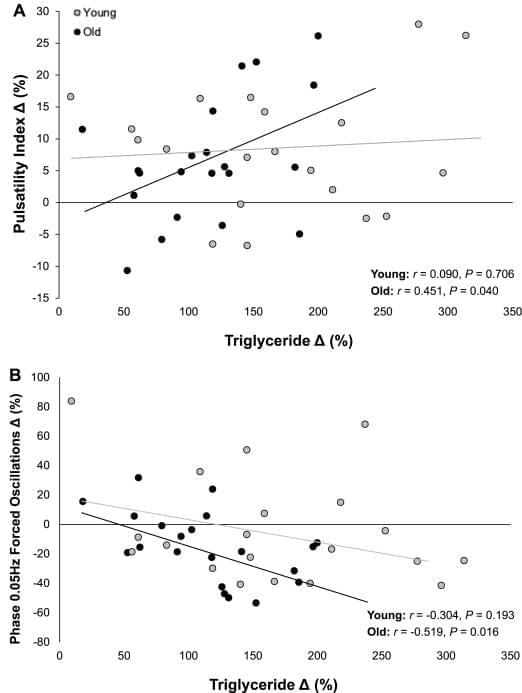
Dietary fat is an important part of our diet. It provides us with a concentrated source of energy, transports vitamins and when stored in the body, protects our organs and helps keep us warm. The two main types of fat that we consume are saturated and unsaturated (monounsaturated and polyunsaturated), which are differentiated by their chemical composition.
But these fats have different effects on our body. For example, it is well established that eating a meal that is high in saturated fat, such as that self-indulgent Friday night takeaway pizza, can be bad for our blood vessels and heart health. And these effects are not simply confined to the heart.
The brain has limited energy stores, which means it is heavily reliant on a continuous supply of blood delivering oxygen and glucose to maintain normal function.
One of the ways the body maintains this supply is through a process known as “dynamic cerebral autoregulation”. This process ensures that blood flow to the brain remains stable despite everyday changes in blood pressure, such as standing up and exercising. It’s like having shock absorbers that help keep our brains cool under pressure.
But when this process is impaired, those swings in blood pressure become harder to manage. That can mean brief episodes of too little or too much blood reaching the brain. Over time, this increases the risk of developing conditions like stroke and dementia.