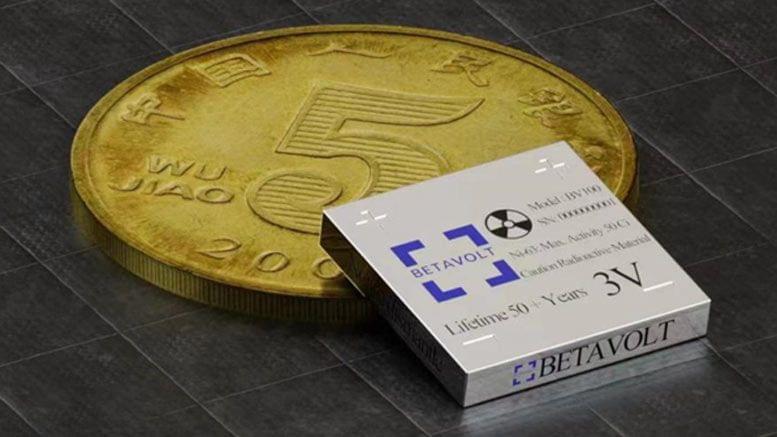
The design uses China’s first diamond semiconductor material.



I want this.
A Chinese company called Betavolt Technology has started working on nuclear batteries, and if this turns into something that actually works, you can say goodbye to smartphone charging. Based on the information we have received, the company is working on batteries across several devices.
The nuclear batteries are able to hold a charge for 50 years. Yes, you have heard this right. If this technology ever sees the light of day and hits the mainstream, it is safe to say that our smartphone batteries will outlive many of us.
The company has talked about how they have pioneered the “miniaturization of atomic energy batteries.” Betavolt Technology managed to stuff 63 nuclear isotopes in a modular that is smaller than a coin. The model is called BV100, and it is capable of producing 100 microwatts of electricity, which should be more than enough when it comes to a smartphone.
Fusion’s success as a renewable energy depends on the creation of an industry to support it, and academia is vital to that industry’s development.
A new study suggests that universities have an essential role to fulfill in the continued growth and success of any modern high-tech industry, and especially the nascent fusion industry; however, the importance of that role is not reflected in the number of fusion-oriented faculty and educational channels currently available. Academia’s responsiveness to the birth of other modern scientific fields, such as aeronautics and nuclear fission, provides a template for the steps universities can take to enable a robust fusion industry.
Insights from Experts.
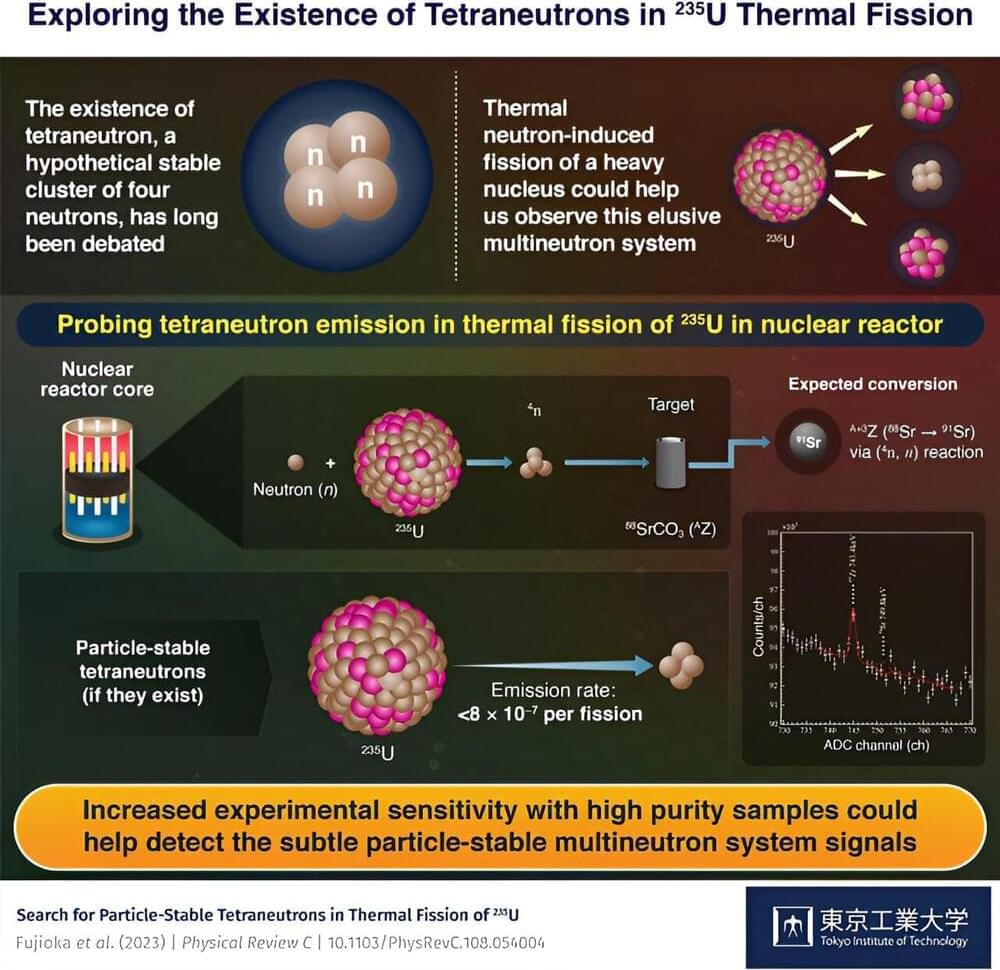
