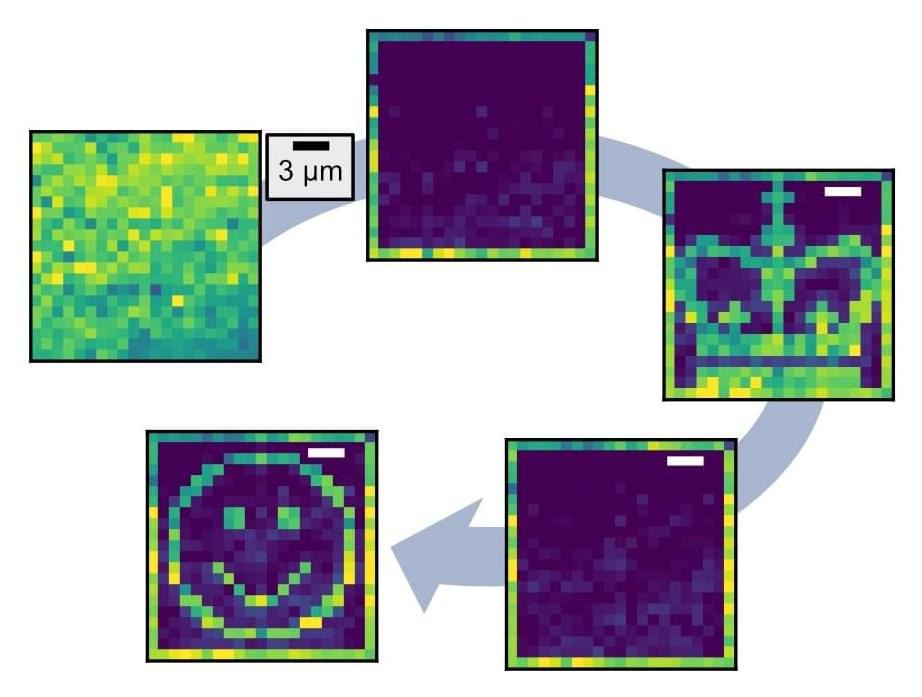
In 2021, lanthanide-doped nanoparticles made waves—or rather, an avalanche—when Changwan Lee, then a Ph.D. student in Jim Schuck’s lab at Columbia Engineering, set off an extreme light-producing chain reaction from ultrasmall crystals developed at the Molecular Foundry at Berkeley Lab. Those same crystals are back again with a blink that can now be deliberately and indefinitely controlled.
“We’ve found the first fully photostable, fully photoswitchable nanoparticle—a holy grail of nanoprobe design,” said Schuck, associate professor of mechanical engineering.
This unique material was synthesized in the laboratories of Emory Chan and Bruce Cohen at the Molecular Foundry, Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory as well as in a national lab in South Korea. The research team also included Yung Doug Suh’s lab at Ulsan National Institute of Science and Technology (UNIST).