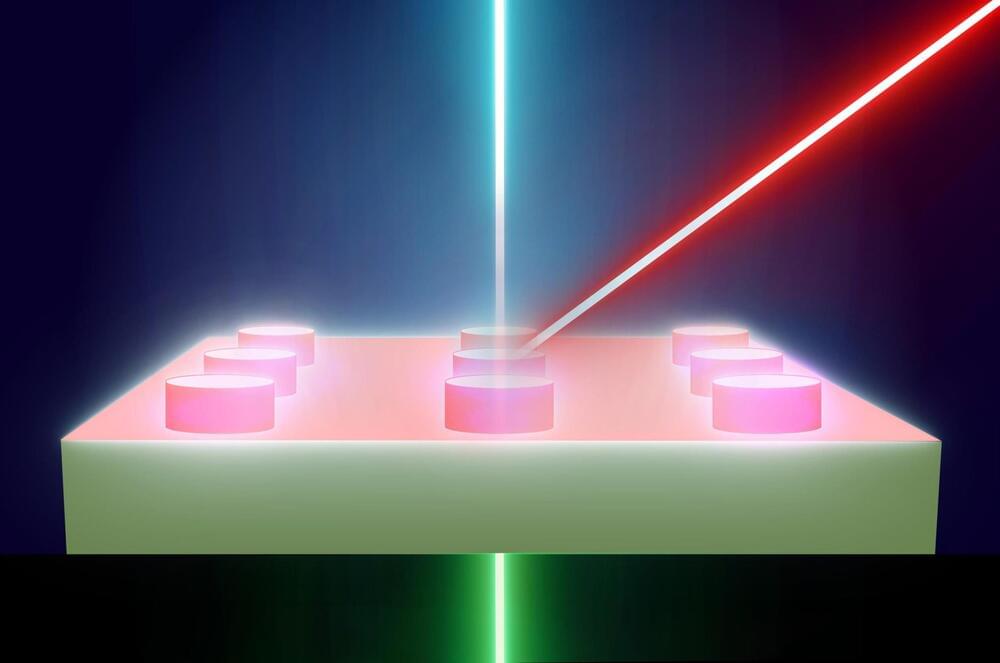
Scientists at the Fritz Haber Institute of the Max Planck Society have developed a revolutionary microscopy method that enables the direct visualization of nanostructures and their optical properties.
This breakthrough allows researchers to observe nanoscale materials, like metamaterials, in unprecedented detail by manipulating light in innovative ways. The method has taken over five years to develop and leverages the unique capabilities of the Free Electron Laser. The implications of this research are vast, offering the potential to advance flat optics, shrink 3D optics to 2D, and create more efficient optical devices.
Tailoring Light With Nanomaterials