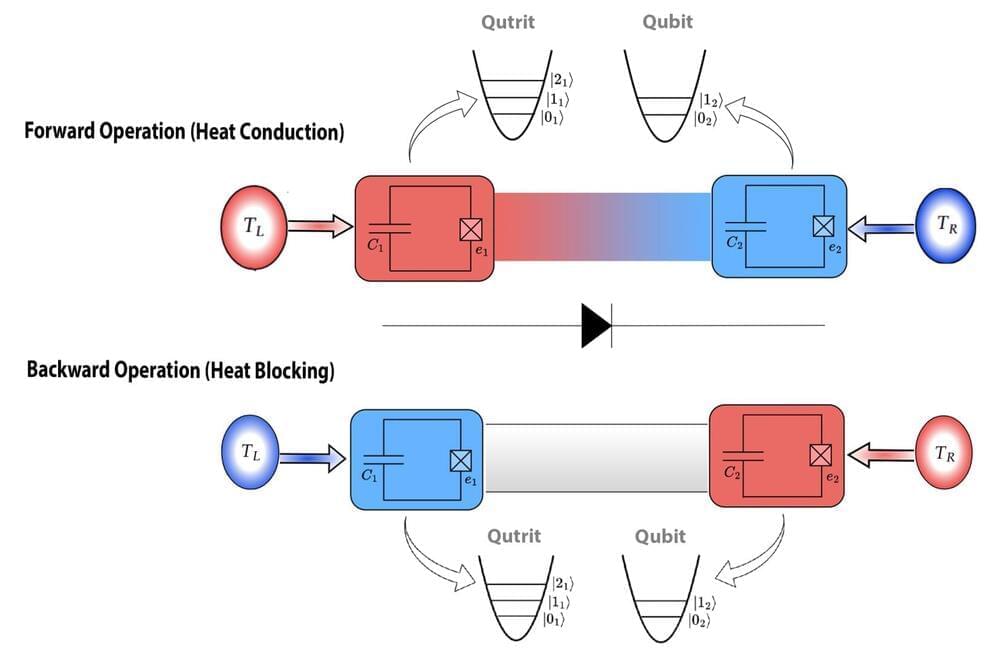
Heat management at the nanoscale has long been a cornerstone of advanced technological applications, ranging from high-performance electronics to quantum computing. Addressing this critical challenge, we have been deeply intrigued by the emerging field of thermotronics, which focuses on manipulating heat flux in ways analogous to how electronics control electric energy. Among its most promising advancements are quantum thermal diodes, which enable directional heat control, and quantum thermal transistors, which regulate heat flow with precision.
Thermal diodes, much like their electrical counterparts, provide unidirectional heat transfer, allowing heat to flow in one direction while blocking it in the reverse. We find this capability revolutionary for heat management, as it has the potential to transform numerous fields.
For instance, thermal diodes can significantly improve the cooling of high-performance electronics, where heat dissipation is a major bottleneck. They could also enable more efficient energy harvesting by converting waste heat into usable energy, contributing to sustainability efforts.