The possible emission rate of particle-stable tetraneutron, a four-neutron system whose existence has been long debated within the scientific community, has been investigated by researchers from Tokyo Tech. They looked into tetraneutron emission from thermal fission of 235 U by irradiating a sample of 88 SrCO3 in a nuclear research reactor and analyzing it via γ-ray spectroscopy.
Tetraneutron is an elusive atomic nucleus consisting of four neutrons, whose existence has been highly debated by scientists. This stems primarily from our lack of knowledge about systems consisting of only neutrons, since most atomic nuclei are usually made of a combination of protons and neutrons. Scientists believe that the experimental observation of a tetraneutron could be the key to exploring new properties of atomic nuclei and answering the age-old question: Can a charge-neutral multineutron system ever exist?
Two recent experimental studies reported the presence of tetraneutrons in bound state and resonant state (a state that decays with time but lives long enough to be detected experimentally). However, theoretical studies indicate that tetraneutrons will not exist in a bound state if the interactions between neutrons are governed by our common understanding of two or three-body nuclear forces.
Fusion is a kind of nuclear power, which could revolutionise how clean energy is produced. As a new wave of experiments heats up, can fusion live up to the hype?
00:33 The future of green energy.
02:00 What is nuclear fusion and how does it work?
03:17 Is it achievable?
Sign up to The Economist’s daily newsletter: https://econ.st/3s9WjPB
Energy security gives climate-friendly nuclear-power plants a new appeal: https://econ.st/3QHgdd1
Listen to our podcast about the importance of private companies in advancing nuclear fusion https://econ.st/49n7aqa.
Fusion power is coming back into fashion: https://econ.st/49jPwDu.
