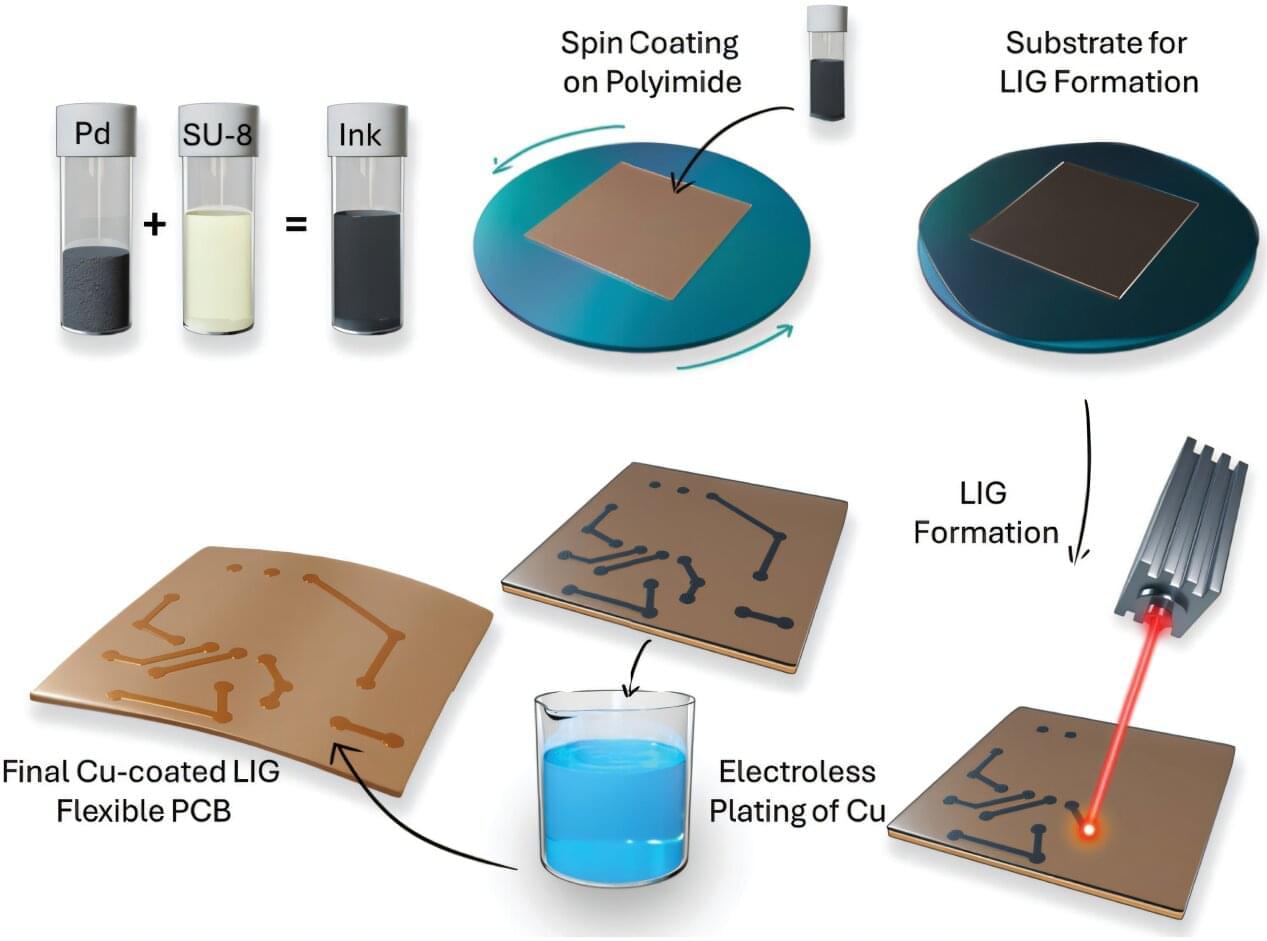
Boise State University researchers have unveiled a cutting-edge approach to manufacturing flexible hybrid circuits—reducing costs, waste, and environmental impact. Their work leverages the properties of laser-induced graphene and was recently featured on the cover of Advanced Materials Technologies.
Laser-induced graphene uses a single-step laser manufacturing process that converts carbon-rich materials into a 3-dimensional conductive and porous structure with some regions of atomically thin graphene. This technique is scalable, cost-effective, and patternable, making it ideal for applications in electronics, sensing, and energy storage.
