Here’s my latest post!
Sleep changes during aging may impact Alzheimer’s disease risk, and with the goal of minimizing that risk, can sleep, in particular, levels of deep sleep, be optimized?
Here’s my latest post!
Sleep changes during aging may impact Alzheimer’s disease risk, and with the goal of minimizing that risk, can sleep, in particular, levels of deep sleep, be optimized?
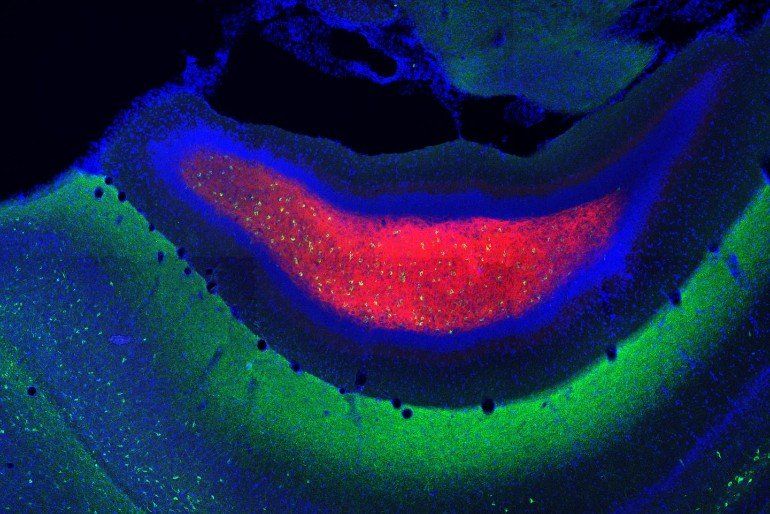
Summary: Researchers have identified a signaling pathway in the hippocampus that plays a critical role in creates novel memories about new environments.
Source: IST Austria
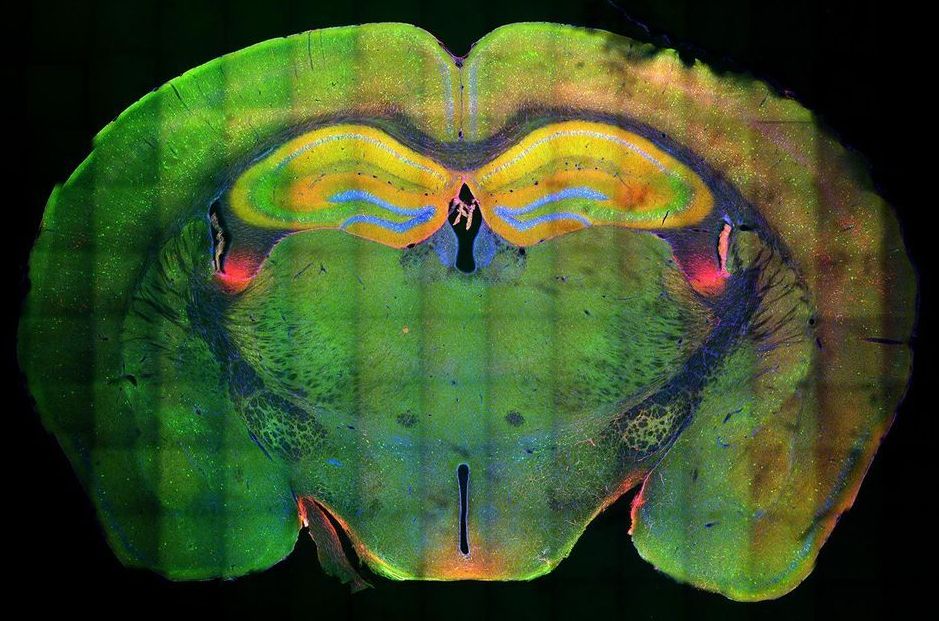
Imagine going to a café you have never been to. You will remember this new environment, but when you visit it again and again fewer new memories about the environment will be formed, only the things that changed will be really memorable. How this long-term memory are regulated is still not fully understood. Ryuichi Shigemoto from the Institute of Science and Technology Austria (IST Austria) in cooperation with researchers from Aarhus University and the National Institute for Physiological Sciences in Japan now have uncovered a new keystone in the formation of memories.
