Modern construction is a precision endeavor. Builders must use components manufactured to meet specific standards — such as beams of a desired composition or rivets of a specific size. The building industry relies on manufacturers to create these components reliably and reproducibly in order to construct secure bridges and sound skyscrapers.
Now imagine construction at a smaller scale — less than 1/100th the thickness of a piece of paper. This is the nanoscale. It is the scale at which scientists are working to develop potentially groundbreaking technologies in fields like quantum computing. It is also a scale where traditional fabrication methods simply will not work. Our standard tools, even miniaturized, are too bulky and too corrosive to reproducibly manufacture components at the nanoscale.
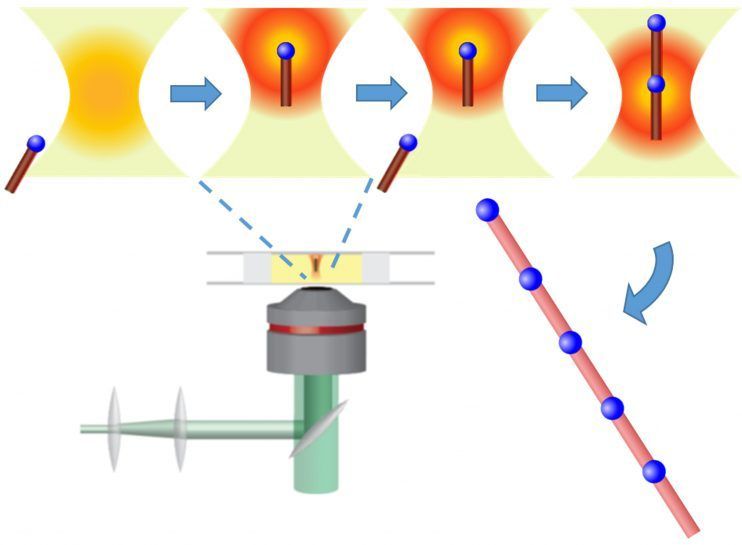
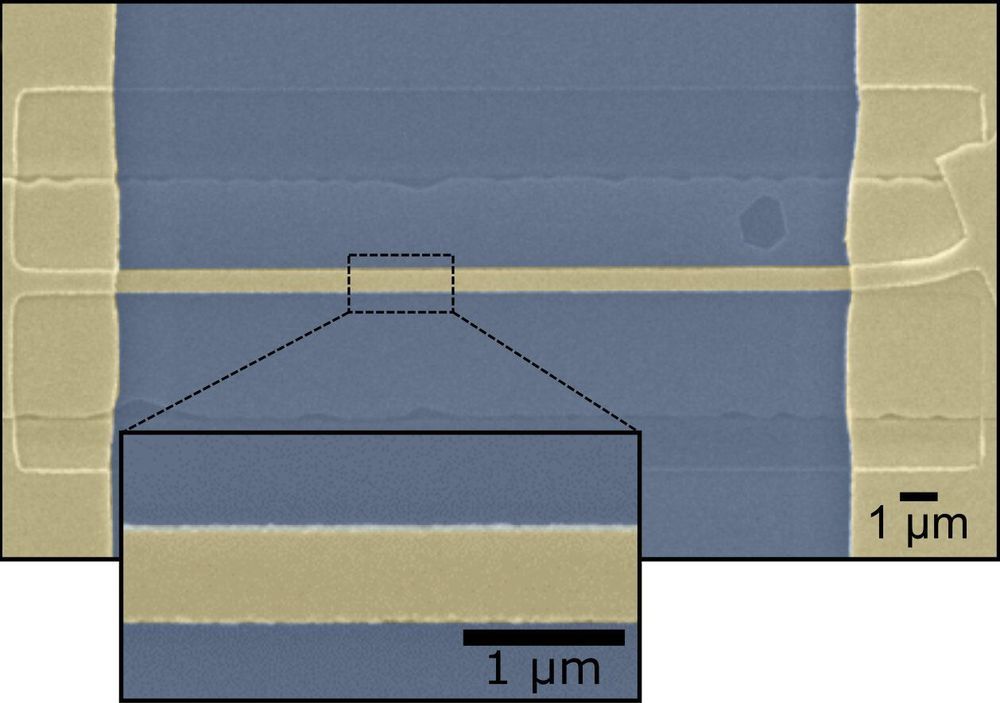
Researchers at the University of Washington have developed a method that could make reproducible manufacturing at the nanoscale possible. The team adapted a light-based technology employed widely in biology — known as optical traps or optical tweezers — to operate in a water-free liquid environment of carbon-rich organic solvents, thereby enabling new potential applications.