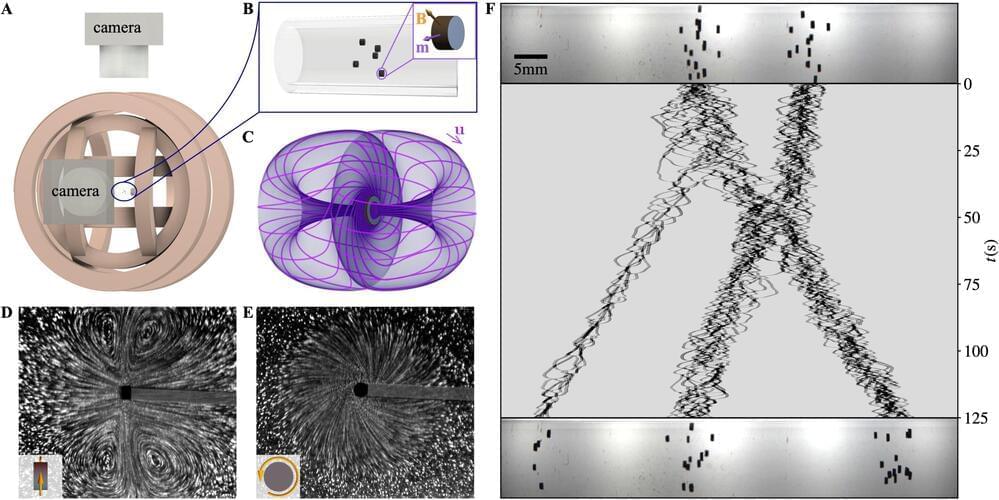
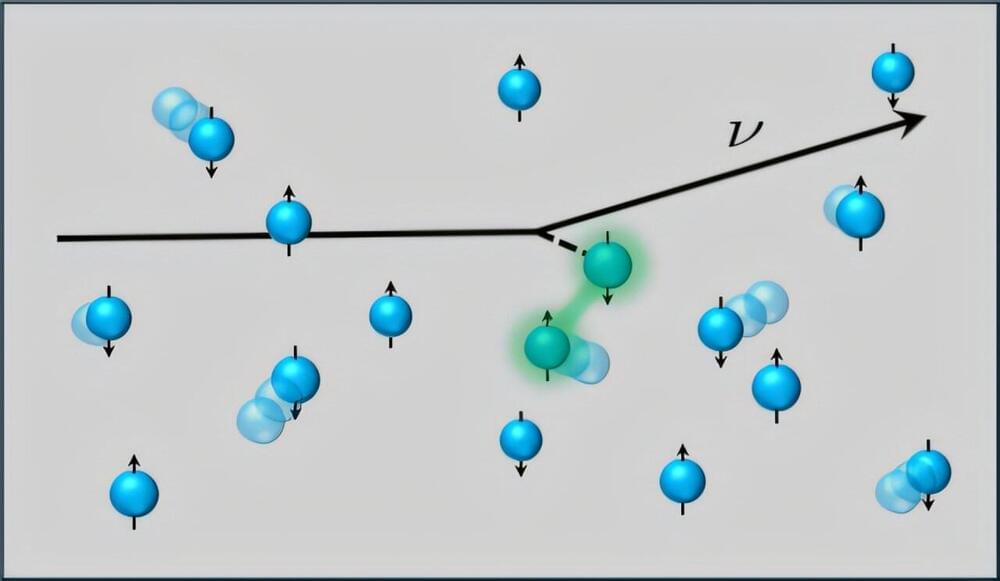
Vorticity, a measure of the local rotation or swirling motion in a fluid, has long been studied by physicists and mathematicians. The dynamics of vorticity is governed by the famed Navier-Stokes equations, which tell us that vorticity is produced by the passage of fluid past walls. Moreover, due to their internal resistance to being sheared, viscous fluids will diffuse the vorticity within them and so any persistent swirling motions will require a constant resupply of vorticity.
Physicists at the University of Chicago and applied mathematicians at the Flatiron Institute recently carried out a study exploring the behavior of viscous fluids in which tiny rotating particles were suspended, acting as local, mobile sources of vorticity. Their paper, published in Nature Physics, outlines fluid behaviors that were never observed before, characterized by self-propulsion, flocking and the emergence of chiral active phases.
“This experiment was a confluence of three curiosities,” William T.M. Irvine, a corresponding author of the paper, told Phys.org. “We had been studying and engineering parity-breaking meta-fluids with fundamentally new properties in 2D and were interested to see how a three-dimensional analog would behave.