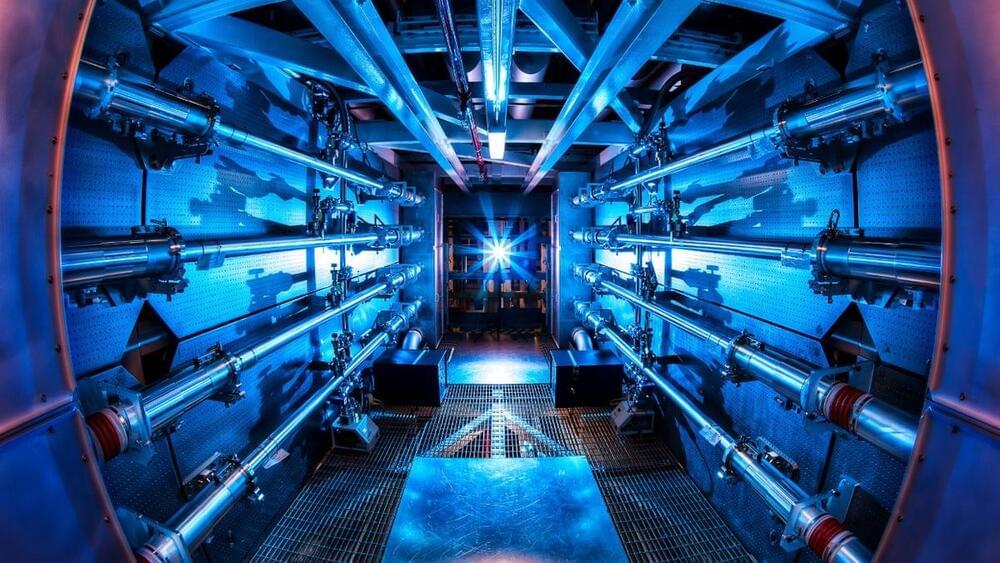

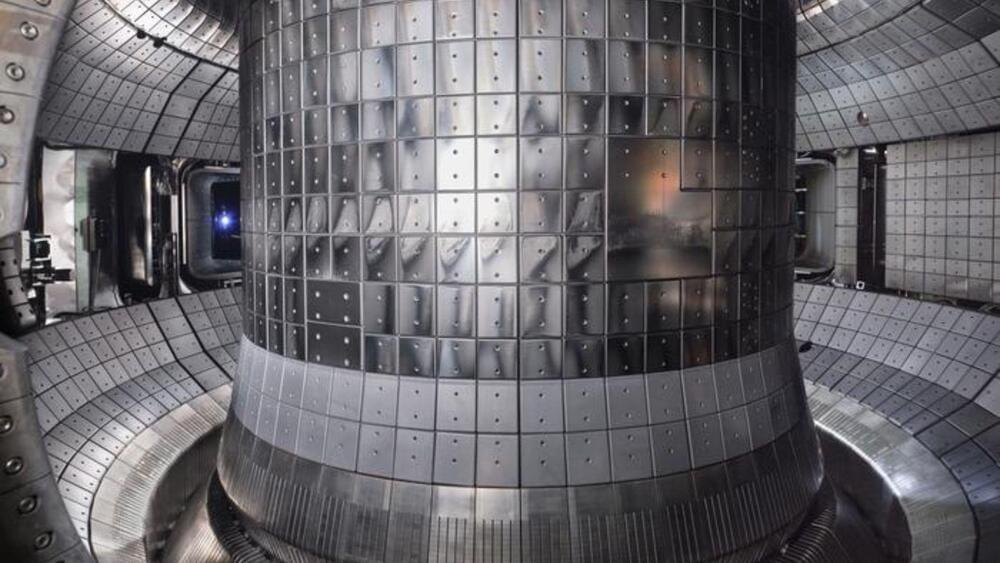
KSTAR, the Korea Institute of Fusion Energy’s (KFE) artificial Sun, has completed a significant modification that would allow it to function for longer periods at higher temperatures. KSTAR stands for Korea Superconducting Tokamak Advanced Research, an advanced nuclear fusion reactor constructed in 2007.
The development in this regard involved the installation of its newly developed tungsten divertors, “allowing it to operate for extended periods sustaining high-temperature plasma over the 100 million degrees,” according to a statement by the institute.
The team claimed they could complete a plasma experiment with the reactor equipped with the new divertor on December 21. In 2021, KSTAR set a new record by running at one million degrees and maintaining super-hot plasma for 30 seconds.

