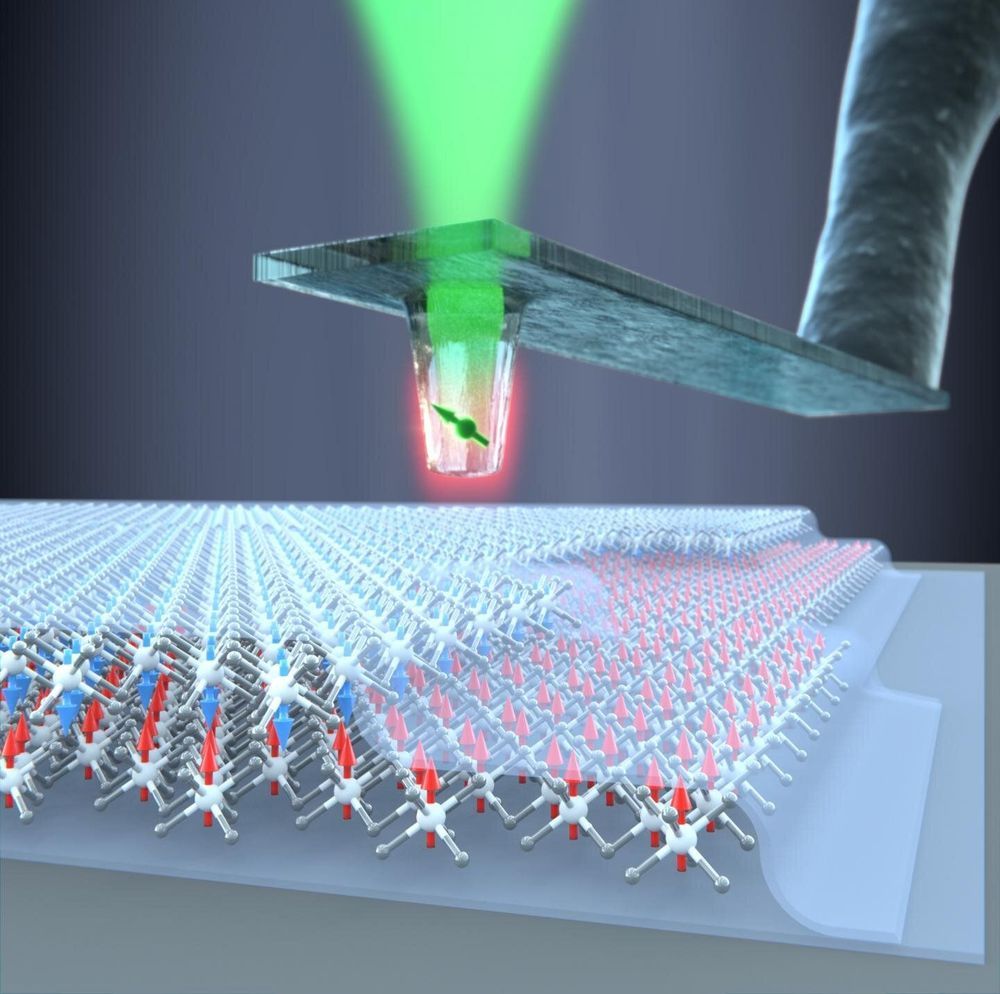
Researchers at Johannes Gutenberg University Mainz (JGU) have succeeded in developing a key constituent of a novel unconventional computing concept. This constituent employs the same magnetic structures that are being researched in connection with storing electronic data on shift registers known as racetracks. In this, researchers investigate so-called skyrmions, which are magnetic vortex-like structures, as potential bit units for data storage. However, the recently announced new approach has a particular relevance to probabilistic computing. This is an alternative concept for electronic data processing where information is transferred in the form of probabilities rather than in the conventional binary form of 1 and 0. The number 2/3, for instance, could be expressed as a long sequence of 1 and 0 digits, with 2/3 being ones and 1/3 being zeros. The key element lacking in this approach was a functioning bit reshuffler, i.e., a device that randomly rearranges a sequence of digits without changing the total number of 1s and 0s in the sequence. That is exactly what the skyrmions are intended to achieve. The results of this research have been published in the journal Nature Nanotechnology.
The researchers used thin magnetic metallic films for their investigations. These were examined in Mainz under a special microscope that made the magnetic alignments in the metallic films visible. The films have the special characteristic of being magnetized in vertical alignment to the film plane, which makes stabilization of the magnetic skyrmions possible in the first place. Skyrmions can basically be imagined as small magnetic vortices, similar to hair whorls. These structures exhibit a so-called topological stabilization that protects them from collapsing too easily – as a hair whorl resists being easily straightened. It is precisely this characteristic that makes skyrmions very promising when it comes to use in technical applications such as, in this particular case, information storage. The advantage is that the increased stability reduces the probability of unintentional data loss and ensures the overall quantity of bits is maintained.