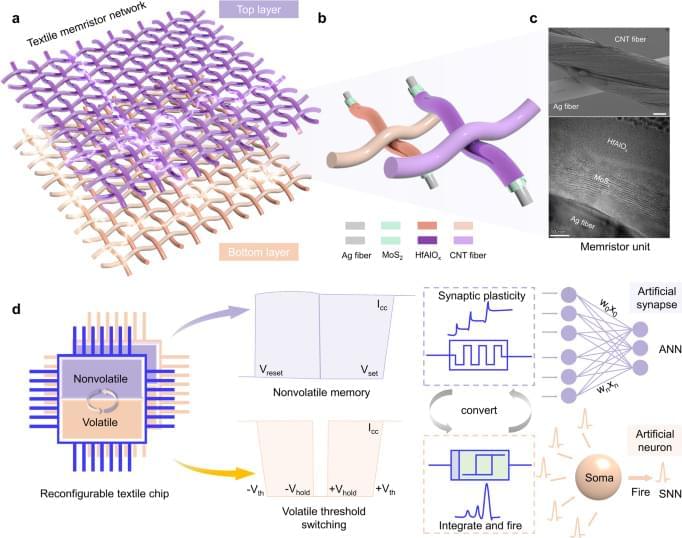
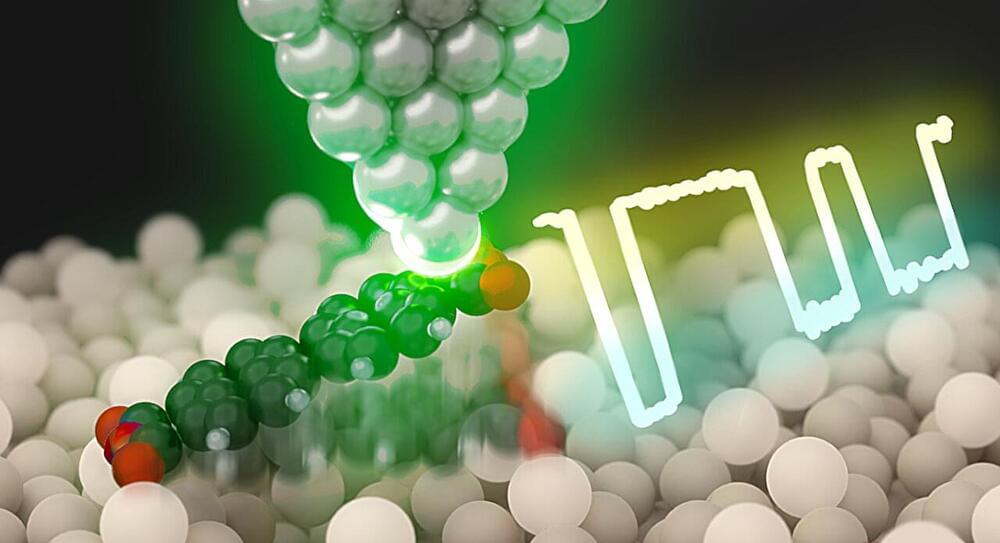
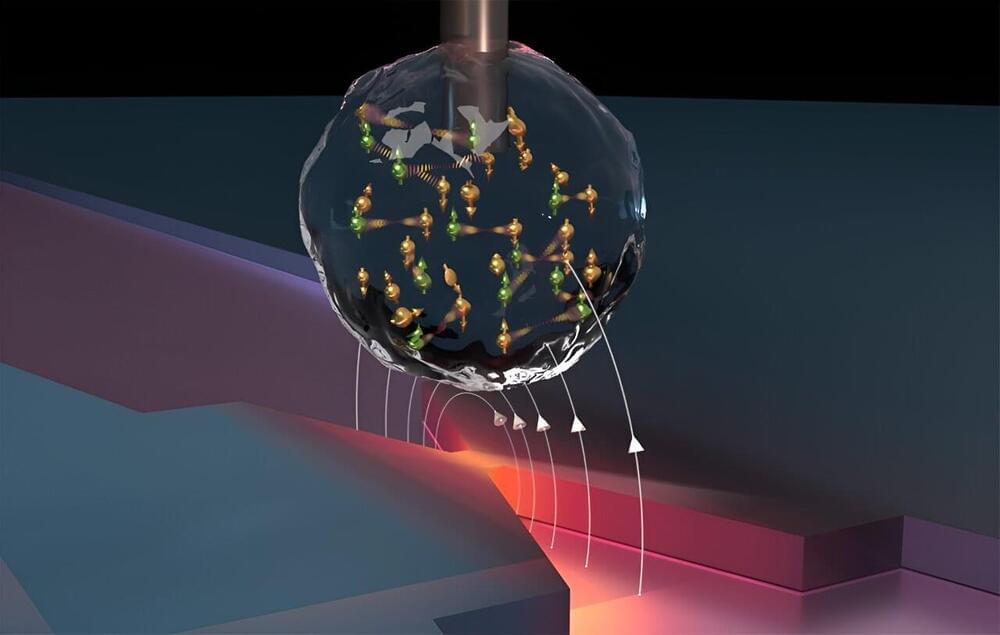
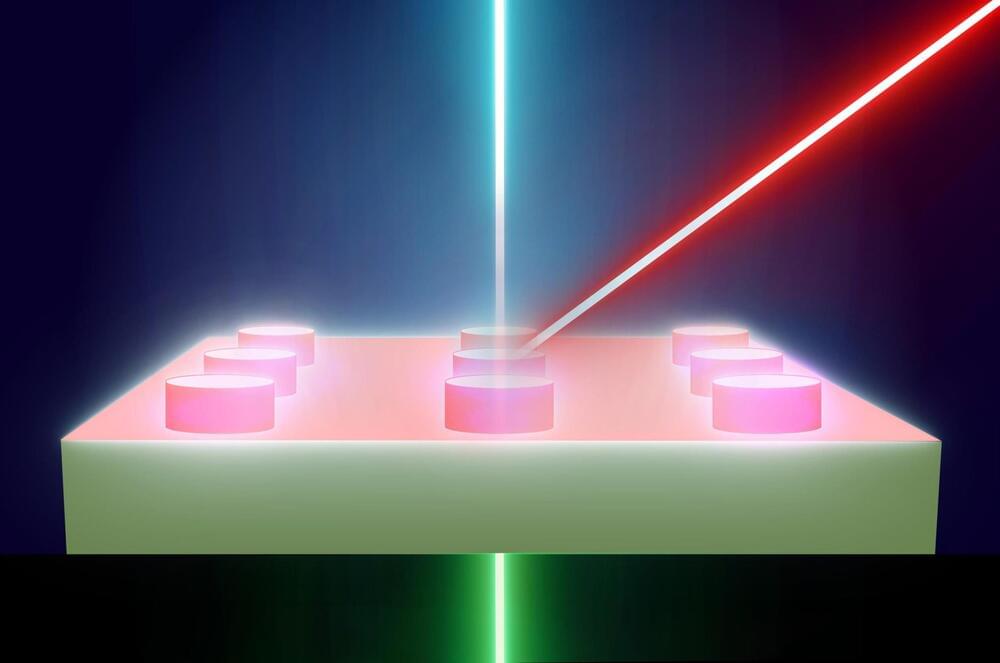
The new research centers on the use of LSPs to achieve atomic-level control of chemical reactions. A team has successfully extended LSP functionality to semiconductor platforms. By using a plasmon-resonant tip in a low-temperature scanning tunneling microscope, they enabled the reversible lift-up and drop-down of single organic molecules on a silicon surface.
The LSP at the tip induces breaking and forming specific chemical bonds between the molecule and silicon, resulting in the reversible switching. The switching rate can be tuned by the tip position with exceptional precision down to 0.01 nanometer. This precise manipulation allows for reversible changes between two different molecular configurations.
An additional key aspect of this breakthrough is the tunability of the optoelectronic function through atomic-level molecular modification. The team confirmed that photoswitching is inhibited for another organic molecule, in which only one oxygen atom not bonding to silicon is substituted for a nitrogen atom. This chemical tailoring is essential for tuning the properties of single-molecule optoelectronic devices, enabling the design of components with specific functionalities and paving the way for more efficient and adaptable nano-optoelectronic systems.