Early PDP-11 models were not overly impressive. The first PDP-11 11/20 cost $20,000, but it shipped with only about 4KB of RAM. It used paper tape as storage and had an ASR-33 teletype printer console that printed 10 characters per second. But it also had an amazing orthogonal 16-bit architecture, eight registers, 65KB of address space, a 1.25 MHz cycle time, and a flexible UNIBUS hardware bus that would support future hardware peripherals. This was a winning combination for its creator, Digital Equipment Corporation.
The initial application for the PDP-11 included real-time hardware control, factory automation, and data processing. As the PDP-11 gained a reputation for flexibility, programmability, and affordability, it saw use in traffic light control systems, the Nike missile defense system, air traffic control, nuclear power plants, Navy pilot training systems, and telecommunications. It also pioneered the word processing and data processing that we now take for granted.
And the PDP-11’s influence is most strikingly evident in the device’s assembly programming.
Check out http://rocketmoney.com/pbsspace or scan the QR code on the screen to start managing your personal finances today. Thank you to Rocket Money for sponsoring today’s video! #rocketmoney #personalfinance.
PBS Member Stations rely on viewers like you. To support your local station, go to: http://to.pbs.org/DonateSPACE
Sign Up on Patreon to get access to the Space Time Discord!
https://www.patreon.com/pbsspacetime.
Two protons next to each other in an atomic nucleus are repelling each other electromagnetically with enough force to lift a medium-sized labradoodle off the ground. Release this energy and you have, well, you have a nuclear explosion. Just as well there’s an even stronger force than the electromagnetism holding our nuclei together. But it’s not the strong force, as you might have imagined. At least not directly. Nuclei are held together by a quirk of nature, without which we would have no complex atoms, no chemistry, and certainly no labradoodles.
Episode Companion Playlist.
Check out the Space Time Merch Store.
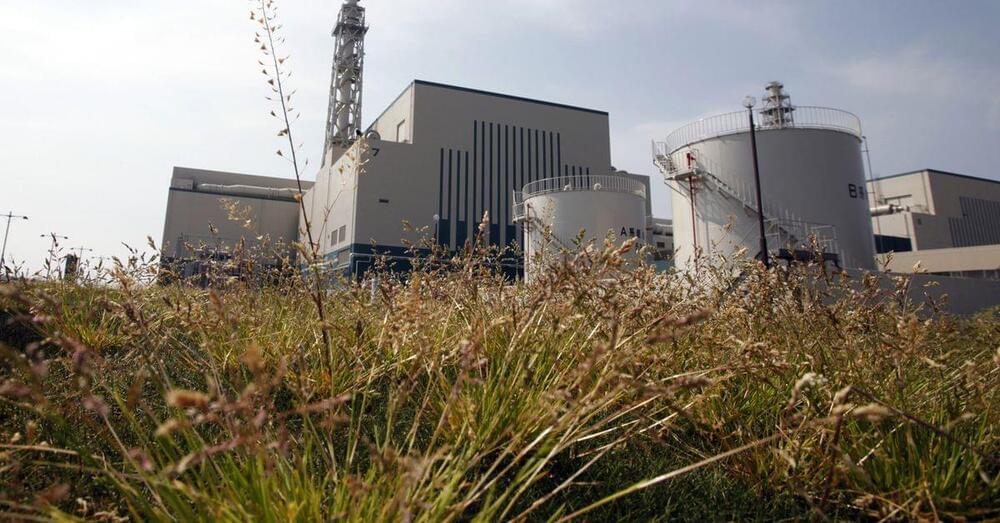

TOKYO, Dec 27 (Reuters) — Japan’s nuclear power regulator on Wednesday lifted an operational ban imposed on Tokyo Electric Power’s (9501.T) Kashiwazaki-Kariwa nuclear power plant two years ago, allowing it to work towards gaining local permission to restart.
Tepco has been eager to bring the world’s largest atomic power plant back online to slash operating costs, but a resumption still needs consent from the local governments of Niigata prefecture, Kashiwazaki city and Kariwa village, where it is located.
When that might happen is unknown.