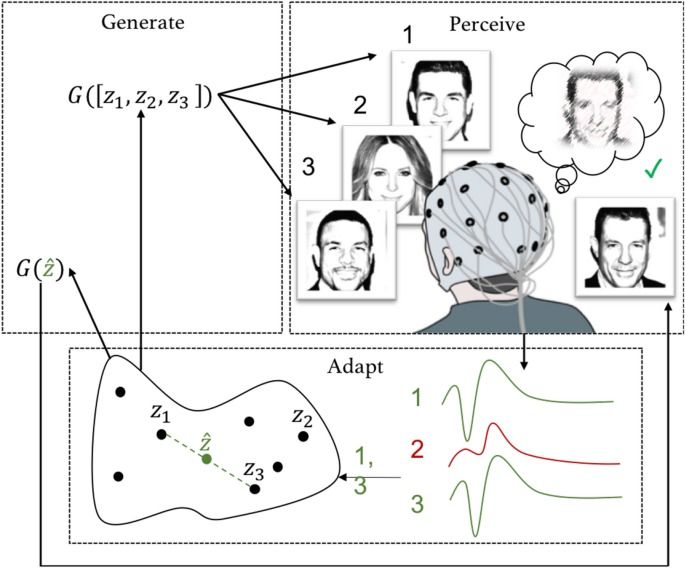
Brain–computer interfaces enable active communication and execution of a pre-defined set of commands, such as typing a letter or moving a cursor. However, they have thus far not been able to infer more complex intentions or adapt more complex output based on brain signals. Here, we present neuroadaptive generative modelling, which uses a participant’s brain signals as feedback to adapt a boundless generative model and generate new information matching the participant’s intentions. We report an experiment validating the paradigm in generating images of human faces. In the experiment, participants were asked to specifically focus on perceptual categories, such as old or young people, while being presented with computer-generated, photorealistic faces with varying visual features. Their EEG signals associated with the images were then used as a feedback signal to update a model of the user’s intentions, from which new images were generated using a generative adversarial network. A double-blind follow-up with the participant evaluating the output shows that neuroadaptive modelling can be utilised to produce images matching the perceptual category features. The approach demonstrates brain-based creative augmentation between computers and humans for producing new information matching the human operator’s perceptual categories.

Summary: A clusterization approach allows researchers to analyze dendritic spines in new ways.
Source: SPbPU
Dendritic spines are small protrusions from a neuron’s dendrite membrane, where contact with neighboring axons is formed to receive synaptic input. These spines have different sizes, shapes, and density. Changes in the characteristics of the dendritic spines are associated with learning and memory and could be a feature of neurodegenerative disorders like Alzheimer’s disease and Huntington’s disease.

Summary: By fusing a cytokine to a blood protein, researchers have developed a new therapy to help treat multiple sclerosis.
Source: University of Chicago
Multiple sclerosis, an autoimmune disease of the central nervous system that affects millions worldwide, can cause debilitating symptoms for those who suffer from it.
If Dr. Ken Berry actually meant to say that you need to eat saturated fat for your nerves and brain, he flunks Biochem 101. First of all, your body can make all the saturated fat you need out of carbs and proteins. You don’t need to eat ANY saturated fat. Second, the most common fatty acid in your brain is the polyunsaturated fatty acid (PUFA) called DHA, which you DO need to eat, because you can’t make it from non-fats (you need to eat it or EPA in things like seafood, or at least the precursor omega-3 PUFA called ALA in cold-climate plants.) Ironically enough, ALA is common in Canola oil, which Dr. Berry deprecates, but not in the tropical plant oils that he likes. More on that later.
A diet with a lot of saturated fat is NOT the best for the heart. The American Heart Association continues to recommend low saturated fat diets (with the missing sat-fat replaced by mono and polyunsaturated fat, not by carbohydrates) because the evidence from animal and human trials and even properly controlled epidemiology, shows these the best diets (see reference below—an extensive review of meta analyses [1]). Examples are the DASH hypertension diet and the closely-related Mediterranean diet (which has lots of olive oil for monounsaturated fatty acid, and seafood for DHA). If Dr. Berry thinks he has something better than the Mediterranean diet for longevity, what is his direct evidence?
Saturated fat, of course, is used by the body to make cholesterol (you don’t need to eat any cholesterol for this reason), and it does raise cholesterol levels and it does increase atherosclerosis in nearly every controlled prospective experimental model in animals and humans. This is the gold standard of evidence in medicine.
One can go only so far with epidemiology, because occasionally when one bad thing (saturated fat) is heavily replaced for calories by another bad thing (certain carbohydrates) one detects no epidemiologic effect from changing just the first thing.
