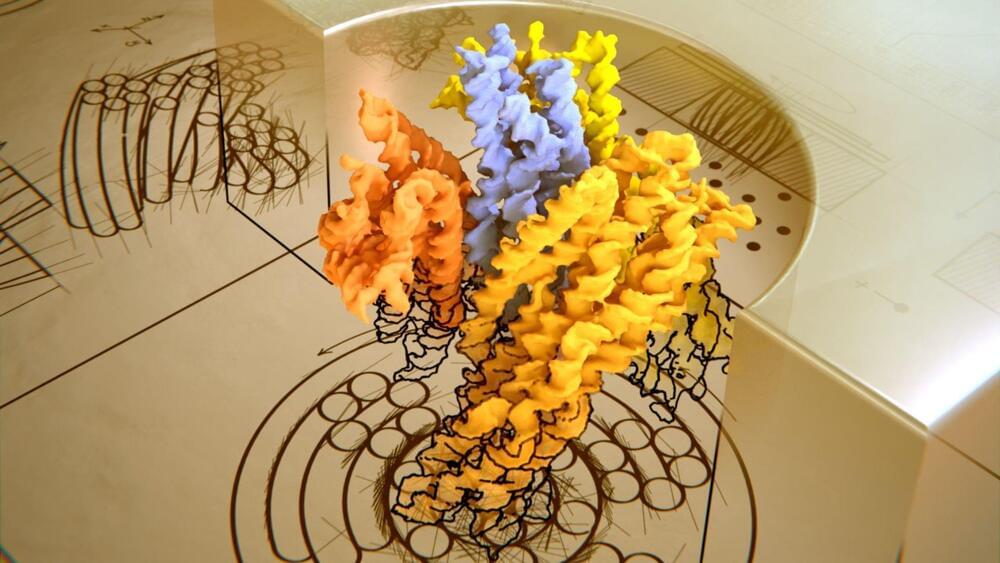
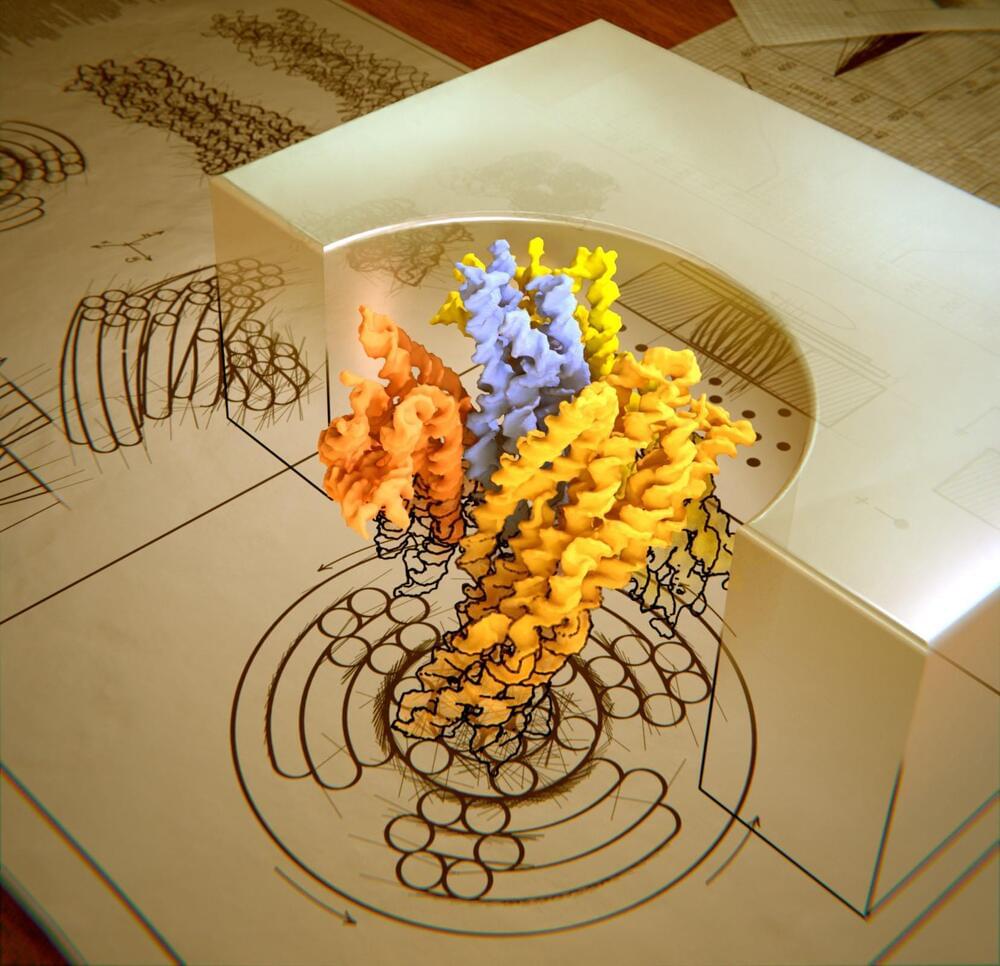
As it lay buried for two millennia, a fragment of glass gradually acquired a nanostructured surface that reflects light like a butterfly’s wings.
The ancient Roman city of Aquileia was situated close to Italy’s modern border with Slovenia. Over the centuries since its founding in 181 BCE, Aquileia suffered floods, earthquakes, sieges, and sackings. Little remains of this ancient city of 100,000 inhabitants, but archaeologists have uncovered relics from that early period. One such specimen is a glass shard discovered in 2012 on farmland in the outskirts of the modern city of Aquileia. The shard is striking in its coloration: an iridescent surface of deep blue and shiny gold atop a substrate of dark green. Now, after subjecting the shard to a string of chemical and physical tests, Giulia Guidetti of Tufts University, Massachusetts, and her collaborators have identified the origin of the shard’s appearance: a chemical transformation of the amorphous glass into a nanolayered material, a photonic crystal [1].
Glassmaking was invented independently by several Bronze Age civilizations (3300 BCE to 1,200 BCE), including those of ancient Egypt and the Indus Valley. Glass beads, vessels, and figurines remained luxury items until the Romans invented the technique of glassblowing in the first century CE. As blowing technology spread, glassware became cheaper and faster to produce in a greater variety of shapes. Items manufactured in the Roman Empire included jars for cosmetics, jugs for condiments, and cups for wine.