As drug-resistant infections continue to rise, researchers are looking for new antimicrobial strategies that are both effective and sustainable. One emerging approach combines nanotechnology with “green” chemistry, using plant extracts instead of harsh chemicals to produce metal oxide nanoparticles.
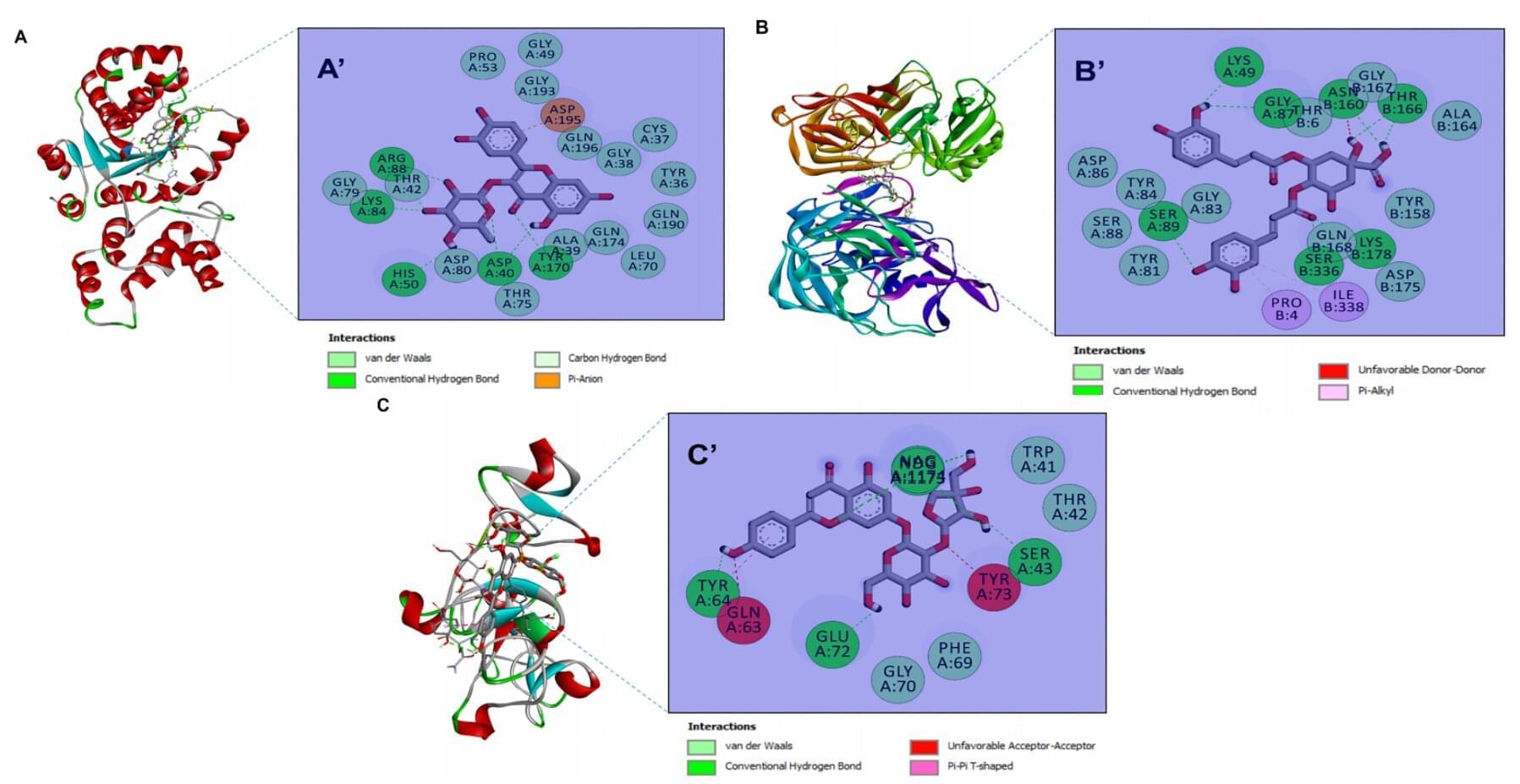
A new study published in Biomolecules and Biomedicine now reports that zinc oxide nanoparticles (ZnONPs) biosynthesized from four desert plants with medicinal properties can inhibit a wide spectrum of bacteria, yeasts and filamentous fungi in laboratory tests. The work also links the plants’ rich phytochemical profiles to nanoparticle stability and potency, and uses computer modeling to explore how key compounds might interact with microbial targets.
The study is the first to produce ZnONPs from species that thrive in harsh, arid environments and are often under-used or even considered invasive. “By turning resilient desert plants into tiny zinc oxide particles, we were able to generate materials that are both eco-friendly to produce and surprisingly active against a range of microbes,” the authors write. “These green nanoparticles could form the basis for future antimicrobial formulations, pending further safety and efficacy testing.”