That happens with various high and low saturated fat diets around the world enough to make saturated fat look benign as a single input variable. It is not. Rather, what these studies really show is that replacing butter with sugar or high glycemic carbs gives you a diet equally bad for the arteries. One cannot see how bad that is, until one compares these with low-carbohydrate, low-saturated-fat diets, which are less common, but better. The double-negative tradeoff of carbs and saturated fats (where carbs are a statistical “confounder”) is one of those occasional cruel misdirectional things that happen with imperfectly controlled past-observations, but (again) it’s why biomedical knowledge consists of more than just epidemiology.
The saturated oils Dr. Berry recommends are by themselves on the edge of PUFA deficiency. This can be dramatic: for example the only way I know to give dogs atherosclerosis nutritionally, is to feed them just coconut oil for fat, and NO monounsaturates or PUFA. Apparently a little PUFA is extremely important for the heart, and larger amounts do no harm. There are hints that high PUFA diets are risks for certain cancers, but that merely underscores the need to get monounsaturates like olive and Canola where one can, and some PUFA foods. I know of no civilization that eats a lot of coconut oil that doesn’t eat seafood as well, so that combination is safe.
Canola oil is merely rapeseed oil bred to remove erucic acid and other potential toxins. It is high in monounsaturates and ALA and of all the plant oils is probably closest to optimal for human nutrition. Olive oil is probably better than Canola for frying, since ALA will oxidize, but Canola’s ALA is very important for vegans who need an omega-3 PUFA plant oil to convert to brain DHA. Seafood and olive oil are a fine replacement for Canola, but the person who cannot eat meat or seafood had better look for a baking and salad oil with ALA in it, and Canola oil is the best for this. Linseed oil is hard to digest and hard to work with, so that leaves Canola as the best omega-3 alternative for vegans. Dr. Berry never mentions his problem with Canola beyond saying it is GMO. But he is wrong there, as it doesn’t have to be. Canola as a product (1970’s) was created with hybrid not GMO techniques, and although GMO Canolas exist now, there also exist certified non-GMO and “organic” Canola oils which are labeled with a butterfly and tested to make sure no GMO Canola has crept in (there are tests available for this too complicated to go into here, but you can be sure).
Interesting Eric Klien
That prompted the researchers, who are part of the Human Brain Project, to look at two features that have become clear in experimental neuroscience data: each neuron retains a memory of previous activity in the form of molecular markers that slowly fade with time; and the brain provides top-down learning signals using things like the neurotransmitter dopamine that modulates the behavior of groups of neurons.
In a paper in Nature Communications, the Austrian team describes how they created artificial analogues of these two features to create a new learning paradigm they call e-prop. While the approach learns slower than backpropagation-based methods, it achieves comparable performance.
More importantly, it allows online learning. That means that rather than processing big batches of data at once, which requires constant transfer to and from memory that contributes significantly to machine learning’s energy bills, the approach simply learns from data as it becomes available. That dramatically cuts the amount of memory and energy it requires, which makes it far more practical to use for on-chip learning in smaller mobile devices.
If Dr. Ken Berry actually meant to say that you need to eat saturated fat for your nerves and brain, he flunks Biochem 101. First of all, your body can make all the saturated fat you need out of carbs and proteins. You don’t need to eat ANY saturated fat. Second, the most common fatty acid in your brain is the polyunsaturated fatty acid (PUFA) called DHA, which you DO need to eat, because you can’t make it from non-fats (you need to eat it in things like seafood, or at least the precursor omega-3 PUFA called ALA in cold-climate plants.) Ironically enough ALAis common in Canola oil, which Dr. Berry deprecates, but not in the tropical plant oils he likes. More on that later. A diet with a lot of saturated fat is NOT the best for the heart. The American Heart Association continues to recommend low saturated fat diets (with the missing sat-fat replaced by mono and polyunsaturated fat, not by carbohydrates) because the evidence from animal and human trials and even properly controlled epidemiology, shows these the best diets (see reference below–an extensive review of meta analyses [1]). Examples are the DASH hypertension diet and the closely-related Mediterranean diet (which has lots of olive oil for monounsaturated fatty acid, and seafood for DHA). If Dr. Berrythinks he has something better than the Mediterranean diet for longevity, what is his direct evidence? Saturated fat, of course, is used by the body to make cholesterol (you don’t need to eat any cholesterol for this reason), and it does raise cholesterol levels and it does increase atherosclerosis in nearly every controlled prospective experimental model in animals and humans. This is the gold standard of evidence in medicine.
One can go only so far with epidemiology, because occasionally when one bad thing (saturated fat) is heavily replaced for calories by another bad thing (certain carbohydrates) one detects no epidemiologic effect from changing just the first thing.