It’s no secret: when we savour a delicious piece of fish or a platter of seafood, we’re not just consuming valuable omega-3s and vitamin D. Alongside these benefits come less appetising elements – countless micro– and nano-plastics.
These plastic particles, measuring less than 5 millimetres, enter our oceans through human waste and penetrate the food chain. According to an Ifremer study, around 24,400 billion microplastics are floating on the ocean’s surface.
These particles are found in all marine organisms – from microalgae to fish, which occupy higher levels of the food chain. This phenomenon not only threatens marine ecosystems but also raises concerns about potential risks to human health.
Check out courses in science, computer science, or mathematics on Brilliant! First 30 days are free and 20% off the annual premium subscription when you use our link ➜ https://brilliant.org/sabine.
Ten years ago, physicists discovered an anomaly that was dubbed the “ATOMKI anomaly”. The decays of certain atomic nuclei disagreed with our current understanding of physics. Particle physicists assigned the anomaly to a new particle, X17, often described as a fifth force. The anomaly was now tested by a follow-up experiment, but this is only the latest twist in a rather confusing story.
Paper: https://journals.aps.org/prl/abstract…
🤓 Check out my new quiz app ➜ http://quizwithit.com/
💌 Support me on Donorbox ➜ https://donorbox.org/swtg.
📝 Transcripts and written news on Substack ➜ https://sciencewtg.substack.com/
👉 Transcript with links to references on Patreon ➜ / sabine.
📩 Free weekly science newsletter ➜ https://sabinehossenfelder.com/newsle…
👂 Audio only podcast ➜ https://open.spotify.com/show/0MkNfXl…
🔗 Join this channel to get access to perks ➜
/ @sabinehossenfelder.
🖼️ On instagram ➜ / sciencewtg.
#science #sciencenews #physics
Quantum mechanics, a realm of the incredibly small, is often characterized by its paradoxical nature. One such paradox is the concept of superposition, where a quantum particle can exist in multiple states simultaneously. These delicate states, however, are notoriously fragile, often collapsing into a single, definite state within mere fractions of a second. Yet, a recent breakthrough has pushed the boundaries of quantum stability, achieving a record-breaking 23-minute lifespan for a specific type of superposition known as a cat state.
The term “cat state” is a whimsical reference to Schrödinger’s famous thought experiment, where a cat is placed in a box with a device that could randomly kill it. Until the box is opened, the cat is both alive and dead, a superposition of two states. In quantum mechanics, cat states manifest when a quantum object, such as an atom or a photon, exists in multiple states simultaneously, defying classical intuition.
While researchers have previously created cat states in laboratories, these states have been fleeting, quickly succumbing to the disruptive influence of their environment. However, a team led by Zheng-Tian Lu at the University of Science and Technology of China has managed to extend the lifespan of a cat state dramatically. They achieved this feat by manipulating a cloud of 10,000 ytterbium atoms, cooled to near absolute zero and trapped by laser light. By carefully controlling the atoms’ quantum states, the researchers were able to induce a superposition where each atom existed in two distinct spin states simultaneously.
In order to achieve the tunneling of atoms, the researchers used three optical tweezers and arranged them in a series. Then they introduced ultracold fermionic atoms (atoms that are cooled down to absolute zero temperatures) in this arrangement.
Using the three tweezers as traps, the researchers were able to control the tunneling rate of atoms by changing the distance between the traps. This approach allowed the researchers to successfully transfer atoms between the two outer tweezers.
“We observe a smooth and high-efficiency transfer of atoms between the two outer traps, with a very low population remaining in the central trap,” the researchers note in their study.

In the vast reaches of space, invisible forces shape the behavior of charged particles in ways that are only now beginning to be fully understood.
A small team of astrophysicists at the University of California, Los Angeles, working with colleagues from the University of Texas at Dallas and the University of Colorado, Boulder, has found evidence that Alfvén waves in space plasmas speed up ion beams, resulting in the creation of small-scale acoustic waves that in turn generate heat in the magnetosphere.
In their study, published in the journal Physical Review Letters, the group used data from the four-spacecraft Magnetospheric Multiscale (MMS) mission that took place in 2015 to prove a theory about heat generation in the magnetosphere.
For several years, astronomers have been studying the impact of the solar wind striking the magnetopause, which defines the outer edges of the magnetosphere. Prior research has shown that as the solar wind arrives, Alfvén waves are generated and the resulting energy heats up the plasma in the magnetosphere. However, the plasma there is too thin to result in a cascade.
When a star dies in a supernova, one possible outcome is for the remains to become a neutron star. Inside a neutron star, the protons and electrons combine into uncharged neutrons. This substance is called neutron matter.
A team of researchers from the United States, China, Turkey, and Germany has performed ab initio (i.e., from the most fundamental principles) simulations to calculate spin and density correlations in neutron matter. They used realistic nuclear interactions at higher densities of neutrons than previously explored. Spin and density are the probability of finding a neutron in a particular position with a particular direction of spin. These correlations determine key aspects of how neutrinos scatter and heat up in a core-collapse supernova.
The research is published in the journal Physical Review Letters.

A new technique employing monochromatic light improves the study of internal structures in materials affected by light scattering, enabling detailed observation of particle concentrations.
When driving through a bank of fog, car headlights are only moderately helpful since the light is scattered by the water particles suspended in the air. A similar situation occurs when trying to observe the inside of a drop of milk in water or the internal structure of an opal gem with white light. In these cases, multiple light scattering effects prevent examination of the interior.
Now, a team of researchers at Johannes Gutenberg University Mainz (JGU) and Heinrich Heine University Düsseldorf (HHU) has overcome this challenge and developed a new method to study the interior of a crystalline drop.