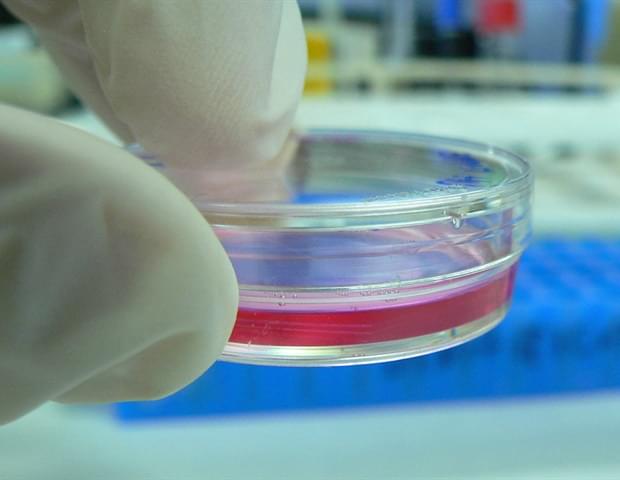
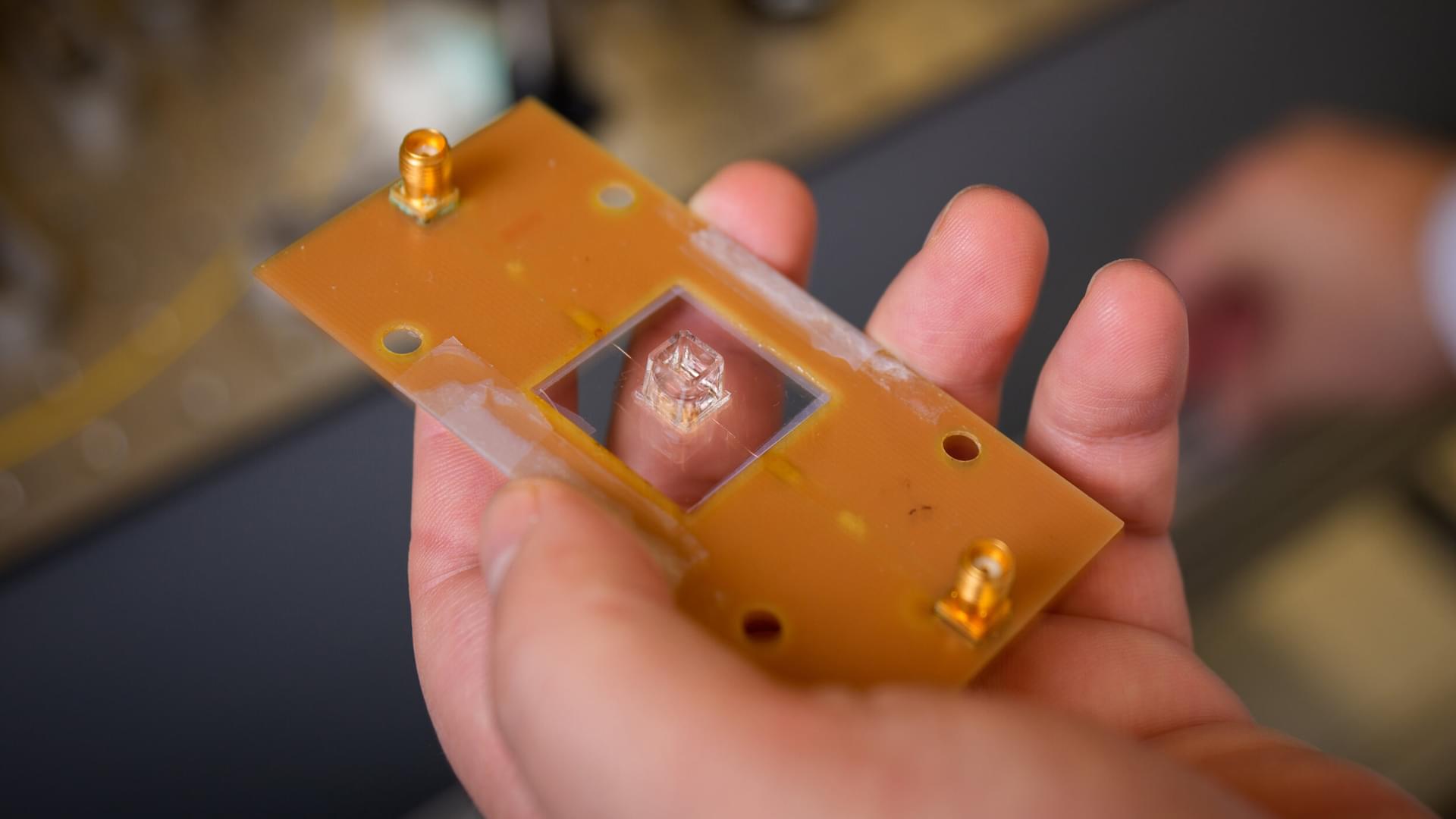
In this work, the researchers used palladium (Pd) nanoparticles embedded in a polymer matrix to form Pd functionalized laser-induced graphene. These Pd nanoparticles act as seed crystals for the electroless deposition of copper on the LIG scaffold, thus forming copper interconnects for flexible printed circuit boards (f-PCBs) through a laser-enabled additive manufacturing process.