That happens with various high and low saturated fat diets around the world enough to make saturated fat look benign as a single input variable. It is not. Rather, what these studies really show is that replacing butter with sugar or high glycemic carbs gives you a diet equally bad for the arteries. One cannot see how bad that is, until one compares these with low-carbohydrate, low-saturated-fat diets, which are less common, but better. The double-negative tradeoff of carbs and saturated fats (where carbs are a statistical “confounder”) is one of those occasional cruel misdirectional things that happen with imperfectly controlled past-observations, but (again) it’s why biomedical knowledge consists of more than just epidemiology. The saturated oils Dr. Berryrecommends are by themselves on the edge of PUFA deficiency. This can be dramatic: for example the only way I know to give dogs atherosclerosis nutritionally, is to feed them just coconut oil for fat, and NO monounsaturates or PUFA. Apparently a little PUFA is extremely important for the heart, and larger amounts do no harm. There are hints that high PUFA diets are risks for certain cancers, but that merely underscores the need to get monounsaturates like olive and Canola where one can, and some PUFA foods. I know of no civilization that eats a lot of coconut oil that doesn’t eat seafood as well, so that combination is safe. Canola oil is merely rapeseed oil bred to remove erucic acid and other potential toxins. It is high in monounsaturates and ALAand of all the plant oils is probably closest to optimal for human nutrition. Olive oil is probably better than Canola for frying, since ALAwill oxidize, but Canola’s ALA is very important for vegans who need an omega-3 PUFA plant oil to convert to brain DHA. Seafood and olive oil are a fine replacement for Canola, but the person who cannot eat meat or seafood had better look for a baking and salad oil with ALA in it, and Canola oil is the best for this. Linseed oil is hard to digest and hard to work with, so that leaves Canola as the best omega-3 alternative for vegans. Dr. Berry never mentions his problem with Canola beyond saying it is GMO. But he is wrong there, as it doesn’t have to be. Canola as a product (1970’s) was created with hybrid not GMO techniques, and although GMO Canolas exist now, there also exist certified non-GMO and “organic” Canola oils which are labeled with a butterfly and tested to make sure no GMO Canola has crept in (there are tests available for this too complicated to go into here, but you can be sure).
In short, the ONLY part of Dr. Berry’s piece I agree with is dumping your hydrogenated shortening products (Crisco, etc.) in the garbage. That’s why I give this segment a D, rather than the F it otherwise deserves.
Steven B. Harris, M.D.
Modifications to chromosomes in “engram” neurons control the encoding and retrieval of memories.
When the brain forms a memory of a new experience, neurons called engram cells encode the details of the memory and are later reactivated whenever we recall it. A new MIT study reveals that this process is controlled by large-scale remodeling of cells’ chromatin.
This remodeling, which allows specific genes involved in storing memories to become more active, takes place in multiple stages spread out over several days. Changes to the density and arrangement of chromatin, a highly compressed structure consisting of DNA and proteins called histones, can control how active specific genes are within a given cell.

In first-of-their-kind observations in the human brain, an international team of researchers has revealed two well-known neurochemicals–dopamine and serotonin–are at work at sub-second speeds to shape how people perceive the world and take action based on their perception.
Furthermore, the neurochemicals appear to integrate people’s perceptions of the world with their actions, indicating dopamine and serotonin have far more expansive roles in the human nervous system than previously known.
Known as neuromodulators, dopamine and serotonin have traditionally been linked to reward processing–how good or how bad people perceive an outcome to be after taking an action.
The study online today in the journal *Neuron* opens the door to a deeper understanding of an expanded role for these systems and their roles in human health.
“An enormous number of people throughout the world are taking pharmaceutical compounds to perturb the dopamine and serotonin transmitter systems to change their behavior and mental health,” said P. Read Montague, senior author of the study and a professor and director of the Center for Human Neuroscience Research and the Human Neuroimaging Laboratory at the Fralin Biomedical Research Institute at Virginia Tech Carilion. “For the first time, moment-to-moment activity in these systems has been measured and determined to be involved in perception and cognitive capacities. These neurotransmitters are simultaneously acting and integrating activity across vastly different time and space scales than anyone expected.”
…
“These neuromodulators play a much broader role in supporting human behavior and thought, and in particular they are involved in how we process the outside world,” Bang said. “For example, if you move through a room and the lights are off, you move differently because you’re uncertain about where objects are. Our work suggests these neuromodulators–serotonin in particular– are playing a role in signaling how uncertain we are about the outside environment.”