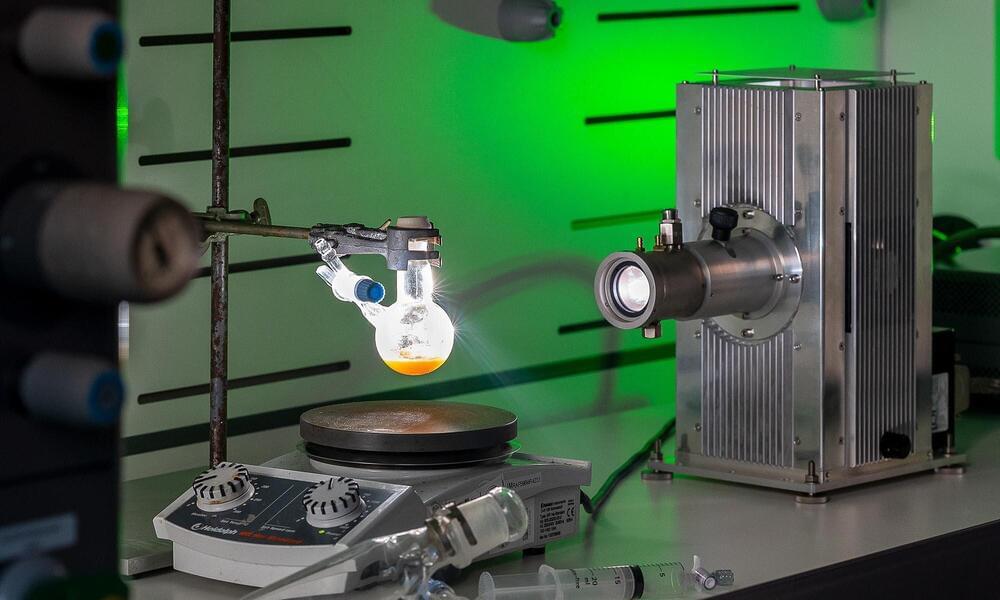
Plants use photosynthesis to harvest energy from sunlight. Now researchers at the Technical University of Munich (TUM) have applied this principle as the basis for developing new sustainable processes which in the future may produce syngas (synthetic gas) for the large-scale chemical industry and be able to charge batteries.
Syngas, a mixture of carbon monoxide and hydrogen, is an important intermediate product in the manufacture of many chemical starter materials such as ammonia, methanol and synthetic hydrocarbon fuels. “Syngas is currently made almost exclusively using fossil raw materials,” says Prof. Roland Fischer from the Chair of Inorganic and Organometallic Chemistry.
A yellow powder, developed by a research team led by Fischer, is to change all that. The scientists were inspired by photosynthesis, the process plants use to produce chemical energy from light. “Nature needs carbon dioxide and water for photosynthesis,” says Fischer. The nanomaterial developed by the researchers imitates the properties of the enzymes involved in photosynthesis. The “nanozyme” produces syngas using carbon dioxide, water and light in a similar manner.